Overview
The key differences between diagnostic and descriptive analytics are rooted in their focus and methodologies. Descriptive analytics summarizes past data to answer the question, “What occurred?” In contrast, diagnostic analytics delves into the underlying reasons behind trends, addressing the inquiry, “Why did it happen?” This distinction is crucial for organizations seeking to leverage data effectively.
Descriptive analytics identifies patterns in historical data, such as sales trends, providing a clear snapshot of past performance. On the other hand, diagnostic analytics employs advanced techniques like regression analysis to uncover the root causes of performance changes. This deeper investigation enables organizations to make informed decisions and strategic adjustments, ultimately enhancing their operational effectiveness.
By understanding these differences, professionals can better utilize analytics to drive business success. Are you leveraging the right analytical approach to uncover insights and inform your strategies?
Introduction
In a world where data drives decision-making, understanding the nuances between diagnostic and descriptive analytics is essential for organizations aiming to enhance operational efficiency. Descriptive analytics provides a retrospective view, summarizing historical data to reveal trends and performance metrics. In contrast, diagnostic analytics delves deeper, uncovering the reasons behind those trends.
As automation technologies like Robotic Process Automation (RPA) become increasingly integrated into business processes, leveraging both analytics types empowers organizations to transform raw data into actionable insights.
This article explores the distinct roles of these analytics, their methodologies, and real-world applications, illustrating how businesses can harness their power to foster innovation and drive growth in an ever-evolving landscape.
Understanding the Basics of Diagnostic and Descriptive Analytics
In the realm of automation technologies such as Robotic Process Automation (RPA), diagnostic and descriptive analytics fulfill distinct yet complementary roles in analysis. Descriptive analysis provides an overview of past information, answering the essential question: ‘What occurred?’ It focuses on identifying trends and patterns from historical data, enabling organizations to understand their performance over time.
For instance, a retail firm may employ descriptive analysis to scrutinize sales data from the previous quarter, revealing peak sales periods and customer preferences.
Conversely, diagnostic analysis delves deeper to uncover the reasons behind these trends, addressing the question: ‘Why did it happen?’ This analysis identifies causal relationships and sequences within the data, which is vital for comprehending trends. For example, if sales drop in a specific month, diagnostic analysis can reveal underlying issues such as supply chain disruptions or shifts in consumer behavior.
As Eric Wilson, Director of Thought Leadership at The Institute of Business Forecasting (IBF), emphasizes, “Companies that utilize experienced demand planners opt for diagnostic analysis as it provides comprehensive insights into an issue and additional information to aid business decisions.”
Understanding the distinctions between diagnostic and descriptive analytics is essential for effective decision-making. By 2025, organizations employing both types of data analysis, supported by innovative tools like EMMA RPA and Microsoft Power Automate, can significantly enhance operational efficiency and strategic planning. These RPA solutions not only minimize errors but also liberate teams to concentrate on more strategic, value-adding tasks, addressing the challenges posed by manual, repetitive workflows.
Recent findings indicate that companies utilizing diagnostic analysis gain a detailed understanding of issues, offering more thorough information to support organizational decisions. This is especially critical in a data-rich environment where informed decision-making is paramount.
Real-world applications vividly illustrate these distinctions. For example, a manufacturing firm might use descriptive analytics to monitor production output while employing diagnostic analytics to investigate the causes of production delays. By integrating both approaches and leveraging RPA solutions, businesses can summarize their historical performance and derive actionable insights that drive future improvements.
Tools like Adobe Analytics facilitate the transformation of data into actionable insights, further enhancing analytical capabilities.
In summary, while diagnostic and descriptive analytics provide a snapshot of past events, diagnostic evaluation offers the context necessary to understand why those events occurred. This dual approach, empowered by RPA and AI-driven enhancements, enables organizations to make data-driven decisions that enhance operational efficiency and capitalize on market opportunities. By addressing task repetition fatigue and improving employee morale, RPA tools play a crucial role in supporting organizations on their journey toward operational excellence.
