Overview
This article delves into best practices for establishing privacy levels for data sources, highlighting the critical need to categorize information as Public, Organizational, or Private. Such classification is essential for ensuring compliance with regulations such as GDPR and CCPA. By outlining effective data management strategies, the article emphasizes the necessity of robust security measures, comprehensive employee training, and the integration of automation and AI to bolster privacy protection. Collectively, these strategies foster trust and safeguard sensitive information in an increasingly scrutinized digital landscape. Are your current practices aligned with these standards? Reflect on how these insights can enhance your organization’s approach to data privacy.
Introduction
In an age where data serves as the lifeblood of organizations, grasping the nuances of data privacy is more critical than ever. Businesses are navigating the complexities of data management and face an urgent need to classify data into distinct privacy levels:
- Public
- Organizational
- Private
Each category carries its own access protocols and security measures, particularly as concerns over data misuse and regulatory compliance intensify. With a staggering 91% of organizations recognizing the necessity of reassuring customers about their data practices, the stakes are undeniably high.
The emergence of technologies like artificial intelligence, coupled with increasing scrutiny over data handling practices, further complicates the landscape. It is essential for organizations to adopt comprehensive strategies that not only protect sensitive information but also foster consumer trust. This article delves into the intricacies of data privacy levels, explores the challenges of implementing these classifications, and outlines best practices for ensuring compliance in an ever-evolving digital environment.
Understanding Privacy Levels in Data Management
The privacy level setting for this data source represents a crucial framework for determining how information is accessed, shared, and protected within an organization. Information classifications typically fall into three categories: Public, Organizational, and Private.
- Public information is unrestricted and can be freely disseminated.
- In contrast, Organizational information is intended for internal use and may necessitate specific protective measures to ensure confidentiality.
- Most critically, Private information, which includes personally identifiable information (PII), is inherently sensitive and requires stringent access controls to comply with regulations such as GDPR and CCPA.
In a digital landscape where visitor interactions—such as comments on a website—can pose privacy risks, understanding these classifications becomes even more vital. When visitors leave comments, organizations collect information including the visitor’s IP address, browser user agent string, and the content of the comments, which aids in spam detection. Additionally, an anonymized string created from the email address may be sent to the Gravatar service to determine if the visitor is using it, introducing another layer of data collection that necessitates careful handling.
The Gravatar service’s confidentiality policy is accessible here: https://automattic.com/privacy/. Once comments are approved, profile pictures become visible to the public, raising further privacy concerns regarding the exposure of personal information.
The importance of these classifications cannot be overstated, especially considering recent findings indicating that 91% of entities recognize the need to reassure customers about the privacy level setting for this data source, particularly in the realm of generative AI. Cisco highlights that “60% of consumers are worried about businesses’ use of AI today, and 65% claim it’s already diminished their trust in those companies,” underscoring the necessity for entities to address these concerns proactively.
As organizations navigate the complexities of information management, effective classification—particularly the privacy level setting for this data source—not only aids in adhering to evolving regulations but also enhances risk management strategies.
For instance, information confidentiality levels have gained significant attention as nations like India (19,589 requests), Turkey (18,883 requests), and Brazil (11,502 requests) have made substantial requests for content removal, reflecting the urgent need for robust information protection practices. Furthermore, with statistics indicating that 60% of consumers express concern over AI usage and 65% feel their trust has weakened, it is imperative for companies to adopt comprehensive classification systems.
By systematically organizing information according to these confidentiality levels, organizations can implement tailored security measures that align with their privacy level setting for this data source while also addressing information collection practices linked to comment sections. This approach ultimately fosters trust and safeguards sensitive information in an increasingly scrutinized digital landscape. Moreover, the use of tools such as antivirus programs, ad blockers, and password managers—utilized by approximately 60% of internet users for safeguarding information—highlights a gap in comprehensive strategies among users, further emphasizing the significance of strong classification and security measures.
