Introduction
In the rapidly evolving landscape of automation, the role of the RPA Supervisor emerges as a cornerstone for organizations looking to harness the full potential of robotic process automation (RPA). As businesses navigate the complexities of AI implementation, the RPA Supervisor not only addresses common challenges such as:
- Data quality
- Misconceptions about automation costs
but also ensures that robotic processes operate seamlessly. With the global healthcare automation market projected to expand significantly, the RPA Supervisor’s ability to monitor, manage, and optimize these processes becomes crucial.
This article delves into the multifaceted responsibilities of the RPA Supervisor, highlighting its impact on:
- Operational efficiency
- Employee satisfaction
- The overall success of automation initiatives
By exploring the benefits, challenges, and strategic considerations associated with this pivotal role, organizations can better position themselves for a future where automation drives innovation and growth.
Introduction to RPA Supervisor: Key Functions and Importance
The RPA Supervisor is essential as a management layer in robotic process automation (RPA) environments, vital for addressing common challenges associated with AI implementation, including issues related to poor master data quality and misunderstandings regarding the complexity and costs of AI adoption. This position is primarily responsible for monitoring, managing, and optimizing the performance of robotic processes, ensuring automation workflows operate smoothly and efficiently. Many organizations hesitate to adopt AI due to uncertainty about where to start and the perceived time-intensive nature of AI projects.