The Role of Descriptive Analytics: What Happened?
Descriptive analysis is essential in examining information, particularly when distinguishing between diagnostic and descriptive analytics. It serves as the foundational step that provides a comprehensive overview of historical performance. By employing statistical techniques, this analysis summarizes information through calculations of averages, totals, and trends over time, emphasizing the differences between diagnostic and descriptive analytics. For instance, Walmart efficiently utilizes detailed analysis to evaluate past sales data, enabling improvements in inventory requirements and enhancing store operations.
This method not only identifies peak sales periods but also reveals overall growth trends, which are crucial for businesses aiming to understand their current market position through diagnostic and descriptive analytics while strategizing for the future.
As we approach 2025, the significance of detailed analysis continues to grow, particularly as companies increasingly integrate artificial intelligence and machine learning into their evaluation processes. This integration fosters more sophisticated predictive capabilities, enhancing decision-making and operational efficiency. As industry expert Andy Morris asserts, “Diagnostic vs descriptive analytics provides vital information about a company’s performance,” facilitating effective communication of performance metrics both internally and externally, which is essential for attracting potential investors and lenders.
Present optimal methods in explanatory analysis underscore the importance of prompt information gathering and examination. Companies are encouraged to streamline their processes, as research indicates that organizations spend an average of 30% of their analytics time on tasks related to diagnostic and descriptive analytics. By optimizing these processes, organizations can focus more on strategic initiatives that drive growth, such as utilizing Power BI services for improved information reporting and actionable insights, or deploying Robotic Process Automation (RPA) to automate manual workflows and enhance operational efficiency, thereby underscoring the importance of understanding diagnostic and descriptive analytics.
RPA can significantly streamline workflows by automating repetitive tasks, reducing errors, and allowing team members to concentrate on more strategic work. Furthermore, leveraging Small Language Models and GenAI Workshops can enhance analytical capabilities by providing tailored AI solutions that improve quality and training processes.
Case studies illustrate the practical applications of diagnostic and descriptive analytics in enhancing organizational performance. For example, in supply chain management, businesses analyze information related to supplier performance, inventory levels, and transportation to identify bottlenecks and inefficiencies. This proactive approach enables timely improvements, ultimately leading to enhanced overall supply chain performance through the utilization of diagnostic and descriptive analytics.
By employing detailed analysis alongside AI-powered solutions, organizations can grasp the distinctions between diagnostic and descriptive analytics to pinpoint specific areas for improvement, ensuring efficient resource allocation.
As organizations navigate the complexities of a knowledge-rich environment, the capacity to summarize past information effectively through diagnostic and descriptive analytics becomes increasingly vital. By leveraging these insights, organizations can transform raw data into actionable intelligence, fostering informed decision-making and promoting innovation. Moreover, the evolving trends in data analysis, particularly the integration with AI and machine learning, alongside customized solutions that leverage Business Intelligence, are set to revolutionize how companies utilize diagnostic and descriptive analytics, making it an even more effective tool for operational efficiency.
Additionally, addressing the challenges of inadequate master data quality is crucial to ensuring that descriptive analysis yields accurate and reliable insights.
The Purpose of Diagnostic Analytics: Why Did It Happen?
The concept of diagnostic versus descriptive analytics underscores the distinction between merely reporting past information and delving deeper to uncover the root causes of performance variations. By leveraging advanced techniques such as:
- data mining
- correlation analysis
- regression analysis
- data drilling
- root cause analysis
organizations can reveal patterns and anomalies that clarify past performance. For instance, when a company faces a sudden decline in sales, diagnostic analysis can identify critical factors, such as shifts in customer preferences or adverse market conditions, that may have contributed to this downturn.
This analytical approach not only aids in pinpointing root causes but also empowers organizations to implement strategic adjustments effectively.