Setting Appropriate Privacy Levels for Data Sources
Establishing appropriate confidentiality levels for information sources in Power BI is crucial for protecting sensitive details and ensuring compliance with regulations. This process entails a comprehensive assessment of the information’s sensitivity, alongside the implementation of stringent access controls. Power BI empowers users to define the privacy level setting for their data sources by categorizing them into three distinct levels: Public, Organizational, and Private.
This classification not only enables effective isolation of information but also mitigates the risk of unintentional leaks during query folding, thereby reinforcing the privacy level setting essential for maintaining data integrity. As Rebecca Kappel aptly notes,
Businesses thrive by leveraging information for insights, product development, and personalization, but this comes with the responsibility to safeguard that information.
Additionally, the collection of user feedback on websites—where data such as IP addresses, browser user agent strings, and anonymized email hashes may be gathered—underscores the importance of robust information protection.
With 91% of organizations expressing concern that generative AI could jeopardize their legal rights and intellectual property, the stakes for information protection are higher than ever. A case study on obtaining customer consent for information usage reveals that effective consent management is vital for safeguarding information, ensuring individuals provide informed and voluntary agreement before their data is collected and processed. Furthermore, considering that 67% of Americans are unaware of their nation’s confidentiality and protection regulations, it is imperative for organizations to commit to regularly assessing and revising their security settings to adapt to any shifts in information sensitivity or compliance requirements.
This proactive strategy guarantees that sensitive information remains adequately protected, fostering trust and aligning with best practices for information management in 2024.
Overcoming Challenges in Privacy Level Implementation
The execution of confidentiality levels frequently encounters substantial challenges, such as employee resistance to change, misunderstandings regarding confidentiality policies, and the complexities of integrating new systems. To navigate these hurdles effectively, a proactive approach is essential. Organizations must prioritize extensive training and awareness initiatives that underscore the critical importance of information protection.
Engaging employees in the policy development process cultivates a culture of compliance and enhances cooperation. Cisco’s findings reveal that over 86% of consumers prioritize information security and seek greater control over their personal details, underscoring the necessity for companies to align with these expectations. Moreover, leveraging Robotic Process Automation (RPA) can streamline manual workflows, significantly enhancing operational efficiency and minimizing errors during implementation.
RPA not only automates repetitive tasks but also empowers teams to concentrate on strategic initiatives, thereby boosting productivity. The UNCTAD’s Data Protection and Privacy Legislation Worldwide resource provides a valuable overview of global information protection laws, crucial for entities striving to comply with diverse regulations. It is concerning that 67% of Americans remain unaware of their country’s data protection laws, highlighting the urgent need for employee training and public awareness.
Furthermore, continuous monitoring and feedback mechanisms are indispensable, enabling organizations to adapt their privacy level settings effectively for this data source. Investing in security AI and automation not only represents financial prudence but also assists organizations in managing regulatory requirements more adeptly. Research indicates that companies that fully implement these technologies report an average breach expense of $3.60 million, which is $1.76 million less than those lacking such capabilities.
The case study titled ‘Cost of Data Breaches with AI and Automation‘ exemplifies this argument, demonstrating how the deployment of security AI and automation can lower breach costs, thereby reinforcing the case for investing in advanced security technologies. By addressing these challenges head-on and integrating tailored AI solutions, companies can enhance their adherence to information security protocols, protect their profits, and achieve significant cost reductions alongside operational improvements.
Best Practices for Ensuring Compliance with Privacy Regulations
Navigating the complexities of confidentiality regulations demands a proactive strategy that integrates privacy level settings for data sources alongside several critical practices. Regular audits of handling procedures are essential for identifying potential vulnerabilities, particularly regarding collection practices such as:
- IP address tracking
- The visibility of profile pictures linked to user comments
- The browser user agent string
To establish a robust privacy level setting, implementing information protection by design and by default is crucial, embedding privacy into the entity’s core processes.
