Overview
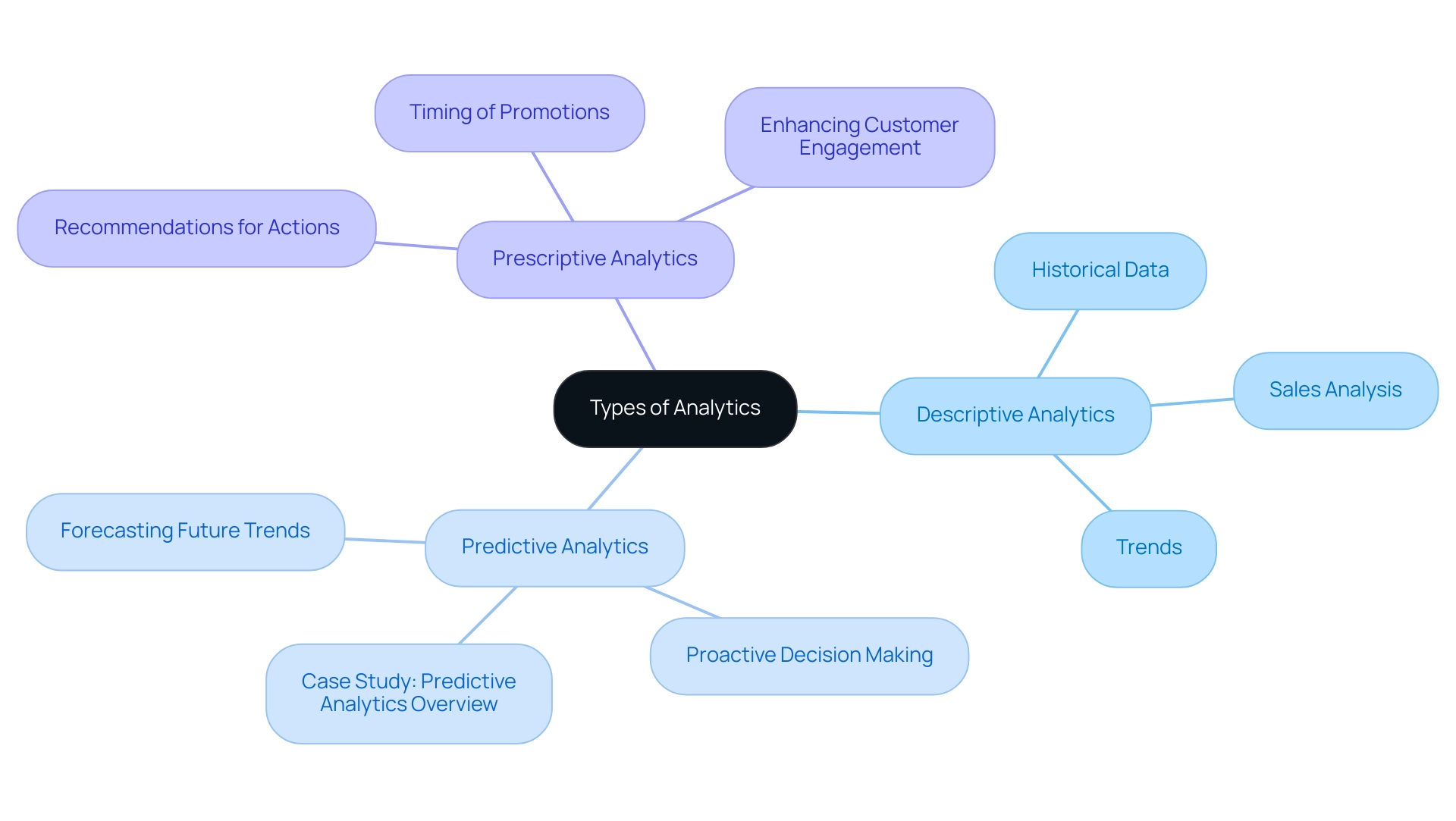
The three primary types of analytics—descriptive, predictive, and prescriptive—each fulfill unique roles in data analysis.
- Descriptive analytics summarizes past data, enabling organizations to identify trends effectively.
- Predictive analytics leverages historical data to forecast future outcomes, allowing for informed decision-making.
