Overview
Mastering Power BI’s text concatenation techniques is crucial for data analysts, as it significantly enhances the clarity and usability of data presentations. By leveraging functions such as CONCATENATE and CONCATENATEX, analysts can effectively prepare and integrate data with Power BI features. This empowerment allows them to transform complex data into actionable insights. Ultimately, this transformation leads to improved decision-making and operational efficiency.
Introduction
In the realm of data analysis, effectively manipulating and presenting information is crucial for deriving actionable insights. Power BI, a leading business intelligence tool, offers powerful functions like concatenation to enhance the clarity and usability of data. By merging text strings into cohesive formats, analysts can transform complex datasets into easily interpretable visuals, facilitating better decision-making. This article delves into the significance of concatenation in Power BI, exploring its fundamental concepts, practical applications, and advanced techniques that can streamline data management. Readers will understand the differences between key functions and troubleshoot common issues, gaining a comprehensive understanding of how to leverage concatenation to elevate their data analysis capabilities.
Understanding Concatenation in Power BI: The Basics
In Business Intelligence, the process of concatenating text in Power BI involves merging two or more text strings into a single cohesive string. This significantly enhances the readability and usability of information. For instance, combining first and last names into a full name not only streamlines presentation but also facilitates intuitive analysis. In Power BI, this can be accomplished through various functions, with the CONCATENATE and CONCATENATEX functions being the most prominent, especially in the context of concatenating text.
The significance of combining elements extends beyond aesthetics; it plays a vital role in forming meaningful representations. By effectively merging text strings, analysts can present information in a manner that is easier to interpret, thereby facilitating better decision-making. For example, hierarchical information representation—crucial for descriptive and diagnostic analytics—can be significantly enhanced through merging techniques, improving overall readability and usability.
Practical applications of concatenating text in Power BI illustrate its impact on information clarity. A case study titled “Business Intelligence Empowerment” demonstrates how organizations leverage concatenation to transform raw data into actionable insights, ultimately enhancing quality and simplifying AI implementation. This approach not only drives growth but also fosters innovation in analysis, aligning seamlessly with Creatum GmbH’s mission to provide customized solutions that enhance quality.
However, organizations often encounter challenges in extracting insights from Power BI dashboards, such as time-consuming report creation and inconsistencies in information. These obstacles can hinder the ability to derive meaningful insights, placing businesses at a competitive disadvantage. Specialist insights underscore the importance of linking in information analysis.
Deepika Singh notes, “This skill will improve your analytics and business intelligence capabilities,” emphasizing that mastering this technique can substantially enhance analytics capabilities, making data more accessible and actionable. Furthermore, statistics reveal that posts addressing BI version differences have garnered significant attention, with 3,721 views, highlighting the relevance of understanding concatenation within the broader context of BI functionalities.