Creating clear information retention guidelines is vital, especially given that 27% of security and IT experts cite alleviating internal audit fatigue from repeated evaluations as a significant regulatory challenge. Notably, organizations can save an average of $520,000 by establishing a formal governance charter, presenting a compelling financial incentive to adopt these measures. Transparency with users about information usage—including how comments and related details may be handled or shared—while securing explicit consent when necessary, fosters trust and supports adherence to the privacy level setting for this data source.
This approach may involve using an anonymized string created from email addresses (a hash) provided to the Gravatar service, enabling users to verify if they have a profile picture associated with their comments. Users can review the Gravatar service confidentiality policy for added assurance. Furthermore, regular training sessions aimed at informing employees about regulatory requirements and privacy principles reinforce an organization’s commitment to safeguarding user information.
As 67% of global executives find ESG regulation overly complex, consulting legal experts is essential for staying informed and ensuring ongoing compliance. This multifaceted approach not only enhances adherence efficiency but also addresses the increasing importance of information protection in organizational strategy, particularly as 91% of business leaders recognize their responsibility toward ESG issues.
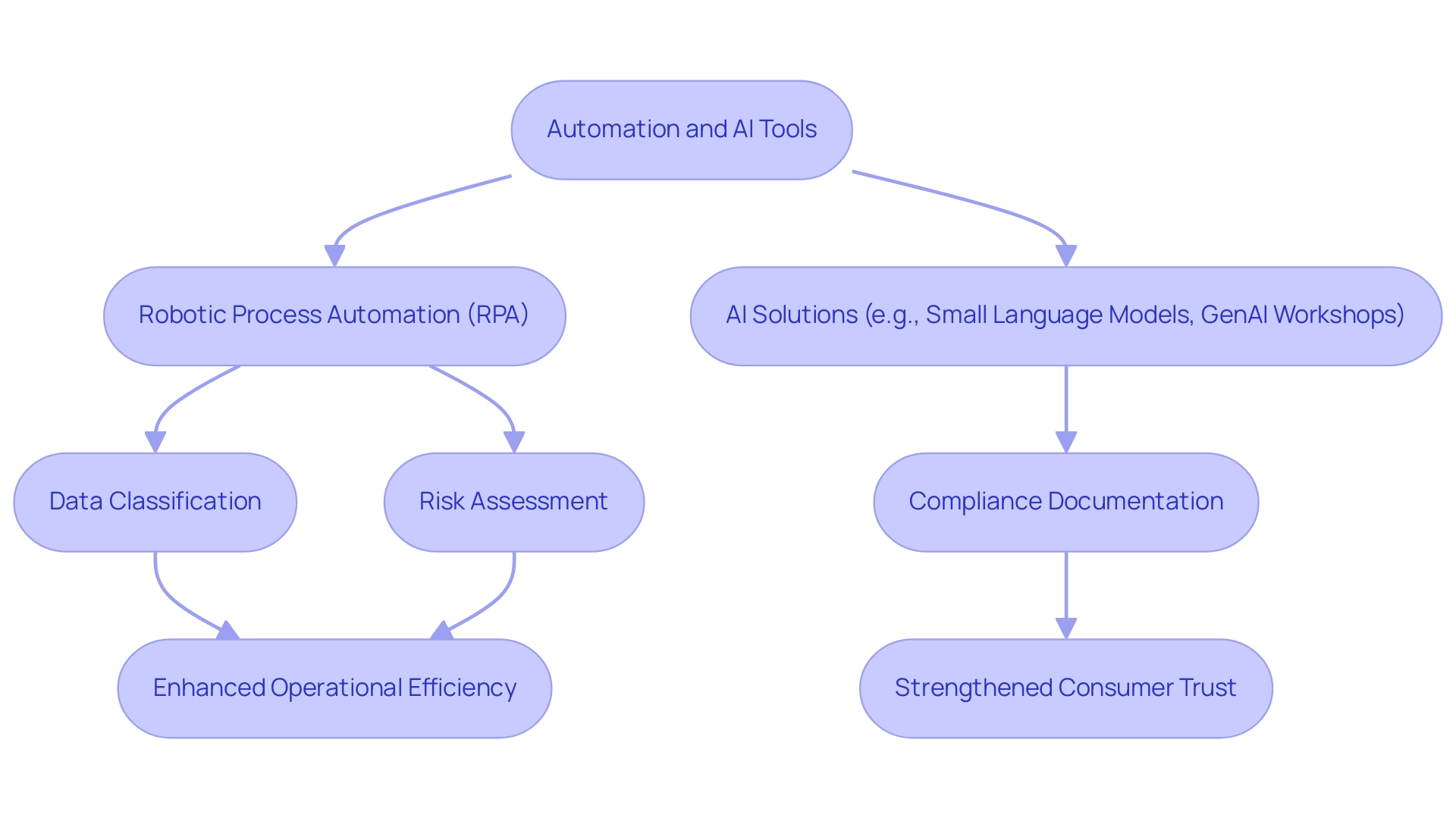
Leveraging Automation and AI for Enhanced Data Privacy Management
Organizations are increasingly adopting automation and artificial intelligence (AI) to enhance their information protection management strategies significantly. By utilizing advanced tools such as Robotic Process Automation (RPA) and tailored AI solutions—like Small Language Models for efficient data analysis and GenAI Workshops for hands-on training—businesses can automate oversight monitoring, streamline data classification, and conduct risk assessments. This not only improves operational efficiency but also positions them effectively within a rapidly evolving AI landscape. AI-driven solutions excel at analyzing vast datasets to identify sensitive information, ensuring privacy level settings for these data sources are managed in accordance with established privacy standards.
Automated workflows, for instance, can simplify the documentation of compliance activities, which is crucial for effectively addressing audits and regulatory inquiries. This approach enhances operational efficiency while strengthening an organization’s ability to identify and respond to potential breaches. Notably, IBM has indicated that phishing remains the primary infection vector, accounting for 41% of occurrences, underscoring the essential need for robust information protection measures.