In this context, the RPA Supervisor serves as a centralized control point, swiftly addressing any issues that may arise during execution. For instance, a case study of a mid-sized healthcare company revealed that implementing GUI mechanization led to a 70% reduction in data entry errors and a 50% acceleration in software testing processes. The global healthcare technology market is anticipated to expand at a rate of 8.415% over the next seven years, emphasizing the significance of RPA in improving operational efficiency in healthcare.
According to PwC, the possible impact of technology and AI on the global economy might attain an astonishing $15.7 trillion by 2030. Furthermore, 35% of small and medium enterprises attribute enhanced customer service and support capabilities to mechanization. In this context, the RPA Manager’s role becomes even more critical, enabling organizations to navigate the complexities of AI implementation and enhance operational consistency and quality.

Operational Mechanics: How RPA Supervisor Orchestrates Automation
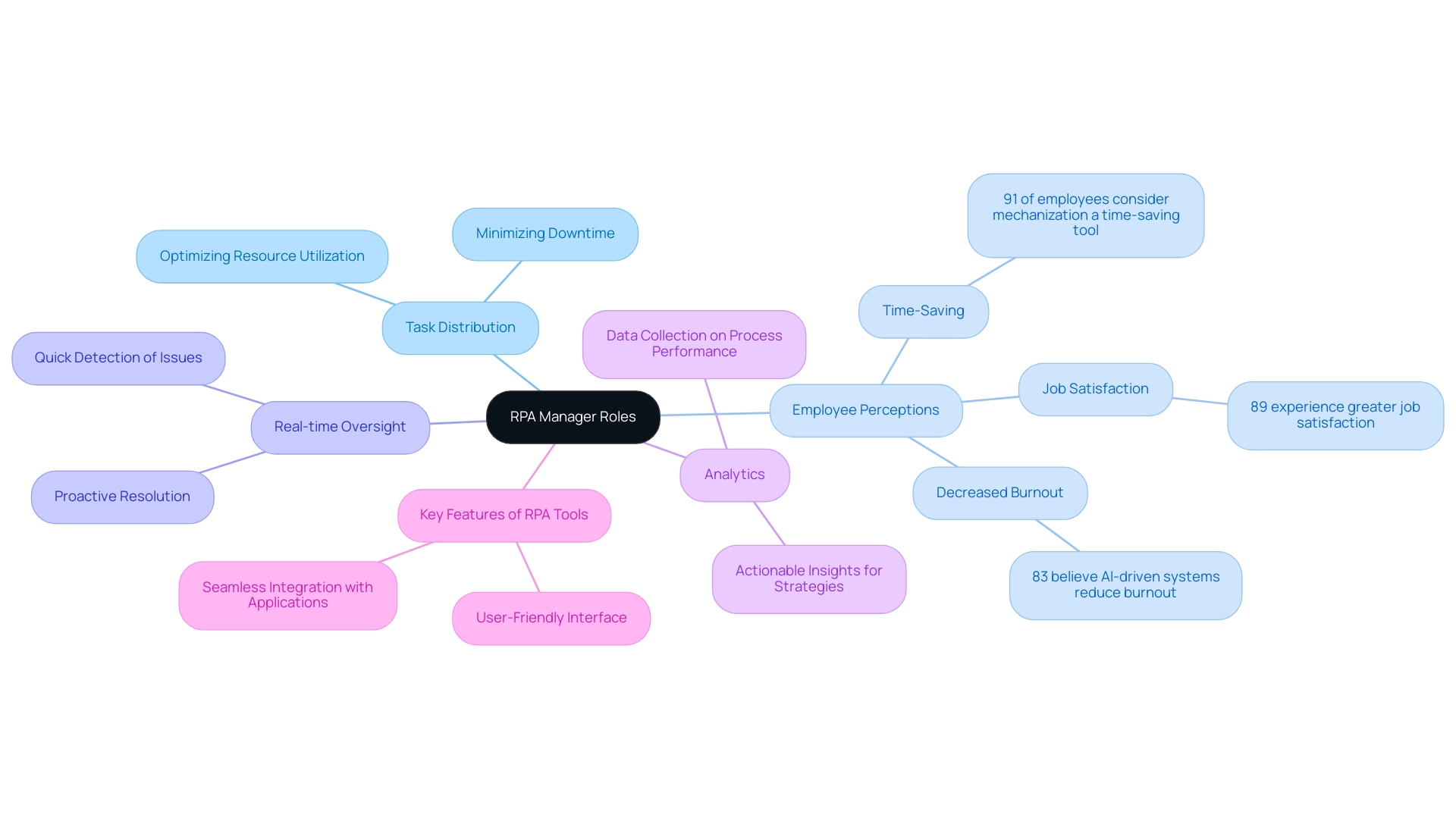
The RPA Manager is vital to the operational structure of robotic process optimization, fulfilling multiple critical roles. Its primary role is to oversee the equitable distribution of tasks among various robots, optimizing resource utilization to enhance productivity and minimize downtime. This orchestration is essential, as studies show that:
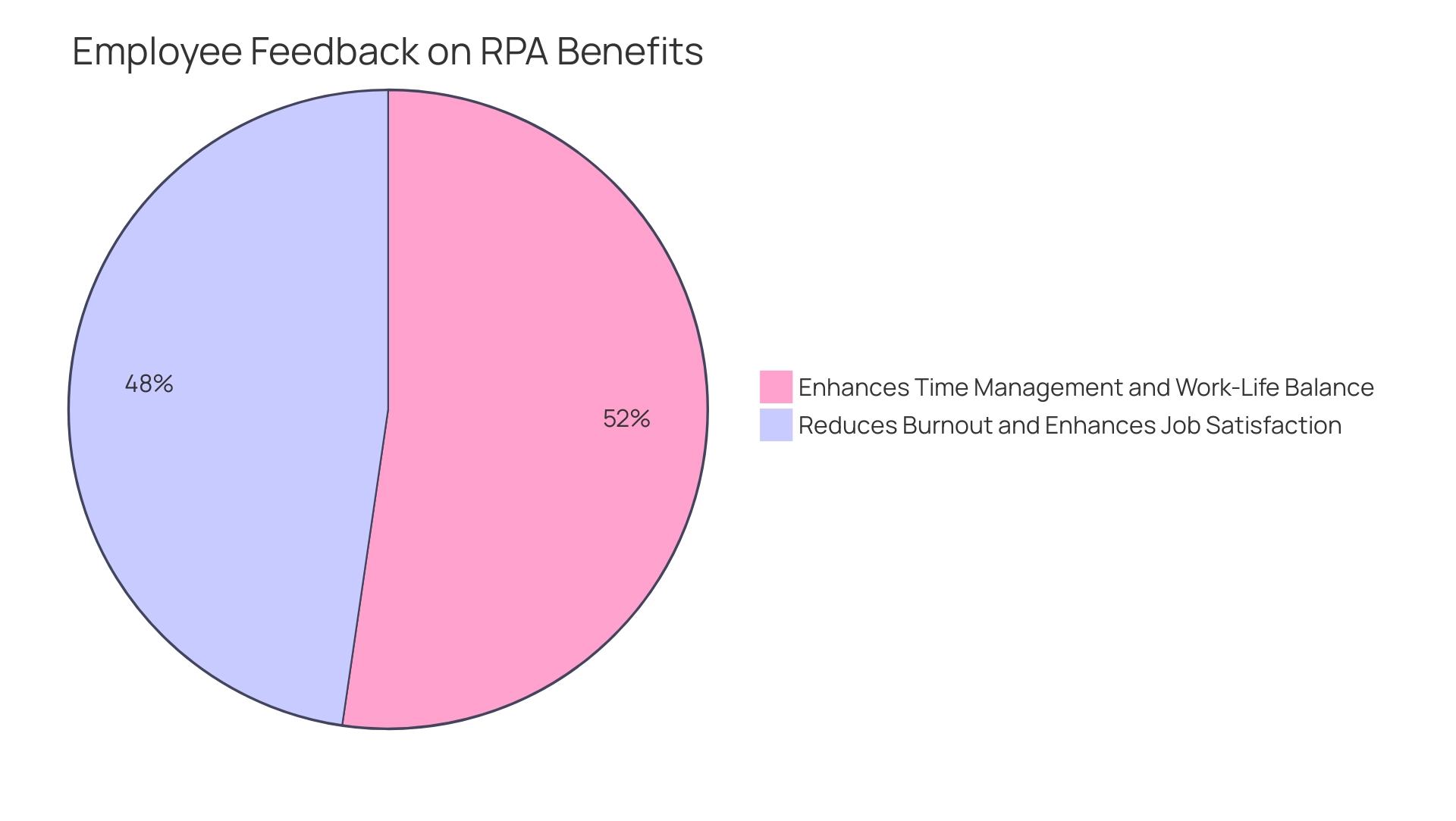
- 91% of employees consider mechanization a time-saving tool that enhances work-life balance.
- 89% experience greater job satisfaction from these efficiencies.
Moreover, 83% of employees utilizing AI-driven systems believe it greatly decreases burnout and improves job satisfaction, emphasizing the substantial positive impact of RPA on employee morale.