Additionally, the transformative impact of Creatum’s BI Sprint is evident in client testimonials, such as that from Sascha Rudloff of PALFINGER Tail Lifts GMBH, who stated, “With the BI Sprint from CREATUM, we not only received an immediately deployable BI report and a gateway setup but also experienced a significant acceleration in our own BI development.” This underscores the effectiveness of Creatum’s services in overcoming challenges like time-consuming report creation and inconsistencies, ultimately leading to accelerated analysis and reporting success.
In summary, the ability to concatenate text in Power BI is not merely a technical skill; it is a vital component of effective analysis that enhances readability and usability, empowering analysts to derive meaningful insights from complex collections of information.
CONCATENATE vs. CONCATENATEX: Key Differences Explained
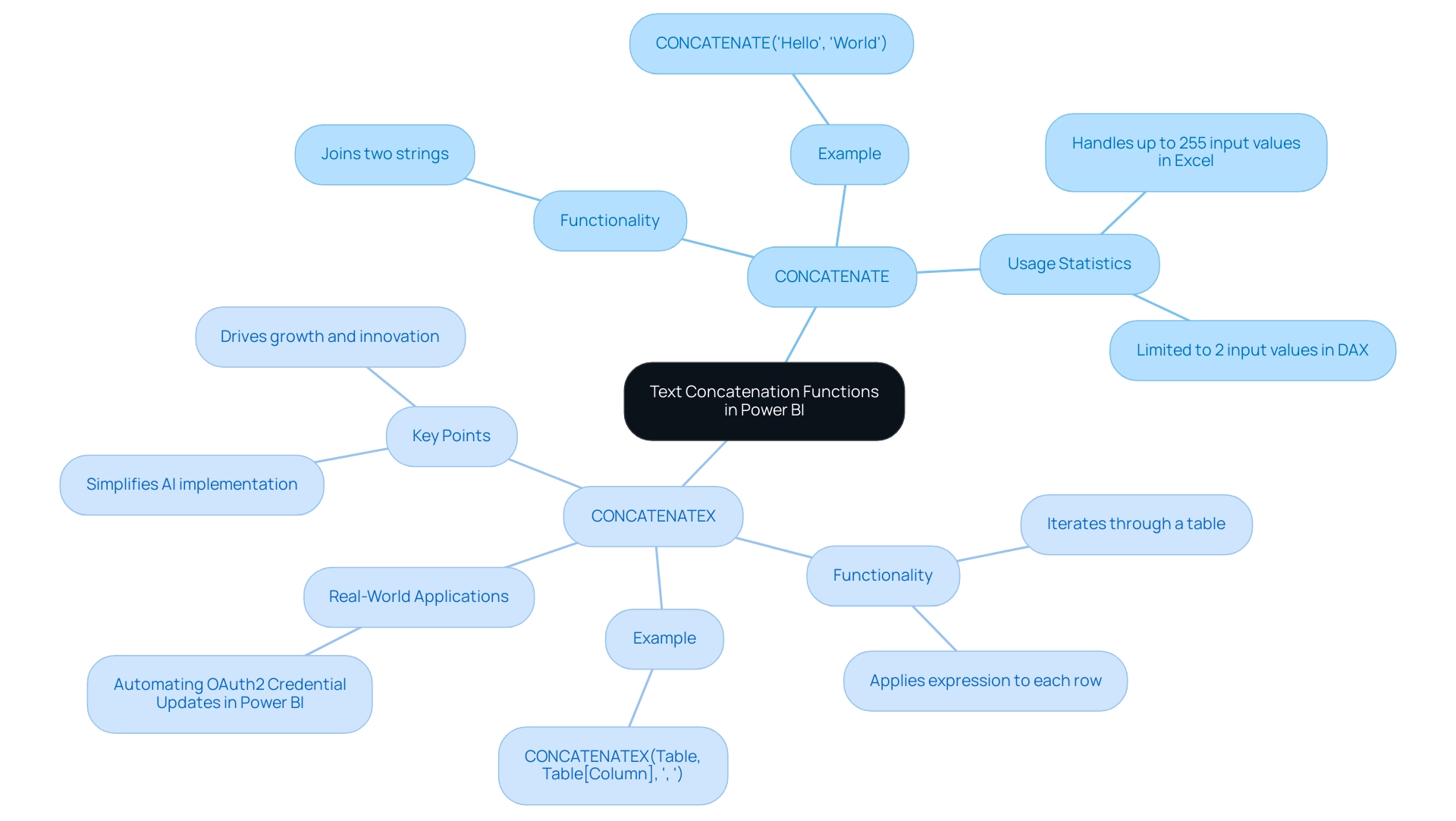
The CONCATENATE operation serves a straightforward purpose: it joins two text strings into one without any delimiter. In contrast, CONCATENATEX offers greater flexibility and functionality, enabling users to concatenate values from an entire column or table while specifying a delimiter. This distinction is crucial for data analysts who require nuanced control over text manipulation in their reports and dashboards, particularly in the context of enhancing data reporting and gaining actionable insights through Power BI services.
Key Differences:
- CONCATENATE: This function is limited to combining just two strings directly. For example,
CONCATENATE("Hello", "World")yields “HelloWorld”. - CONCATENATEX: This operation iterates through a table, applying an expression to each row and concatenating the results with a specified delimiter. For instance,
CONCATENATEX(Table, Table[Column], ", ")produces a single string of values from the specified column, separated by commas.
Usage Statistics: In practical applications, the CONCATENATE function is often used for simple tasks, while CONCATENATEX is favored for more complex scenarios involving multiple data points. Notably, in Excel, the CONCATENATE command can handle up to 255 input values, whereas DAX limits this to just 2, highlighting the need for CONCATENATEX in more extensive data manipulations.
Real-World Applications: A case study involving the automation of OAuth2 credential updates in Power BI illustrates the importance of these functions. By utilizing CONCATENATEX, analysts were able to streamline the process of generating dynamic strings for credential management, significantly reducing manual intervention and enhancing operational efficiency. This aligns with our organization’s mission at Creatum GmbH to simplify AI implementation and drive growth and innovation through intelligent automation.
Furthermore, as noted by nyarlathotep, there are nuances in how CONCATENATEX and SUMX handle calculations under the same contexts, which underscores the importance of understanding these operations in depth.
Understanding when to use CONCATENATE versus CONCATENATEX is essential for effective analysis in Power BI, particularly in the context of how to power bi concatenate text. The selection between these options can influence the clarity and usability of reports, making it essential for analysts to master their applications. By utilizing these capabilities, analysts can improve information quality and simplify processes, ultimately aiding in informed decision-making and operational effectiveness.