- Prescriptive analytics goes a step further by recommending actions to optimize results.
Together, these analytics types significantly enhance decision-making and operational efficiency within organizations, demonstrating their critical importance in today’s data-driven landscape.
Introduction
In the modern business landscape, the ability to harness data effectively determines an organization’s success. Analytics serves as the backbone of business intelligence, enabling companies to make informed decisions by uncovering patterns and insights from vast amounts of data. As organizations navigate an increasingly complex digital environment, understanding the three primary types of analytics—descriptive, predictive, and prescriptive—becomes essential. Each type plays a unique role in guiding strategic planning and enhancing operational efficiency. They allow businesses to not only understand past performance but also anticipate future trends and recommend optimal actions. As the reliance on data-driven strategies intensifies, the integration of these analytics forms a critical framework for fostering innovation and maintaining a competitive edge.
Understanding Analytics: The Backbone of Business Intelligence
Analytics represents a systematic computational analysis of data, serving as a cornerstone of business intelligence. It empowers organizations to make informed, data-driven decisions by revealing patterns, trends, and insights that guide strategic planning and operational enhancements. In today’s data-rich environment, understanding data analysis is crucial for organizations aiming to boost their efficiency and effectiveness.
This essential comprehension enables companies to leverage analytics, categorized into three main types: descriptive, predictive, and prescriptive, each serving a unique function in operational success.
Descriptive analysis focuses on summarizing past information to identify trends and patterns. For instance, businesses can analyze historical sales data to understand customer behavior, informing inventory management and marketing strategies. In contrast, predictive analysis employs statistical models and machine learning techniques to forecast future outcomes based on historical data. This analysis is particularly valuable for operational efficiency, allowing organizations to anticipate demand fluctuations and optimize resource allocation accordingly.
Utilizing AI solutions, including Small Language Models and GenAI Workshops, can further enhance predictive capabilities by improving data quality and providing tailored insights. Prescriptive analysis advances this process by recommending actions based on predictive insights. For example, a company might use prescriptive analysis to identify the optimal course of action for inventory replenishment, considering factors such as lead times and demand forecasts. This proactive approach not only enhances operational efficiency but also drives data-driven decision-making across the organization. Furthermore, Robotic Process Automation (RPA) can automate manual workflows, reducing errors and enabling teams to focus on more strategic tasks, thereby improving overall operational efficiency.
The evolution of business intelligence emphasizes that descriptive, predictive, and other analytics types are vital for data evaluation. As organizations increasingly adopt artificial intelligence and machine learning, they gain access to real-time insights and self-service capabilities that empower teams to make informed decisions swiftly. Successful implementations of analytics have demonstrated substantial advancements in operational efficiency, with companies reporting improved governance and deeper insights into their operations.
For example, a case study on GUI automation in a mid-sized organization revealed a 70% reduction in information entry errors and an 80% improvement in workflow efficiency, showcasing the transformative impact of these technologies.
Moreover, addressing challenges related to data inconsistency and governance is crucial for effective reporting. Organizations must ensure their data is accurate and reliable to make informed decisions. By 2025, the significance of data analysis in business intelligence will continue to grow, as companies strive to maintain competitiveness in a constantly evolving landscape.
The statistic regarding edge computing reducing cloud storage and bandwidth costs illustrates the practical benefits of data analysis, particularly for remote construction sites with limited connectivity. Additionally, a recent statement from KPMG indicates that CEOs are facing a skills gap, with 46% experiencing a deficiency in analytical skills and 38% encountering a shortage of AI capabilities, highlighting the challenges organizations face in effectively utilizing insights. By adopting these analytical categories and incorporating tools like Power BI for enhanced reporting and actionable insights, enterprises can transform raw data into valuable knowledge, ultimately fostering growth and innovation.
Furthermore, the recent updates regarding Databricks filing for its IPO underscore current trends and investor confidence in innovative data management and analytical solutions, emphasizing the critical role of analysis in the dynamic business environment.
Descriptive Analytics: Analyzing Historical Data to Understand What Happened
Descriptive, predictive, and prescriptive analytics serve as powerful tools that analyze historical information to uncover trends and patterns, effectively answering the question, ‘What happened?’ By summarizing past events, these analytics provide valuable insights into performance metrics. For instance, in 2025, a notable example in the retail sector involved a company examining five years of sales information to identify seasonal trends, enabling them to optimize inventory levels and enhance operational efficiency.