In the realm of operational efficiency, adopting technologies like Robotic Process Automation (RPA) can significantly enhance processes. RPA solutions, such as EMMA RPA, which offers intelligent automation capabilities, and Microsoft Power Automate, designed for seamless workflow automation, are tailored to automate manual workflows. This automation liberates teams to focus on more strategic, value-adding work. Such integration not only boosts employee morale by alleviating repetitive task fatigue but also fosters a streamlined workflow, enabling organizations to swiftly adapt to market changes.
The purpose of diagnostic analysis in business is multifaceted. It serves as a crucial tool for comprehending past events, allowing organizations to learn from experiences and refine operational strategies. A notable example is Rocket Moving Services, where implementing diagnostic analysis resulted in an 18% increase in customer satisfaction.
As Christopher Vardanyan, co-founder of Rocket Moving Services, stated, “diagnostic analysis has played a key role in improving our local moving services.” By examining customer feedback and operational data, we identified that utilizing larger trucks allowed us to accommodate more items in one trip, thus reducing the need for multiple trips. This adjustment led to shorter overall moving times and lower fuel and labor costs for both our company and our clients.
This optimization not only enhanced efficiency but also yielded substantial cost savings for both the company and its clients.
Current trends in information extraction and correlation analysis highlight the growing importance of diagnostic versus descriptive analytics in identifying performance issues. Techniques such as hypothesis testing are increasingly employed to uncover the reasons behind observed trends. For example, manufacturing firms utilize diagnostic analysis to identify inefficiencies in their production processes by analyzing data to uncover root causes of delays.
This leads to optimized processes, reduced production costs, and improved overall efficiency.
In 2025, experts emphasize the significance of diagnostic versus descriptive analytics in understanding business performance. By employing comparative analysis, organizations can evaluate different datasets or periods to identify discrepancies and potential causes of performance changes. Furthermore, by addressing the challenges of technology implementation, organizations can leverage RPA to streamline operations and overcome barriers to efficiency.
This comprehensive approach not only enhances operational efficiency but also cultivates a culture of continuous improvement, ultimately driving growth and innovation.
Methodologies: How Descriptive and Diagnostic Analytics Differ
Descriptive analysis primarily relies on fundamental statistical techniques such as mean, median, and mode to provide a clear summary of information. These techniques are essential for presenting a snapshot of performance metrics, enabling organizations to swiftly recognize trends and patterns. For instance, a company might observe that sales figures peaked in a particular quarter.
However, the true value of analytics becomes apparent when we transition to diagnostic analytics, which employs more sophisticated methodologies like regression analysis, clustering, and time-series analysis. These techniques delve deeper into the data, uncovering the underlying reasons for observed trends and answering critical questions such as ‘why did it happen?’ In today’s overwhelming AI landscape, businesses often struggle to pinpoint suitable analytical tools tailored to their unique needs, making it crucial to have solutions that cut through the noise.
A practical illustration of this distinction can be seen in the case of Canadian Tire, which achieved nearly a 20% increase in sales by leveraging AI-powered insights to examine purchasing behavior. This diagnostic approach enabled them to identify key factors driving customer purchases, such as effective marketing strategies and seasonal demand shifts. As we approach 2025, the methodologies employed in both descriptive and diagnostic analytics continue to evolve, with organizations increasingly adopting advanced statistical techniques to enhance their analytical capabilities.
For instance, regression analysis not only identifies relationships between variables but also aids in predicting future outcomes based on historical information. As Anik Sengupta, a Staff Engineer, notes, ‘Regression analysis identifies the relationship between a dependent variable and one or more independent variables.’ This predictive power is invaluable for organizations aiming to make informed decisions in a rapidly changing environment.
Moreover, the current landscape underscores the importance of understanding these methodologies. Experts in the field emphasize that a robust analytical framework is crucial for organizations seeking to optimize their operations and drive growth. By distinguishing between diagnostic and descriptive analytics, organizations can better utilize their information, transforming raw details into actionable insights that guide strategic initiatives.