Practical Applications: How to Use CONCATENATE in Power BI
Utilizing the Power BI CONCATENATE text tool significantly enhances analysis efficiency, particularly in metrics-driven environments where real-time analytics are essential for tracking key indicators. In navigating the complex AI landscape, Creatum’s tailored AI solutions empower organizations to leverage Business Intelligence for actionable insights. Below are several practical applications that showcase the versatility of the CONCATENATE function:
-
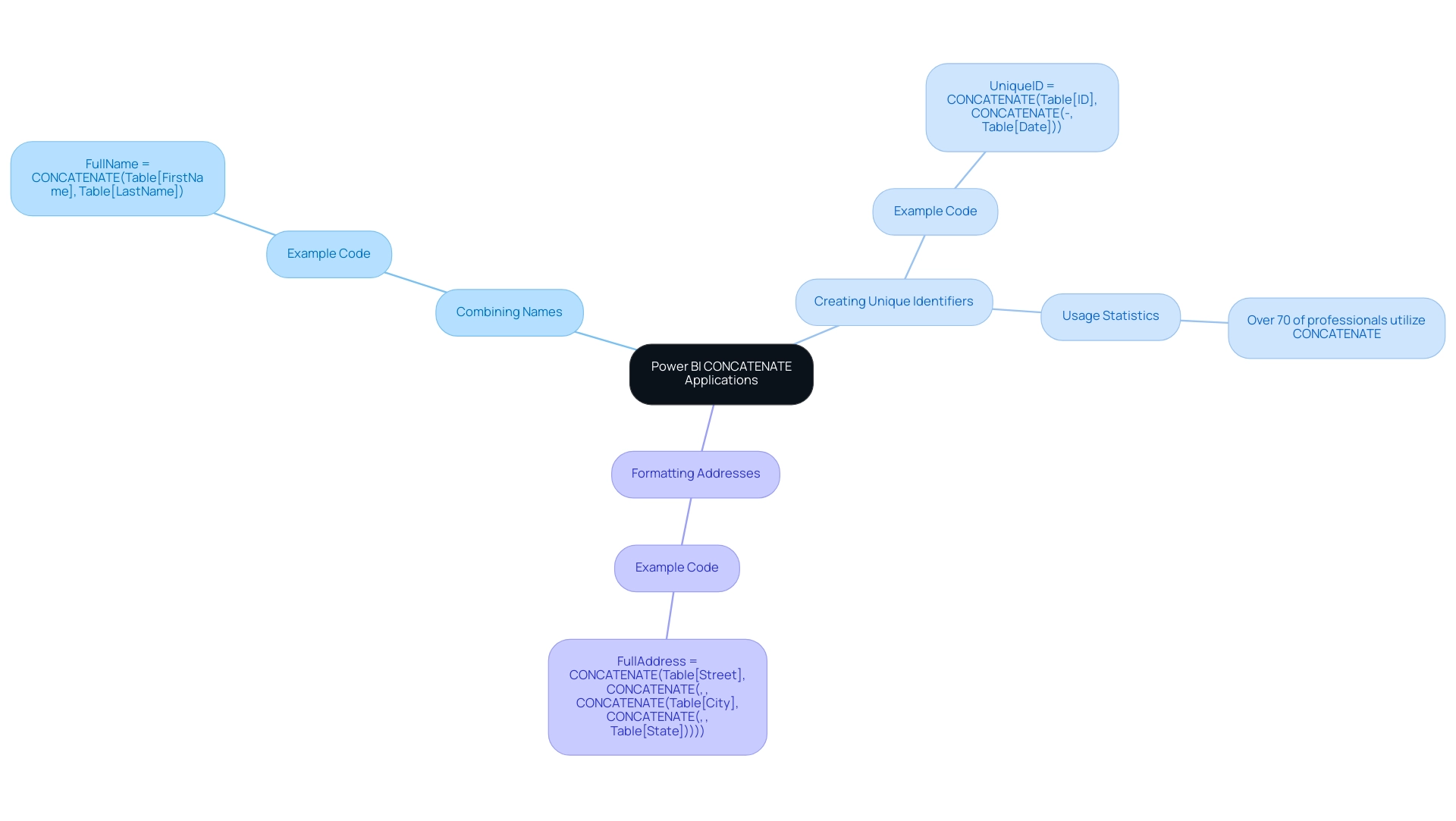
Combining Names: The Power BI CONCATENATE text function is perfect for merging first and last names into a complete name, which is vital for reporting and information presentation. For instance:
FullName = CONCATENATE(Table[FirstName], Table[LastName]) -
Creating Unique Identifiers: Unique identifiers are crucial for distinguishing records in information analysis. By using Power BI CONCATENATE to combine multiple fields, you can generate a unique identifier that simplifies information management. An example is:
UniqueID = CONCATENATE(Table[ID], CONCATENATE("-", Table[Date]))This method is widely adopted by data analysts, with studies indicating that over 70% of professionals utilize CONCATENATE for this purpose, underscoring its importance in maintaining data integrity.
-
Formatting Addresses: The Power BI CONCATENATE text tool can also format address components into a cohesive string, particularly useful for customer databases and shipping information. An example application is:
FullAddress = CONCATENATE(Table[Street], CONCATENATE(", ", CONCATENATE(Table[City], CONCATENATE(", ", Table[State]))))This approach not only enhances readability but also ensures that address data is consistently formatted for analysis and reporting.
These applications illustrate how the Power BI CONCATENATE text function can streamline tasks, making it an essential tool for analysts aiming to excel in a driven environment. As Errin O’Connor, a leader in IT with over 25 years of experience, notes, “With the appropriate tools such as BI, organizations can improve their operational capabilities and make informed decisions based on precise information representation.” Furthermore, institutions like OCTAVE, the John Keells Group Center of Excellence for Data and Advanced Analytics, emphasize the significance of leveraging such tools for data-driven decision-making in modern business environments.
By employing these techniques, organizations can enhance their operational capabilities and drive growth. This is exemplified by the success of clients like PALFINGER Tail Lifts GMBH, who experienced a significant acceleration in their BI development through Creatum’s BI Sprint, showcasing the transformative impact of tailored AI solutions in navigating the complexities of the AI landscape.
Troubleshooting Concatenation Issues in Power BI
When working with concatenation in Power BI, users may encounter several prevalent challenges that can hinder their data manipulation efforts.