This approach not only improved stock management but also contributed to a significant increase in sales. A case in point is Narellan Pools, which achieved a 23% sales boost while reducing media budget spending through effective data analysis.
Descriptive, predictive, and prescriptive analytics profoundly impact operational performance. Recent statistics indicate that the adoption of advanced reporting tools has surged by over 40%, allowing analysts to generate comprehensive reports more efficiently. This trend highlights the increasing acknowledgment that these three main types of analytics are essential for promoting organizational success.
As Sarah Lee noted, “Recent statistics indicate a significant surge in the adoption of data visualization tools: Over the last few years, the frequency of interactive dashboards and advanced graphical software usage has increased by over 40%.” This underscores the growing significance of descriptive, predictive, and diagnostic analysis in contemporary business practices.
Moreover, companies are increasingly utilizing analytics to optimize inventory management. Retailers, for example, leverage historical sales data to forecast demand accurately, ensuring that stock levels align with consumer behavior. This strategy minimizes excess inventory and enhances customer satisfaction by preventing stockouts.
The integration of Robotic Process Automation (RPA) by Creatum GmbH can further streamline these processes, automating repetitive tasks and allowing teams to focus on strategic decision-making. This not only reduces errors but also frees up resources for more value-adding work.
Expert opinions emphasize that descriptive, predictive, and prescriptive analysis are crucial in enhancing decision-making processes. By providing a clear understanding of past performance, organizations can make informed strategic choices that drive growth and innovation. Additionally, the case study on Supply Chain Management with NetSuite illustrates how descriptive data analysis enhances operational efficiency by ensuring a smooth flow of goods from suppliers to customers.
As businesses continue to navigate an information-rich environment, the ability to extract meaningful insights from historical information remains essential for maintaining a competitive edge. Tailored solutions that improve information quality and streamline AI application further enable entities to utilize descriptive insights effectively, tackling the issues of inadequate master information quality and obstacles to AI integration.
Predictive Analytics: Forecasting Future Trends and Outcomes
Predictive analysis stands as one of the three primary types of analytics, alongside descriptive and diagnostic analytics. It employs statistical algorithms and machine learning methods to scrutinize past data, enabling organizations to forecast future outcomes. This approach directly addresses the pivotal question: ‘What could happen?’ For example, financial institutions leverage predictive modeling to evaluate the likelihood of loan defaults by analyzing historical borrower data, encompassing factors like payment history and credit utilization.
FICO exemplifies this by stating, “By analyzing data such as payment history, credit utilization, and loan balances, FICO can predict the likelihood of default and assign a credit score.” Recent advancements in predictive analysis have significantly enhanced forecasting accuracy, with studies revealing that organizations employing these techniques can attain up to 95% accuracy in their predictions.
The growing demand for predictive analysis, coupled with the acknowledgment that descriptive, predictive, and prescriptive analytics constitute the three main types, is particularly pronounced in the financial sector. Here, institutions are increasingly adopting these solutions to refine decision-making processes. By 2025, the integration of predictive analysis into financial strategies is expected to accelerate, driven by the need for customization and performance enhancement. Notably, the services sector associated with predictive analysis is projected to experience substantial growth, boasting a compound annual growth rate (CAGR) that exceeds other analytical segments.
A compelling case study that underscores this trend is the partnership between Tesco PLC and Teradata, which utilizes Vantage for real-time data querying to bolster its predictive capabilities. Such collaborations demonstrate how organizations harness predictive data analysis to optimize operational strategies and improve customer engagement. Furthermore, the customization options for geographic analysis within the Predictive Analytics market are becoming increasingly vital, enabling businesses to tailor solutions to their unique requirements.
Moreover, expert insights indicate that as predictive analytics evolves, its applications will extend beyond traditional forecasting. This evolution reinforces the significance of descriptive, predictive, and prescriptive analytics in shaping broader strategic decisions across various sectors. By anticipating future trends, organizations can proactively adjust their marketing strategies and optimize resource allocation, ultimately fostering growth and innovation in a competitive landscape. Additionally, integrating Power BI services can enhance reporting and deliver actionable insights, while leveraging AI solutions through Small Language Models and GenAI Workshops can address quality and governance challenges, ensuring businesses are well-equipped to make informed decisions.