Aside from task management, the RPA Manager facilitates real-time oversight of robotic processes, enabling the quick detection and resolution of possible issues. This proactive approach not only enhances operational efficiency but also promotes continuous improvement by collecting data on process performance. By utilizing analytics, the RPA Supervisor can provide actionable insights that guide future operational strategies.
Key features of EMMA RPA include its user-friendly interface that simplifies the management of complex workflows, while Microsoft Power Automate offers seamless integration with existing applications to streamline processes. As Deloitte points out, while scaling RPA poses challenges—with only 3% of organizations successfully expanding their digital workforce—the right orchestration and monitoring practices can dramatically improve the effectiveness of RPA initiatives. By addressing these scaling challenges through efficient task orchestration and proactive monitoring, the RPA supervisor plays a vital role in driving operational excellence and ensuring the successful implementation of automation technologies.
Benefits of Implementing an RPA Supervisor
The implementation of an RPA Manager brings a myriad of advantages that can significantly elevate organizational performance. A key benefit is the substantial reduction in operational errors; with the RPA Manager closely monitoring robotic processes, potential issues can be swiftly identified and resolved, enhancing the accuracy of automated tasks. This oversight is crucial, as Bill Gates aptly stated, ‘Automation applied to an efficient operation will magnify the efficiency; applied to an inefficient operation will magnify the inefficiency.’