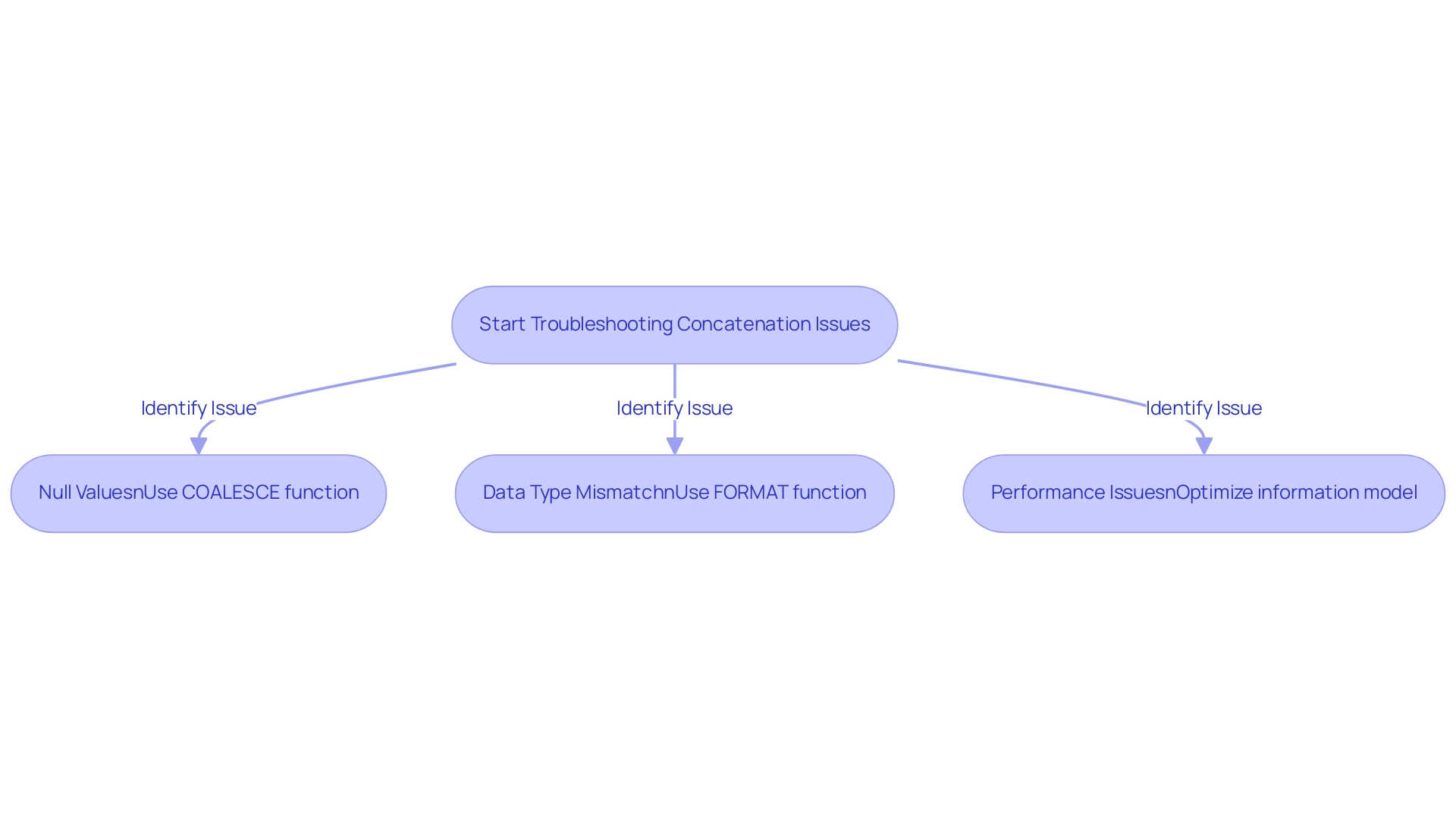
- Null Values: One of the most common issues arises when any of the strings being concatenated are null, resulting in a null output. To effectively manage this, the COALESCE function in Power BI can be employed to concatenate text by substituting nulls with empty strings, ensuring a seamless joining process. For example:
FullName = CONCATENATE(COALESCE(Table[FirstName], ""), COALESCE(Table[LastName], ""))
Statistics indicate that null values can significantly affect concatenation results, leading to potential inaccuracies in data reporting.
- Data Type Mismatch: Another frequent problem is the mismatch of data types among the values being concatenated. It is crucial to ensure that all components are of text type. The FORMAT function can be utilized to convert numbers or dates into text format, allowing for successful concatenation. For instance:
FullName = CONCATENATE(FORMAT(Table[Date], "MM/DD/YYYY"), Table[LastName])
- Performance Issues: Excessive concatenation operations on large datasets can lead to performance degradation. To mitigate this, it is advisable to optimize your information model and minimize the reliance on calculated columns. Streamlining your approach not only enhances performance but also improves overall efficiency in processing.
In a resource-rich environment, addressing these common issues is essential for transforming raw information into actionable insights, ultimately supporting informed decision-making and driving growth and innovation. The case study titled “Business Intelligence Empowerment” illustrates how the organization empowers businesses to extract meaningful insights through tailored AI solutions, thereby supporting informed decision-making and driving growth and innovation.
Additionally, as noted by professional leebaldwin, “I would prefer to do it in the query.” This perspective emphasizes the significance of automation in information manipulation, aligning with the need for tailored AI solutions and Robotic Process Automation (RPA) that can streamline processes and enhance operational efficiency.