Prescriptive Analytics: Guiding Decisions for Optimal Outcomes
Prescriptive analysis transcends mere prediction by not only forecasting future outcomes but also recommending specific actions to achieve desired results. It effectively addresses the critical question: ‘What should we do?’ For instance, in 2025, logistics companies are increasingly utilizing prescriptive data analysis to optimize delivery routes by examining real-time traffic information alongside historical delivery performance.
This method not only simplifies operations but also significantly boosts efficiency by decreasing delivery times and expenses. Recent studies suggest that prescriptive analysis can lead to a 20-30% enhancement in operational efficiency, particularly in logistics. Companies such as UPS and FedEx have effectively harnessed these insights to refine their routing strategies, resulting in substantial cost savings and heightened customer satisfaction.
Moreover, by incorporating Robotic Process Automation (RPA) into these processes, companies can further automate manual workflows, thereby boosting productivity and enabling teams to concentrate on strategic initiatives.
Furthermore, prescriptive data analysis serves as a vital decision-making tool in dynamic environments, especially in customer churn management. By employing advanced algorithms and optimization techniques, organizations can adapt their strategies in real-time, ensuring they remain competitive and responsive to market changes. Notably, swarm intelligence techniques have emerged as powerful resources for enhancing decision-making in these dynamic situations.
Expert views underscore the transformative capability of prescriptive analysis in guiding decision-making processes. Mike Henry, a dedicated expert in the Customer Experience (CX) field, emphasizes the importance of utilizing data analysis to uncover trends and best practices. As companies navigate the complexities of large information sets, the ability to derive actionable insights from predictive models becomes paramount.
This not only contributes to operational efficiency but also empowers organizations to make informed, strategic choices that foster growth and innovation in an increasingly information-driven environment.
Additionally, a recent survey on applications of prescriptive analysis highlights that descriptive, predictive, and prescriptive are the three primary types of analytics, underscoring the need for improved decision-making assistance in the context of large-scale information processing. The study concludes that optimization techniques significantly enhance the effectiveness of prescriptive analysis across various applications, addressing key issues and comparing different methodologies to improve research effectiveness in this area. In light of the projected shortage of up to 250,000 information analysis professionals in the US by 2024, the urgency for businesses to adopt prescriptive analysis, alongside customized AI solutions and Business Intelligence, becomes even more critical.
Comparing Descriptive, Predictive, and Prescriptive Analytics: Key Differences and Applications
Descriptive, predictive, and prescriptive analytics represent the three primary types of analytics, each playing a vital role in the data ecosystem with distinct yet complementary purposes. Descriptive analytics focuses on summarizing historical information, providing insights into past performance and trends. For instance, a retail company may analyze last year’s sales figures to identify peak shopping periods and customer preferences, enabling a better understanding of effective strategies.
Integrating Robotic Process Automation (RPA) from Creatum GmbH allows organizations to streamline the collection and reporting of this information, significantly enhancing operational efficiency and reducing manual errors.
Conversely, predictive analysis employs historical data and statistical methods to forecast future trends. By discerning patterns within past data, companies can anticipate upcoming outcomes. For example, a business might leverage predictive analysis to project sales for the next quarter based on seasonal trends and consumer behavior, facilitating proactive inventory management and marketing strategies.
This approach not only bolsters strategic planning but also enhances operational efficiency, as evidenced in the case study titled “Predictive Analytics Overview.” Tailored AI solutions can further streamline this process, ensuring that the right technologies align with specific business objectives.
Prescriptive analysis advances this concept by recommending specific actions to optimize results. It can indicate the best timing for promotions or price adjustments to boost foot traffic and increase basket size. For instance, a restaurant chain may utilize prescriptive analysis to determine optimal times for discounts, thereby maximizing customer engagement and revenue.
Statistics reveal that prescriptive analysis effectively recommends the timing of promotions and price changes to achieve these objectives, particularly when supported by robust Business Intelligence tools like Power BI from Creatum GmbH, which enhance data reporting and provide actionable insights through features such as the 3-Day Power BI Sprint and General Management App.