Furthermore, advancements in technology are facilitating real-time prescriptive analysis, further enhancing organizations’ abilities to examine and react to trends. Harnessing Business Intelligence alongside RPA solutions stands at the forefront of this evolution, as RPA can automate data collection and processing, driving data-driven insights and operational efficiency for sustained business growth.
Real-World Applications: Leveraging Descriptive and Diagnostic Analytics
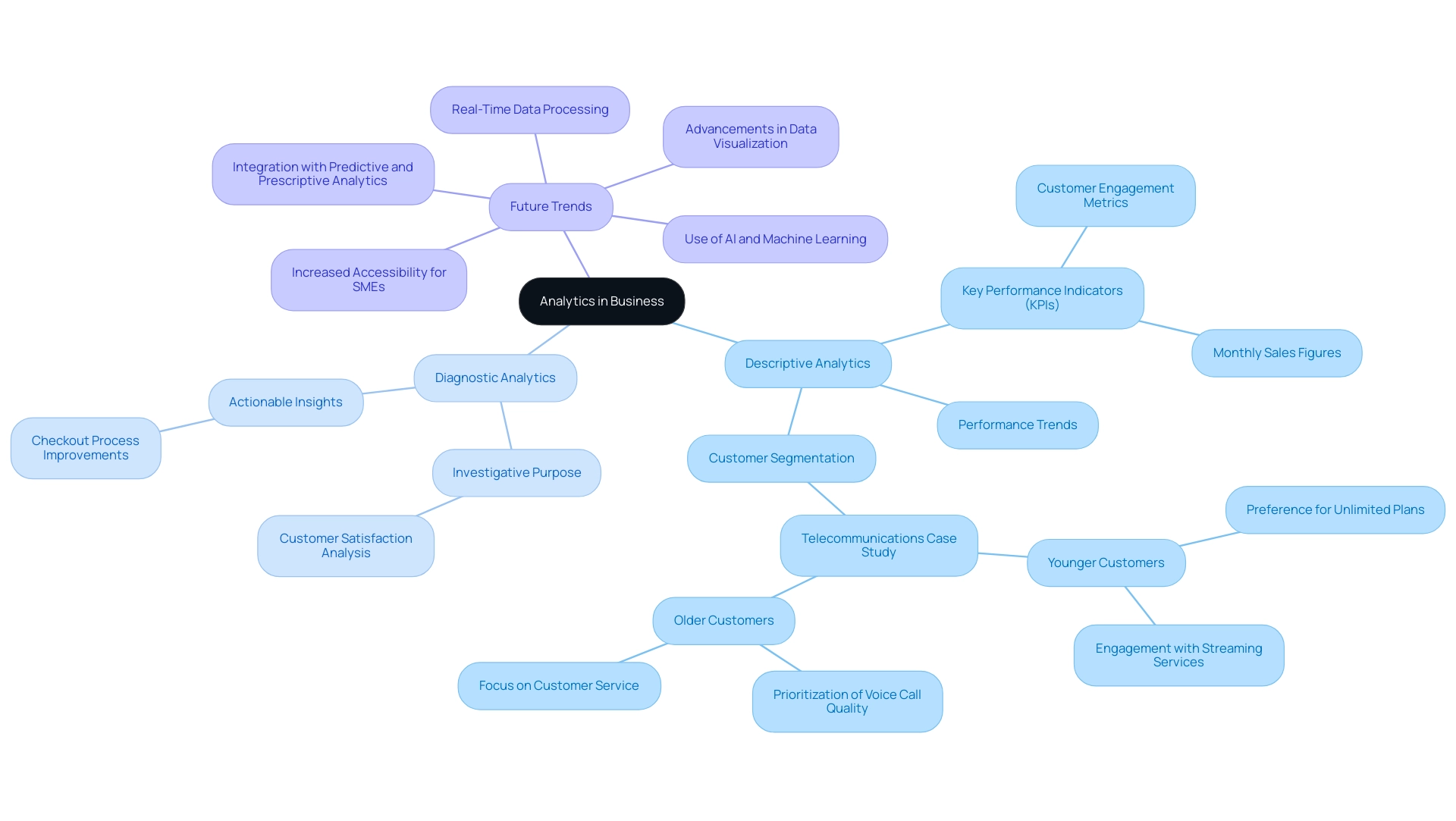
Businesses effectively utilize descriptive data analysis to create comprehensive reports encapsulating key performance indicators (KPIs), such as monthly sales figures and customer engagement metrics. This approach enables organizations to monitor performance trends over time, providing a clear picture of operational health. In contrast, the distinction between diagnostic and descriptive analytics reveals that diagnostic analysis serves a more investigative purpose, allowing companies to delve into specific challenges, such as pinpointing the causes behind a dip in customer satisfaction scores.