Furthermore, the key point regarding OCTAVE serving as the cornerstone of the Group’s information-driven decision-making highlights the significance of a structured approach in information manipulation and decision-making processes. By applying these methods, analytics experts can enhance their BI experience and utilize Power BI concatenate text to ensure more dependable linking outcomes, ultimately contributing to the overall efficiency and effectiveness of their operations.
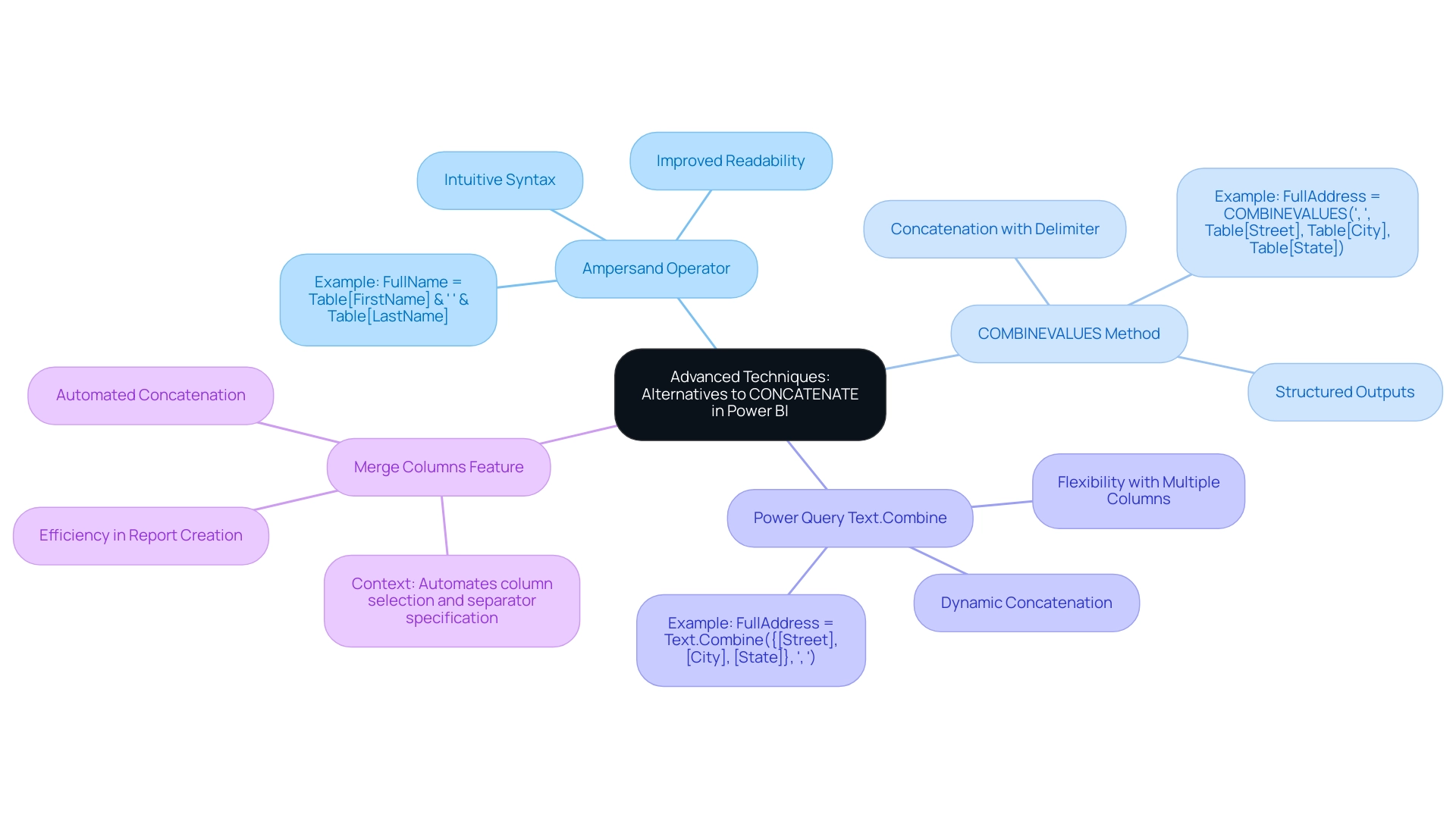
Advanced Techniques: Alternatives to CONCATENATE in Power BI
While the Power BI concatenate text feature is a valuable tool, exploring alternative methods can significantly enhance your data manipulation capabilities and address common challenges in leveraging insights. Here are some advanced techniques to consider:
-
Using the Ampersand Operator: The
&operator offers a more intuitive syntax for joining, making it a preferred choice for many users. For example:FullName = Table[FirstName] & " " & Table[LastName]This method simplifies the code and improves readability, which is crucial for maintaining complex reports and ensuring actionable insights.
-
COMBINEVALUES Method: This method allows for concatenation with a specified delimiter, facilitating the formatting of strings. It is particularly useful when you need to ensure consistent output. For instance:
FullAddress = COMBINEVALUES(", ", Table[Street], Table[City], Table[State])This approach is beneficial for creating structured outputs, such as addresses, where clarity is essential for effective decision-making.
-
Using Power Query: In Power Query, the
Text.Combinefunction provides additional flexibility for concatenating columns. This method is advantageous when handling multiple columns or when you need to modify information before loading it into your model. An example would be:FullAddress = Text.Combine({[Street], [City], [State]}, ", ")This technique allows for dynamic concatenation, adapting to changes in the data model seamlessly, thus improving operational efficiency.