The integration of these data analysis types—descriptive, predictive, and prescriptive—is essential for organizations aiming to refine their decision-making processes. By successfully integrating these analytics, companies can achieve a comprehensive view of their operations, leading to more informed strategies and improved operational efficiency. As Dan Vesset noted, to measure accurately against KPIs, organizations must catalog and prepare the appropriate information sources to extract necessary data and calculate metrics based on the current state of the organization.
Industry trends indicate an increasing adoption of these analytical tools, with organizations recognizing their value in driving growth and innovation. By understanding the key differences and applications of each type, businesses can tailor their analysis strategies to align with specific objectives and data infrastructures while addressing data inconsistency and governance challenges in business reporting for enhanced decision-making.
Additionally, it is crucial to acknowledge that diagnostic analytics is retrospective, offering insights to address past issues or replicate successes, which further clarifies its distinctions from the three main types of analytics discussed.
Conclusion
Understanding the pivotal role of analytics in business intelligence underscores its necessity in today’s data-driven environment. This article elaborates on the three primary types of analytics—descriptive, predictive, and prescriptive—each serving a unique function in enhancing operational efficiency and strategic decision-making. Descriptive analytics allows organizations to glean valuable insights from historical data, while predictive analytics empowers businesses to anticipate future trends and outcomes. Prescriptive analytics takes this further by recommending specific actions to optimize results, effectively guiding organizations towards informed decisions.
The integration of these analytics types forms a comprehensive framework that enables companies to not only understand their past performance but also plan for future scenarios with confidence. As organizations face increasing complexity in their operations, leveraging these analytics becomes essential for maintaining a competitive edge. The transformative impact of analytics is evident through numerous case studies demonstrating significant improvements in efficiency and decision-making processes.
As the reliance on data-driven strategies continues to grow, the adoption of advanced analytics tools and techniques will be crucial for organizations striving to innovate and succeed in an ever-evolving marketplace. Embracing this analytics framework not only fosters a culture of informed decision-making but also positions businesses to navigate challenges effectively, ensuring long-term growth and sustainability. Ultimately, the ability to harness the power of analytics will define the success of organizations in the modern business landscape.
Frequently Asked Questions
What is analytics and why is it important for businesses?
Analytics is a systematic computational analysis of data that serves as a cornerstone of business intelligence. It helps organizations make informed, data-driven decisions by revealing patterns, trends, and insights that guide strategic planning and operational enhancements.
What are the three main types of analytics?
The three main types of analytics are descriptive, predictive, and prescriptive analytics. Each type serves a unique function in enhancing operational success.
What does descriptive analysis focus on?
Descriptive analysis focuses on summarizing past information to identify trends and patterns. For example, businesses can analyze historical sales data to understand customer behavior, which aids in inventory management and marketing strategies.
How does predictive analysis differ from descriptive analysis?
Predictive analysis uses statistical models and machine learning techniques to forecast future outcomes based on historical data, allowing organizations to anticipate demand fluctuations and optimize resource allocation.
What is the role of prescriptive analysis in business?
Prescriptive analysis recommends actions based on predictive insights. For instance, it can help a company identify the best course of action for inventory replenishment by considering factors like lead times and demand forecasts.
How can AI and automation enhance analytics?
AI solutions, including Small Language Models and GenAI Workshops, can improve data quality and provide tailored insights. Additionally, Robotic Process Automation (RPA) can automate manual workflows, reducing errors and allowing teams to focus on strategic tasks.
What are some benefits of implementing analytics in organizations?
Successful implementations of analytics can lead to substantial advancements in operational efficiency, improved governance, and deeper insights into operations. For example, a case study demonstrated a 70% reduction in information entry errors and an 80% improvement in workflow efficiency.
What challenges do organizations face regarding data analysis?
Organizations often face challenges related to data inconsistency and governance, which can hinder effective reporting. Ensuring data accuracy and reliability is crucial for making informed decisions.
How is the significance of data analysis expected to evolve by 2025?
By 2025, the importance of data analysis in business intelligence is expected to grow as companies strive to maintain competitiveness in a constantly evolving landscape.
What tools can help organizations transform raw data into valuable insights?
Tools like Power BI can enhance reporting and provide actionable insights, enabling enterprises to convert raw data into valuable knowledge that fosters growth and innovation.