Alarmingly, $17,700 is lost every minute due to phishing attacks, highlighting the urgency of addressing information protection and security. Furthermore, entities that have fully deployed security AI and automation experience an average data breach cost of $3.60 million—$1.76 million less than their counterparts that do not leverage such capabilities. By utilizing AI tools for regulatory monitoring and RPA for efficient workflow automation, organizations can foster a culture of transparency and trust, increasingly valued by consumers. A recent study revealed that only 29% of individuals find it easy to understand how well companies protect their personal information, yet 64% believe that clear data protection policies enhance trust.
This disparity in transparency presents a significant gap that organizations must address. Thus, incorporating AI into confidentiality strategies not only meets compliance requirements but also cultivates consumer trust by ensuring that privacy level settings for data sources are communicated clearly and effectively. Additionally, harnessing Business Intelligence can transform raw data into actionable insights, further supporting informed decision-making in data privacy management.
Conclusion
Data privacy represents a multifaceted challenge that organizations must adeptly navigate in today’s data-driven landscape. By understanding and implementing distinct privacy levels—Public, Organizational, and Private—businesses can establish effective protocols that safeguard sensitive information while fostering consumer trust. Each level carries its own set of access controls and security measures, crucial not only for compliance with regulations like GDPR and CCPA but also for mitigating risks associated with data misuse.
As organizations increasingly leverage technology, including artificial intelligence and automation, they must remain vigilant in their data management practices. Implementation challenges, such as employee resistance and the complexities of regulatory compliance, can be effectively addressed through comprehensive training and the integration of advanced tools that streamline processes and enhance operational efficiency. By prioritizing transparency and consent, organizations can cultivate a culture of trust with consumers, who are increasingly concerned about how their data is handled.
In conclusion, the stakes are high for organizations to adopt robust data privacy strategies that not only comply with evolving regulations but also align with consumer expectations. As data privacy becomes a cornerstone of organizational integrity, the commitment to safeguarding information will ultimately strengthen relationships with customers and enhance overall business resilience. Taking proactive steps today will pave the way for a secure and trustworthy digital environment tomorrow.