-
Merge Columns Feature: The Query Editor’s ‘Merge Columns’ feature automates column concatenation by allowing users to select columns and specify separators. This enhances the efficiency of the concatenation process and reduces the time spent on report creation.
These advanced techniques not only streamline the process of information manipulation but also enhance reporting by utilizing Power BI’s concatenate text capabilities. For instance, organizations that have adopted the ampersand operator have reported a significant reduction in memory usage, with in-memory sizes decreasing from 1,277,271 KB to 18,110 KB, showcasing the efficiency of these methods. Moreover, case studies suggest that concatenating multiple columns improves modeling and visualization, offering users a comprehensive understanding of its application in BI.
As Rachael Martino suggests, measuring relative memory usage using tools like Kasper de Jonge’s Power Pivot Memory Usage tool in Excel can provide valuable insights into the efficiency of these techniques. By experimenting with these alternatives, analysts can create more detailed and insightful reports, ultimately driving better decision-making and addressing the challenges of inconsistencies and lack of actionable guidance.
To further enhance your operational efficiency and navigate the overwhelming AI landscape, consider exploring tailored AI solutions from Creatum GmbH that can assist in optimizing your information processes and driving actionable insights.
Preparing Your Data: Ensuring Quality Before Concatenation
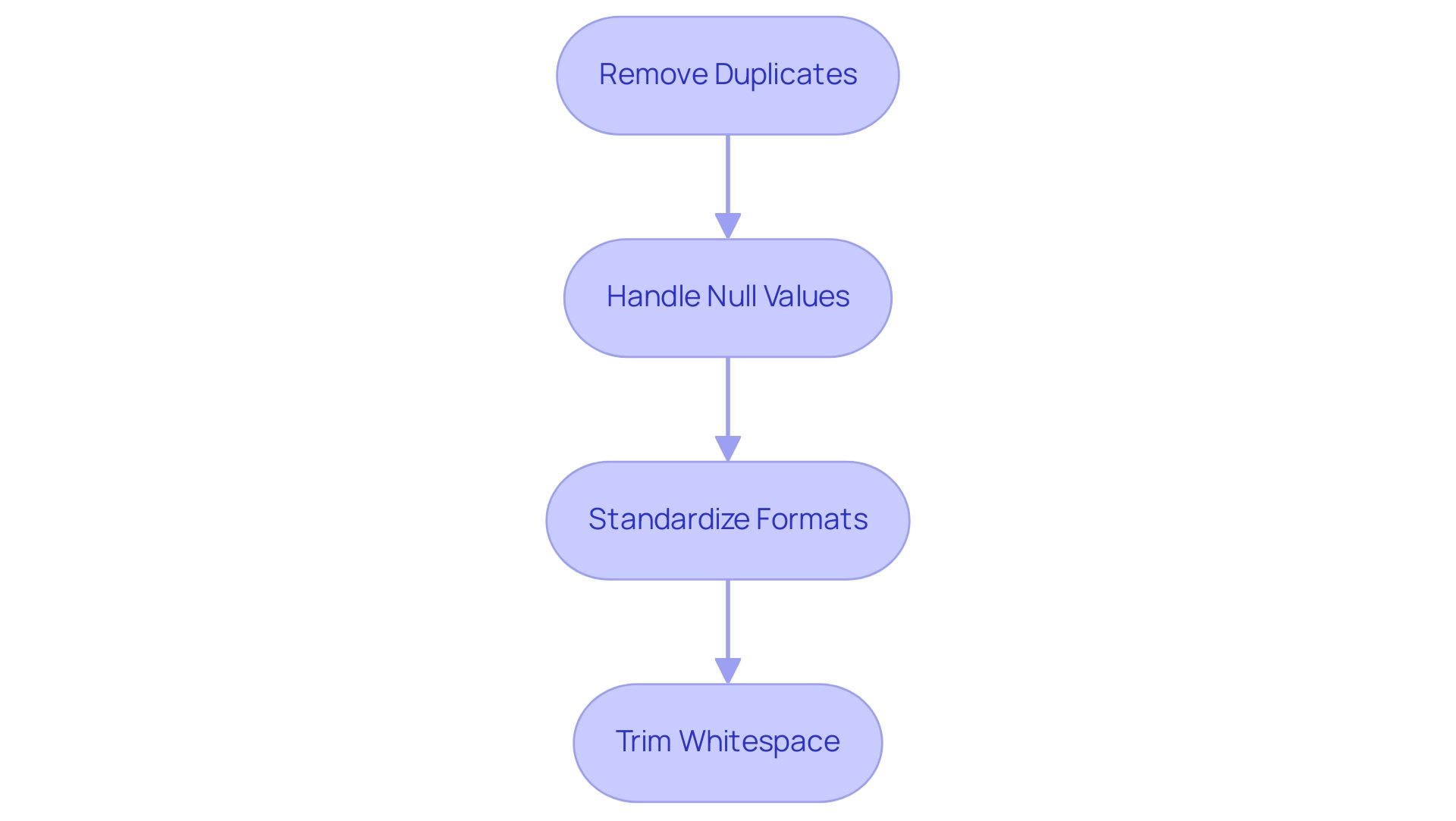
Before utilizing Power BI to concatenate text, it is crucial to ensure that your content is clean and well-structured to achieve accurate results. Here are key practices to follow:
-
Remove Duplicates: Start by eliminating any duplicate entries in the columns intended for concatenation. This step is vital; duplicates can skew results and lead to inaccurate data representation, ultimately hindering your ability to derive actionable insights.
