Introduction
In the evolving landscape of data analytics, organizations are presented with powerful tools that can transform their decision-making processes. Descriptive and diagnostic analytics stand out as essential methodologies, each offering unique insights into performance and underlying causes of trends.
As businesses strive to become more data-driven, understanding the differences between these analytics types is crucial for optimizing operations and enhancing strategic initiatives. With the right tools and techniques, such as Power BI and Robotic Process Automation, companies can not only streamline their reporting processes but also gain actionable insights that drive success.
This article delves into the fundamentals of descriptive and diagnostic analytics, their applications across various industries, and the benefits and challenges they present, equipping organizations with the knowledge to harness data effectively and stay ahead in a competitive market.
Understanding Descriptive and Diagnostic Analytics
Descriptive analysis plays an essential role in summarizing past information, allowing businesses to recognize trends and patterns that guide strategic choices. By leveraging tools such as dashboards and visual reports, organizations can gain insights into past performance within specified timeframes. For example, a retail firm could employ descriptive analysis to assess quarterly sales information, revealing peak shopping periods and pinpointing top-selling items that generate income.
This information is invaluable for optimizing inventory and enhancing customer experience. In 2024, as 36% of information leaders indicate their budgeting for analysis staying constant, the dependence on descriptive tools will be essential for companies to utilize historical information effectively.
Conversely, investigative examination delves deeper into the details, aiming to uncover the causes behind particular results. Methods such as information mining and correlation analysis are used to reveal the relationships and causes behind observed trends. For example, if a retail store experiences a sales decline during a particular period, diagnostic analytics could reveal that adverse weather conditions led to reduced foot traffic.
This insight not only clarifies past performance but also equips businesses with the knowledge needed to devise effective strategies moving forward.
However, businesses often face challenges in leveraging insights from their information, including time-consuming report creation and inconsistencies. Tools such as Power BI can tackle these issues by offering efficient reporting capabilities and ensuring consistency. The 3-Day Power BI Sprint enables organizations to swiftly develop professionally crafted reports, while the General Management App provides extensive management and intelligent evaluations to improve oversight and decision-making.
With the expected rise of up to 1.4 million new positions in information science and analysis between 2023 and 2027, fueled by a 30-35% surge in demand for information-related roles, the significance of these analytical methods in decision-making cannot be overstated. As companies progress towards becoming more data-driven, the capability to utilize both descriptive and diagnostic analytics, along with Business Intelligence tools like Power BI and RPA solutions, will be crucial for sustained success. These tools not only improve reporting and consistency but also provide actionable insights through features like the 3-Day Power BI Sprint for rapid report creation and General Management Apps for comprehensive oversight.
Furthermore, not being able to derive significant insights from information can place companies at a competitive disadvantage, highlighting the urgency of embracing these advanced analytical methods and tools. As indicated by NewVantage Partners, 28.3% of Chief Data Officers report to the Chief Operating Officer, emphasizing the organizational significance of data-related roles in driving business strategy.
Applications of Descriptive vs. Diagnostic Analytics in Various Industries
Descriptive and diagnostic analytics play a crucial role in industries such as retail and finance, where organizations examine sales reports and financial statements to gain insights into their performance. For instance, banks utilize descriptive analysis to track transaction volumes and gauge customer engagement metrics, ensuring they stay attuned to client needs and market trends. In 2024, the applications of descriptive analysis continue to evolve, with retail companies utilizing extensive information examination to deliver personalized customer experiences, optimize inventory management, and enhance supply chain efficiency.
Conversely, analytical methods are especially influential in the healthcare sector, where they assist providers in examining patient histories and treatment outcomes to identify root causes of patient readmission rates. This approach not only improves patient care but also enhances operational efficiency. Recent case studies highlight the significance of analytical processes; for instance, hospitals are increasingly utilizing GUI automation to simplify information entry, software testing, and legacy system integration, resulting in a 70% decrease in entry mistakes and an 80% enhancement in workflow efficiency.
These measurable outcomes demonstrate the transformative impact of automation in healthcare service delivery.