By optimizing task allocation, the RPA supervisor ensures that robotic systems operate at their peak capacity, which results in faster processing times and a notable decrease in operational costs. Furthermore, this role liberates human resources from mundane, repetitive tasks, enabling teams to concentrate on higher-value activities that foster innovation and strategic growth. In a rapidly evolving AI landscape, companies such as Coca-Cola have experienced significant improvements in operational efficiency and employee satisfaction following the integration of the RPA supervisor.
With 91% of employees affirming that automation enhances time management and work-life balance, and 83% believing that AI-powered automation can help reduce burnout and enhance job satisfaction, the positive impact of RPA is clear. Moreover, by applying Business Intelligence to transform raw data into actionable insights, entities can make informed decisions that drive growth and innovation. Lean Six Sigma principles can further optimize processes, making the RPA supervisor a vital tool for driving employee satisfaction and reducing burnout.
However, entities must navigate the challenges posed by the rapidly evolving AI landscape to fully realize these benefits.
Challenges and Considerations in RPA Supervision
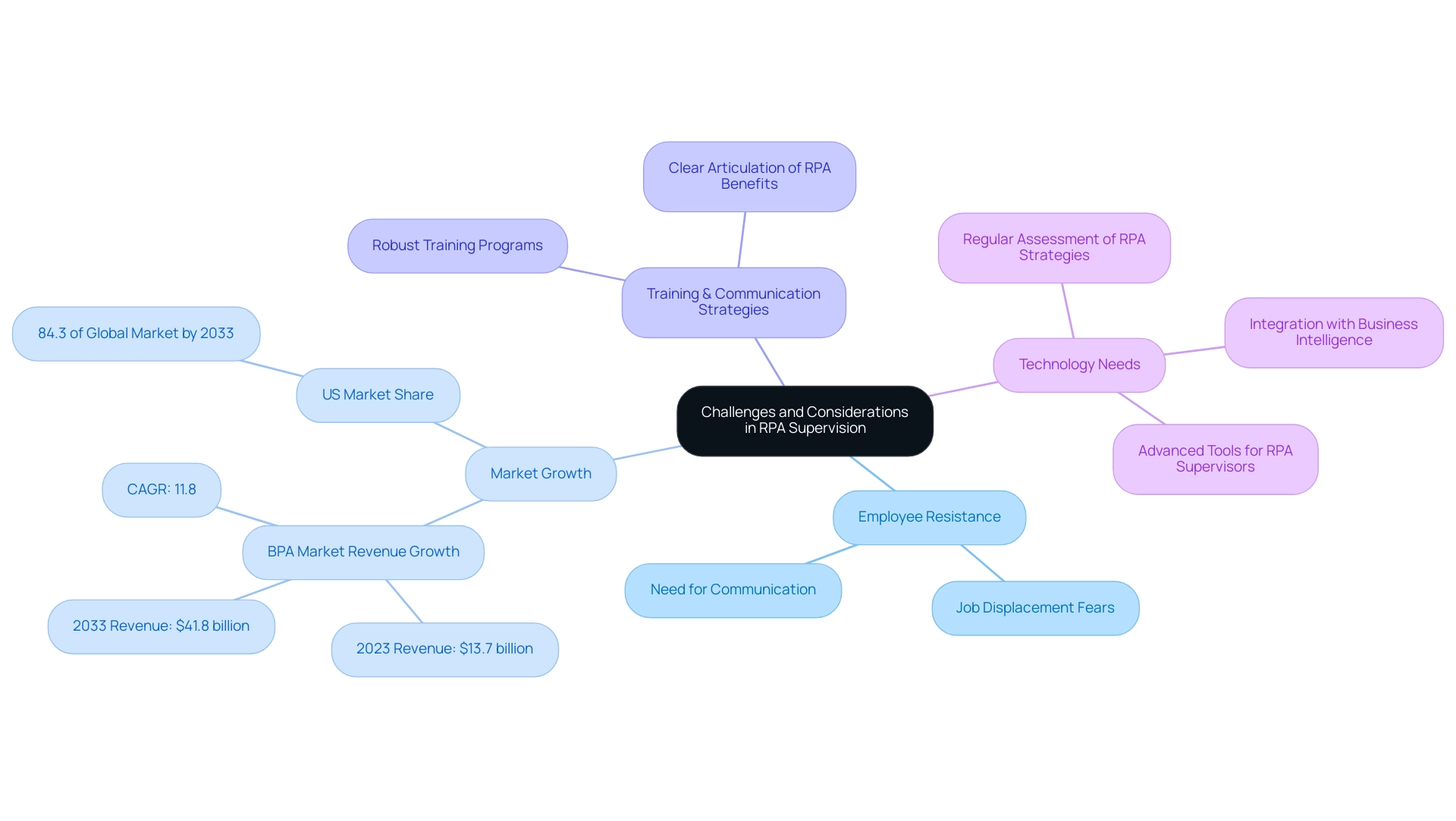
The implementation of an RPA supervisor brings remarkable benefits, such as boosting efficiency and reducing errors, but organizations face several challenges that must be addressed for a successful transition. A primary hurdle is the resistance from employees who may harbor fears about job displacement due to mechanization. With research indicating that by 2030, nearly 47% of jobs in the US face a high risk of being impacted by machinery, addressing these concerns is more urgent than ever.
Furthermore, the Business Process Automation (BPA) market is anticipated to expand from an estimated revenue of $13.7 billion in 2023 to $41.8 billion by 2033, emphasizing a significant transition towards streamlining across various sectors. To mitigate resistance, it is essential to implement robust communication and training strategies that clearly articulate the advantages of RPA, demonstrating how it can enhance employees’ current roles rather than replace them. Tajammul Pangarkar, CMO at Prudour Pvt Ltd, highlights the significance of adjusting to these changes, stating, ‘In the ever-evolving tech landscape, understanding the role of mechanization is crucial for future success.’