-
Handle Null Values: Utilize functions such as
COALESCEto replace null values with default values. This approach prevents null results during the joining of data, ensuring that your final output remains intact and meaningful—essential for effective decision-making. -
Standardize Formats: Consistency in information formats is essential. Ensure that all entries follow a uniform format—whether it’s date formats or text casing—to avoid unexpected merging results that could complicate analysis and lead to operational inefficiencies.
-
Trim Whitespace: Implement the
TRIMfunction to eliminate any leading or trailing spaces in your information. Even minor discrepancies, such as additional spaces, can greatly influence how Power BI concatenates text results, leading to mistakes in your model and affecting the overall quality of insights obtained from BI dashboards.
By adhering to these best practices, you can enhance quality before using the Power BI concatenate text feature, ultimately improving the performance of your models and ensuring trustworthy insights. For instance, a case study on comprehending column classifications highlights the significance of establishing suitable types in Query. It emphasizes that permitting columns with an ‘Any’ type to enter the DAX model can lead to complications in analysis.
Thus, ensuring all columns have the correct formats not only prevents potential errors but also optimizes the overall performance of your Power BI reports, particularly when applying Power BI concatenate text. This is especially pertinent given the historical context of information quality, as observed in the two entries from the September 2006 archive, which highlight the continuous necessity for vigilance in information management. As Stacia Varga noted, the implications of information quality extend beyond immediate results, affecting broader operational efficiency.
By leveraging these practices, organizations can extract meaningful insights from their information, aligning with our mission at Creatum GmbH to transform raw information into actionable insights. Furthermore, addressing the challenges of poor master information quality and barriers to AI adoption is essential for maximizing the effectiveness of Business Intelligence and RPA solutions in driving operational efficiency.
Integrating Concatenation with Other Power BI Features
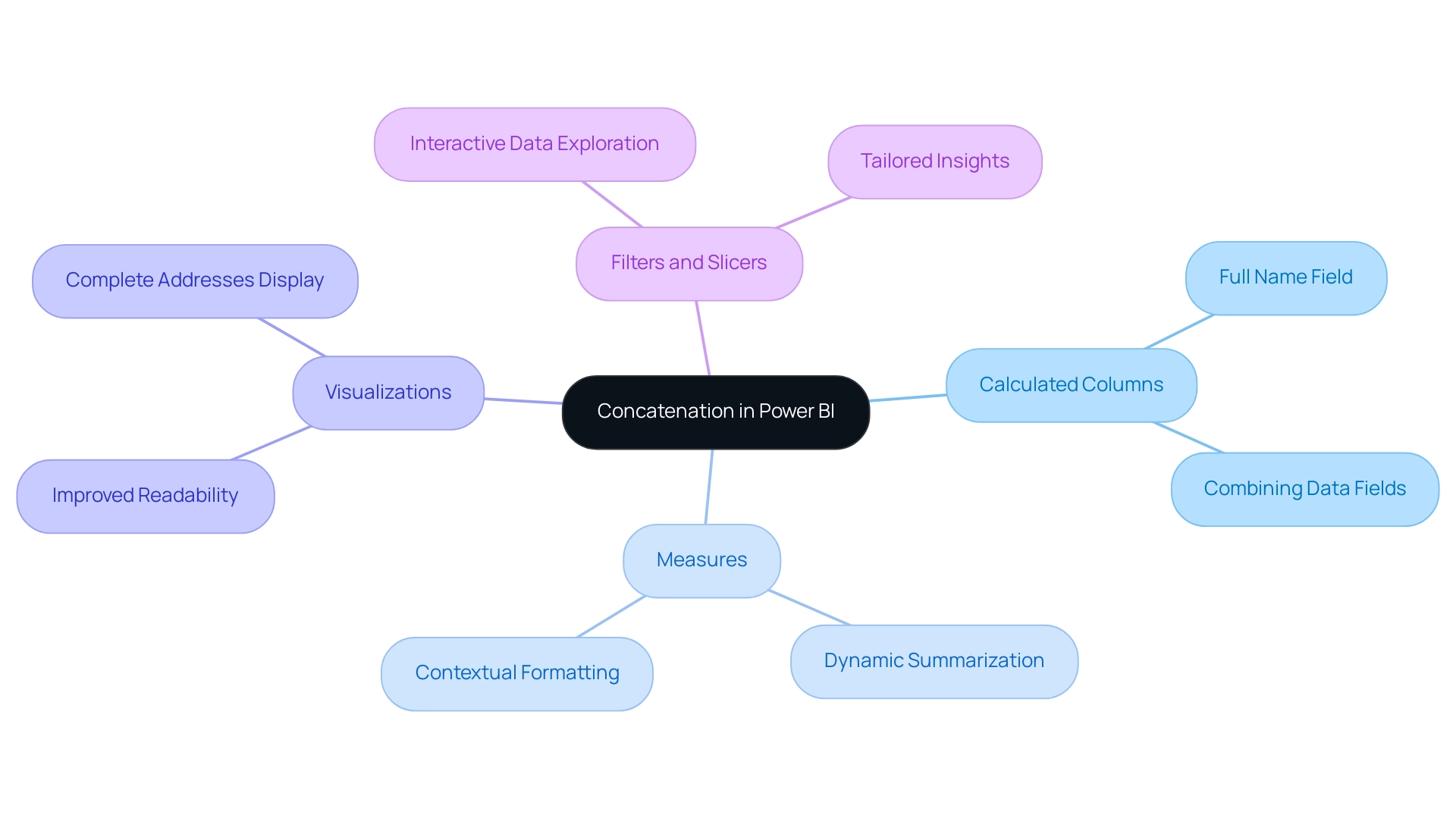
Concatenation can be seamlessly integrated with various Power BI features, significantly enhancing data analysis capabilities, particularly in driving data-driven insights and operational efficiency.