Moreover, leveraging Robotic Process Automation (RPA) can address the challenges posed by manual, repetitive tasks that slow down operations. RPA solutions, such as automated data entry and process monitoring, enable healthcare entities to boost efficiency, reduce errors, and free up teams for strategic initiatives. This not only improves operational efficiency but also enables entities to navigate the rapidly evolving AI landscape with customized solutions that align with their specific business objectives.
Moreover, diagnostic analysis can be applied in manufacturing to examine production delays, allowing firms to identify inefficiencies that obstruct their processes. Both descriptive and diagnostic analytics are valuable in marketing, as they help organizations evaluate campaign effectiveness and comprehend customer behavior more deeply.
The recent acquisitions in the data analysis landscape, such as IBM’s purchase of Turbonomic for $1.5 billion in 2023, highlight the growing acknowledgment of the importance of advanced data analysis in enhancing operational efficiency and customer insights. As IBM stated, ‘In 2023, IBM acquired Turbonomic, an AI-powered application resource management (ARM) platform, for $1.5 billion.’ Furthermore, Microsoft’s purchase of Nuance Communications for $19.7 billion further demonstrates the trend of utilizing sophisticated data analysis to improve operational efficiency.
As industry leaders adopt these technologies, the potential for enhanced decision-making and strategic planning becomes even more evident.
Key Differences Between Descriptive and Diagnostic Analytics
The fundamental distinction between descriptive and diagnostic analytics resides in their specific objectives, particularly in enhancing operational efficiency through innovative technologies like Robotic Process Automation (RPA). Descriptive analytics answers the essential question of ‘What happened?’ by providing a retrospective overview of trends and patterns.
This method usually utilizes fundamental statistical techniques and visualization tools, such as those provided by Power BI, to summarize historical information, offering a clear snapshot of performance metrics. Conversely, evaluative analysis explores further by addressing the question of ‘Why did it occur?’ Through advanced methodologies such as regression analysis and information mining, evaluative studies aim to reveal underlying causes and correlations that clarify observed outcomes.
For example, in healthcare, assessment tools can link patient symptoms to detect infectious agents, effectively clarifying sudden increases in emergency room visits, which facilitates improved decision-making. Skills.ai acts as a proficient analysis partner, providing valuable tools for scientists to utilize these evaluation techniques effectively. The integration of RPA can further streamline these processes by automating repetitive manual tasks, ensuring that workflows are efficient and freeing up resources for more strategic analysis.
While descriptive and diagnostic analytics lay the groundwork for understanding business performance, the diagnostic examination builds upon this foundation, delivering profound insights that guide corrective actions and strategic adjustments. As Codal states, ‘Whether a custom profitability forecast solution or a Google Analytics dashboard to better understand customer behavior, we assist businesses in achieving a comprehensive analytics solution.’ Additionally, leveraging AI through Small Language Models enhances information quality by enabling more precise analysis, while GenAI Workshops provide hands-on training that equips teams with the skills needed to effectively implement AI solutions.
This layered approach not only enhances operational efficiency but also empowers entities to make informed decisions that drive success. Statistics indicate that Codal has effectively provided a microservices back-end to store and examine medical device information, showcasing the significant influence of analysis in healthcare and various sectors.
Benefits and Challenges of Descriptive and Diagnostic Analytics
Descriptive analysis acts as a powerful instrument for companies, providing swift insights into performance metrics and enabling the creation of reports and dashboards effortlessly. Its user-friendly nature allows teams to quickly track key performance indicators (KPIs) and generate actionable data. For example, in the case study named ‘Progress to Goals,’ descriptive analysis is used to track progress toward KPIs, such as monthly unique page views, allowing entities to evaluate if they are on course to achieve their objectives and implement necessary changes to enhance performance.
However, it is important to recognize that while descriptive analysis can highlight trends, it often falls short in explaining the underlying reasons for these patterns. In contrast, analytical assessment explores further, providing essential insights into causation and allowing entities to proactively tackle operational challenges. This depth of analysis, however, comes with its own set of complexities; implementing diagnostic analytics can be resource-intensive and requires specialized skills and tools.