Furthermore, equipping the RPA supervisor with advanced tools and technologies is vital for effectively managing complex automation workflows. Investing in comprehensive training programs for RPA supervisors not only maximizes their potential but also ensures that each RPA supervisor can lead their teams through this transition successfully. For instance, case studies reveal that entities facing challenges during RPA Supervisor implementation often struggled with employee buy-in and required tailored training approaches to address specific fears and misconceptions.
Regular assessment of RPA strategies is also essential to align with changing business needs, ensuring that RPA Supervisors continue to be integral to the entity’s operational goals. By proactively addressing employee apprehensions and continuously refining RPA implementation approaches, organizations can pave the way for a smoother transition and enhanced productivity. Additionally, leveraging Business Intelligence in conjunction with RPA can transform raw data into actionable insights, further supporting informed decision-making that drives growth and innovation.
Conclusion
The role of the RPA Supervisor is pivotal in navigating the complexities of robotic process automation, serving as a bridge between technology and operational excellence. By addressing key challenges such as data quality and misconceptions about automation costs, the RPA Supervisor empowers organizations to fully leverage the potential of AI. With the healthcare automation market set to grow significantly, the importance of this role cannot be overstated, as it directly impacts operational efficiency, employee satisfaction, and the success of automation initiatives.
Implementing an RPA Supervisor not only enhances the accuracy and speed of automated processes but also alleviates the burden of repetitive tasks from human resources. This shift allows teams to focus on higher-value activities that foster innovation and drive strategic growth. The positive feedback from employees regarding automation’s impact on work-life balance and job satisfaction underscores the transformative power of this role in the workplace.
However, organizations must remain vigilant about the challenges that accompany automation, particularly employee resistance and the need for effective communication and training. By fostering a culture that embraces change and investing in the continuous development of RPA Supervisors, businesses can ensure a smoother transition to automation. Ultimately, the RPA Supervisor stands as a critical asset in driving not only operational excellence but also a future where innovation and growth become the norm in an increasingly automated world.
Discover how our tailored RPA solutions can optimize your operations—contact us today to learn more!