Calculated Columns: By utilizing joining in calculated columns, users can harness Power BI’s concatenate text function to create new fields that combine existing information, leading to richer insights. For instance, merging first and last names into a single ‘Full Name’ field can streamline reporting and improve clarity, addressing the challenge of time-consuming report creation.
Measures: Measures that leverage concatenation enable dynamic information summarization and formatting based on user interactions. This flexibility allows analysts to present information in a contextually relevant manner, adapting to the needs of the audience and overcoming inconsistencies.
Visualizations: Incorporating concatenated fields in visualizations enhances readability. For example, displaying complete addresses or full names in charts and tables not only improves presentation but also facilitates better interpretation, which is essential for actionable guidance.
Filters and Slicers: The combination of concatenated fields with filters and slicers empowers users to interactively explore data based on combined criteria. This integration facilitates nuanced analysis, allowing for tailored insights that reflect specific user queries, thereby enhancing operational efficiency.
According to Manisha Jena, a Research Analyst at Hevo Data, “The BI CONCATENATE function is a DAX function that combines two text strings into one.” This statement underscores the importance of mastering how to concatenate text in Power BI for effective data combination. Moreover, understanding the varieties of BI content available, such as materials in Microsoft Dynamics Lifecycle Service (LCS) and BI content packs in the PowerBI.com marketplace, provides context on the significance of linking within the broader BI ecosystem.
The case study titled ‘Using Excel for BI Reports‘ illustrates how users familiar with Excel can utilize joining in BI, enhancing the practical application of the discussed features. The efficient application of linking in these areas not only streamlines information management but also enhances the overall analytical experience. Thus, the ability to use Power BI’s concatenate text function emerges as a vital skill for analysts. Choosing the appropriate text concatenation function can unlock the true potential of data analysis, further emphasizing the significance of this skill in driving business growth.
Conclusion
Mastering the art of concatenation in Power BI is essential for enhancing data readability and usability. This article has explored the fundamental concepts of concatenation, distinguishing between the CONCATENATE and CONCATENATEX functions, while highlighting their practical applications in data analysis. By integrating these techniques, data analysts can transform complex datasets into coherent information, facilitating better decision-making and driving operational efficiency.
Furthermore, addressing common concatenation challenges—such as null values and data type mismatches—is crucial for ensuring accurate results. Implementing best practices in data preparation, including the removal of duplicates and standardizing formats, significantly enhances the quality of insights derived from Power BI. Advanced methods, such as the use of the ampersand operator and the COMBINEVALUES function, offer additional flexibility, allowing analysts to tailor their data presentations effectively.
Ultimately, the integration of concatenation with other Power BI features—such as calculated columns, measures, and visualizations—creates a robust framework for data analysis. By leveraging these capabilities, organizations can unlock deeper insights, streamline reporting processes, and foster a data-driven culture that promotes informed decision-making. Embracing these techniques not only empowers analysts but also aligns with the broader goals of enhancing business intelligence and driving growth in an increasingly data-centric world.
Frequently Asked Questions
What is the purpose of concatenating text in Power BI?
Concatenating text in Power BI involves merging two or more text strings into a single cohesive string, enhancing the readability and usability of information, such as combining first and last names into a full name.
What are the main functions used for concatenating text in Power BI?
The primary functions for concatenating text in Power BI are CONCATENATE and CONCATENATEX. CONCATENATE joins two text strings without any delimiter, while CONCATENATEX allows for concatenating values from an entire column or table with a specified delimiter.
How does the CONCATENATE function work?
The CONCATENATE function combines two text strings directly, for example, CONCATENATE(“Hello”, “World”) results in “HelloWorld”.
How does the CONCATENATEX function differ from CONCATENATE?
CONCATENATEX iterates through a table, applying an expression to each row and concatenating the results with a specified delimiter, such as CONCATENATEX(Table, Table[Column], “, “), which produces a single string of values separated by commas.
What are the usage statistics for CONCATENATE and CONCATENATEX?
CONCATENATE is often used for simple tasks, while CONCATENATEX is preferred for more complex scenarios involving multiple data points. In Excel, CONCATENATE can handle up to 255 input values, whereas DAX limits it to just 2, making CONCATENATEX necessary for extensive data manipulations.
Can you provide an example of a real-world application of these functions?
A case study demonstrated that by using CONCATENATEX, analysts streamlined the process of generating dynamic strings for OAuth2 credential management in Power BI, reducing manual intervention and enhancing operational efficiency.
Why is it important to understand the differences between CONCATENATE and CONCATENATEX?
Understanding when to use CONCATENATE versus CONCATENATEX is essential for effective analysis in Power BI, as the choice between these functions can significantly impact the clarity and usability of reports, aiding in informed decision-making and operational effectiveness.