By meticulously analyzing feedback information and correlating it with operational changes, businesses can identify actionable insights for targeted improvements.
In today’s overwhelming AI landscape, businesses often struggle to identify the right solutions that meet their specific needs. Tailored solutions can help cut through the noise to harness the power of Business Intelligence. For example, a telecommunications firm utilized descriptive analysis to segment its customer base, revealing distinct usage patterns and preferences across various demographic groups.
This analysis indicated that younger customers favored unlimited plans and heavily engaged with streaming services, while older customers prioritized voice call quality and customer service. Such insights can guide focused marketing approaches and service improvements, ultimately boosting operational efficiency and company growth. Moreover, the distinction between diagnostic and descriptive analytics can lead to substantial enhancements in customer satisfaction.
A retail company, for example, might uncover that extended checkout times correlate with decreased customer satisfaction. By streamlining their checkout processes based on these findings, they can enhance the overall customer experience. This proactive approach not only addresses urgent issues but also nurtures long-term loyalty and satisfaction among clients.
As companies continue to adopt these analytical methods, the integration of real-time data processing and improvements in data visualization will further enable informed decision-making. Future trends in descriptive analysis include integration with predictive and prescriptive approaches, which will enhance the depth of insights available. Significantly, Narellan Pools experienced a sales rise while utilizing just 70% of its media budget, demonstrating the impact of data analysis in enhancing sales performance.
Andy Morris, a Principal Product Marketing Specialist, emphasizes that ‘descriptive analysis provides vital information about a company’s performance.’ The future of descriptive analytics is poised to include greater accessibility for small and medium-sized enterprises, enabling them to leverage data-driven insights to enhance operational efficiency and customer satisfaction. To learn more about how tailored AI solutions can align with your business goals and challenges, reach out to us today, reinforcing the significance of BI and RPA in today’s data-rich environment.
Conclusion
Understanding the distinct yet complementary roles of descriptive and diagnostic analytics is crucial for organizations aiming to enhance operational efficiency and drive growth. Descriptive analytics offers a foundational overview of historical performance, enabling businesses to identify trends and metrics that inform current strategies. By employing techniques that summarize past data, organizations can gain a clearer understanding of their market position and operational health.
In contrast, diagnostic analytics delves deeper to uncover the reasons behind observed trends. This analytical approach allows businesses to identify root causes of performance fluctuations, facilitating informed decision-making and strategic adjustments. The integration of automation technologies, such as Robotic Process Automation (RPA), further enhances these analytical capabilities by streamlining workflows and reducing manual errors. This empowers teams to concentrate on more strategic initiatives.
Real-world applications of both analytics types underscore their significance in driving operational improvements and customer satisfaction. By leveraging data-driven insights, companies can not only address immediate challenges but also cultivate a culture of continuous improvement and innovation. As the analytics landscape evolves, organizations that effectively harness both descriptive and diagnostic analytics will be better equipped to navigate the complexities of a data-rich environment. This ultimately leads to sustained business growth and enhanced competitive advantage.