A major obstacle entities encounter is ensuring information quality and integration, as incorrect or poorly combined details can lead to misleading conclusions. Here, leveraging Robotic Process Automation (RPA) can automate manual workflows, enhancing operational efficiency and freeing up valuable resources for strategic initiatives. For example, RPA can reduce errors by automating data entry tasks, which minimizes human intervention and the potential for mistakes.
Additionally, investing in training is crucial, with programs like the Python for Data Science Bootcamp, which requires 30 hours and costs $1,495, serving as an example of the commitment needed to empower teams. Moreover, the integration of tailored AI solutions alongside RPA can address specific business challenges, ensuring that entities are equipped with the right technologies. The integration of AI-powered OEE dashboards also plays a vital role in transforming manufacturing processes, reinforcing the necessity of investment in technology alongside training.
To effectively leverage the strengths of both descriptive and diagnostic data analysis, organizations must prioritize these investments, empowering their teams to harness the full potential of these types. As Catherine Cote aptly states, ‘Descriptive analysis is especially useful for communicating change over time and uses trends as a springboard for further examination to drive decision-making.’ This underscores the significance of combining both analytical methods with RPA and BI to improve overall business performance.
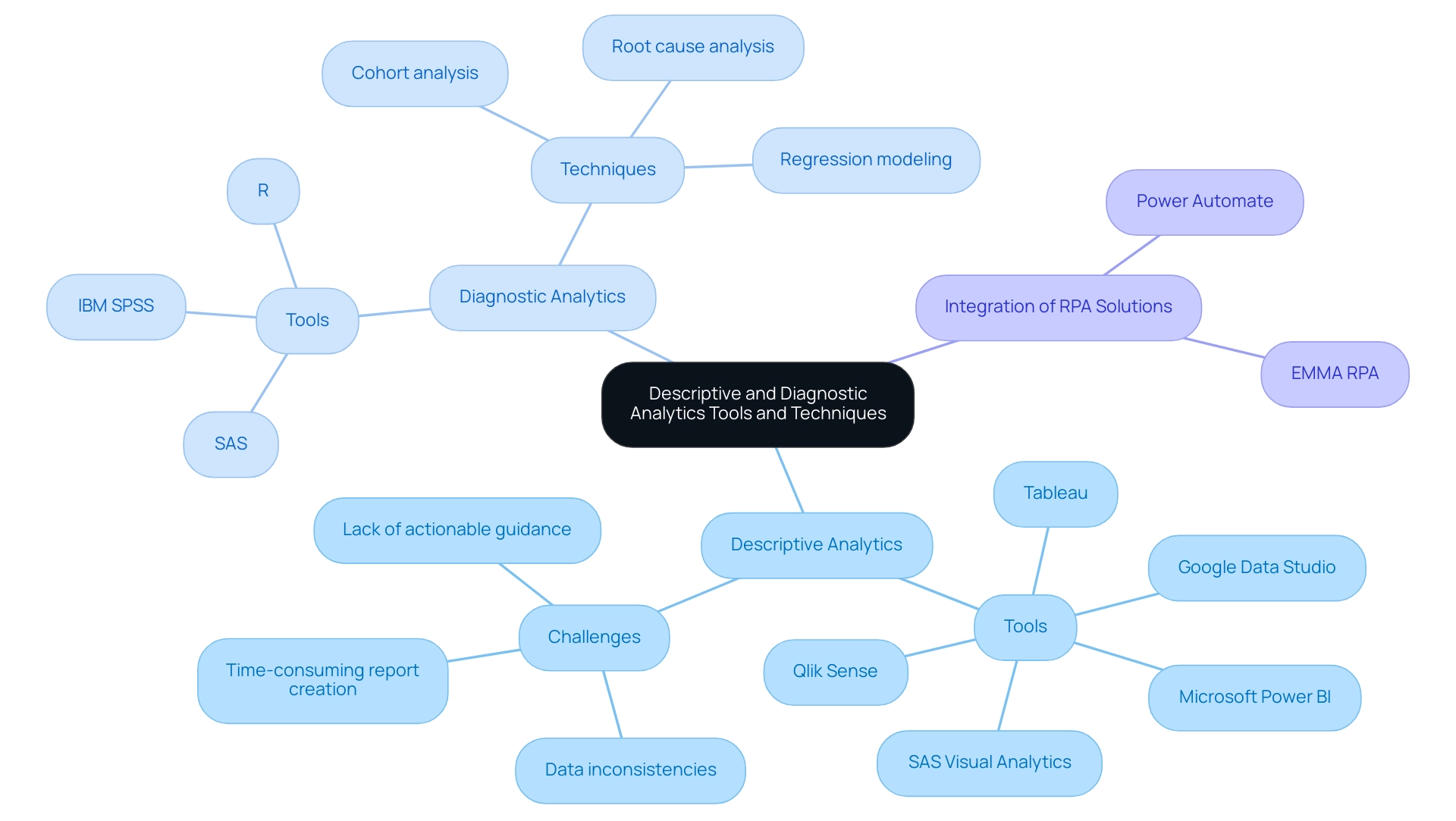
Tools and Techniques for Effective Descriptive and Diagnostic Analytics
Descriptive analytics tools, including Tableau, Microsoft Power BI, and Google Data Studio, are highly regarded for their intuitive interfaces that enhance visualization and reporting. These platforms empower entities to design comprehensive dashboards that effectively summarize key performance indicators, enabling quick decision-making and insight generation. However, many organizations face challenges in leveraging these insights due to:
- Time-consuming report creation
- Data inconsistencies
- Lack of actionable guidance
These challenges can leave them at a competitive disadvantage.
For instance, in healthcare, data analysis tools enable professionals to develop personalized treatment plans based on a patient’s medical history and genetic profile, significantly improving outcomes and optimizing resource allocation. In contrast, diagnostic analytics often necessitates more sophisticated software solutions, such as SAS, IBM SPSS, and R, which feature advanced statistical analysis capabilities. Techniques such as:
- Cohort analysis
- Root cause analysis
- Regression modeling
are crucial in this field, enabling organizations to explore their information more thoroughly and derive valuable insights.
Creatum’s 3-Day Power BI Sprint addresses the need for streamlined report creation by delivering a fully functional, professionally designed report on a topic of your choice in just three days. This service not only saves time but also converts raw information into actionable insights, enabling you to focus on utilizing insights rather than grappling with report-building challenges. According to recent statistics, leading descriptive data tools include:
- Microsoft Power BI
- Tableau
- Google Data Studio
- Qlik Sense
- SAS Visual Analytics
This underscores their effectiveness in the market.
As Aashi Verma observes, ‘The convergence of technology and data examination not only enhances efficiency but also promotes innovation across various sectors.’ Organizations must strategically assess their unique requirements and capabilities when selecting tools to fully leverage the benefits of both descriptive and diagnostic analytics, thereby enhancing their operational efficiency and decision-making processes. Moreover, integrating RPA solutions like EMMA RPA and Power Automate can further streamline operations, addressing task repetition fatigue and outdated systems, ultimately driving business growth.
Conclusion
Harnessing the power of descriptive and diagnostic analytics is essential for organizations aiming to optimize their operations and enhance strategic initiatives. Descriptive analytics provides a comprehensive overview of historical performance, enabling businesses to identify trends and make informed decisions. Tools like Power BI and Tableau facilitate this process, allowing teams to create intuitive dashboards that summarize key performance indicators effortlessly.
On the other hand, diagnostic analytics digs deeper, uncovering the reasons behind specific outcomes. This level of analysis enables organizations to address operational challenges proactively, making it crucial for sectors like healthcare and manufacturing. By utilizing advanced methodologies and techniques, businesses can gain insights that foster continuous improvement and innovation.
However, the journey to effective analytics is not without challenges. Organizations must prioritize data quality and integration while investing in training and advanced tools to fully leverage these analytics types. The integration of Robotic Process Automation alongside analytics can streamline workflows, enhance data accuracy, and free up resources for strategic initiatives.
As the demand for data-driven decision-making continues to rise, adopting both descriptive and diagnostic analytics will be pivotal for sustained success. By understanding their distinct roles and effectively implementing the right tools and techniques, organizations can transform their data into actionable insights that drive growth and maintain a competitive advantage in an increasingly complex market.

