Introduction
In the dynamic world of business, analytics has emerged as a cornerstone for informed decision-making and operational excellence. By understanding the four primary types of business analytics—descriptive, diagnostic, predictive, and prescriptive—organizations can unlock a treasure trove of insights that drive strategic initiatives and foster growth. Each type plays a distinctive role, from summarizing historical performance to forecasting future trends and recommending actionable strategies.
However, the journey to effective analytics is not without its challenges, including data privacy concerns and the need for robust training. As organizations navigate this complex landscape, the integration of advanced tools like Robotic Process Automation (RPA) and tailored AI solutions becomes essential.
This article delves into the intricacies of business analytics, highlighting practical applications and future trends that empower businesses to enhance performance and gain a competitive edge in an increasingly data-driven marketplace.
Exploring the Four Types of Business Analytics
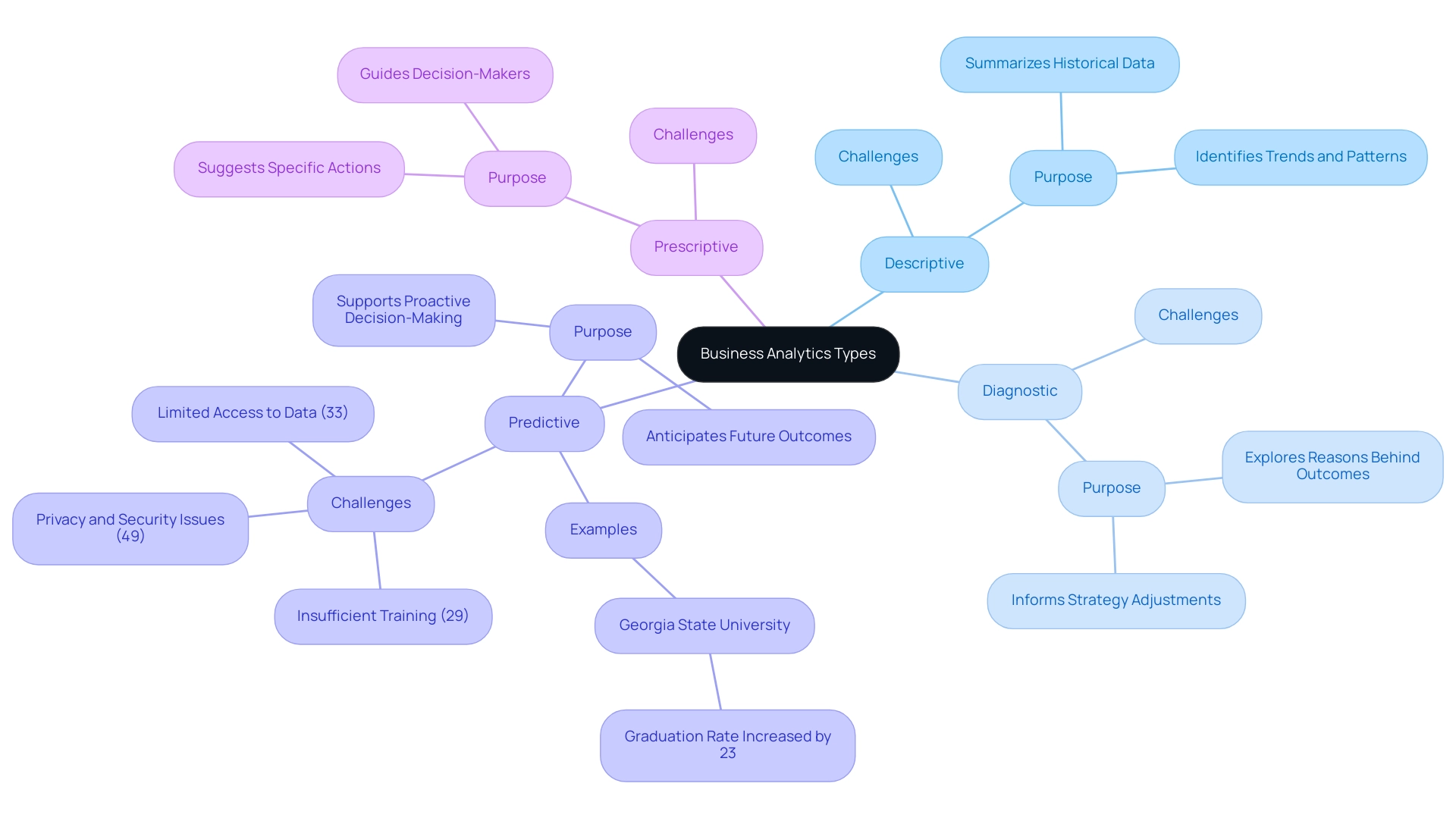
Business analytics types can be categorized into four primary categories: descriptive, diagnostic, predictive, and prescriptive. Descriptive analysis plays a vital role in summarizing historical data, allowing organizations to identify trends and patterns through intuitive dashboards and comprehensive reports. This fundamental layer of analysis is crucial for companies seeking to comprehend their historical performance.
Building on this, diagnostic examination delves deeper, exploring the reasons behind historical outcomes. By uncovering the factors contributing to success or failure, businesses can make informed adjustments to their strategies. Predictive analysis leverages statistical models and machine learning techniques to anticipate future outcomes, empowering organizations to proactively address potential challenges before they arise.
A notable example is the use of predictive analysis in higher education, where approximately 1,400 universities have adopted these techniques to tackle low graduation rates. For instance, Georgia State University has successfully raised its graduation rate by 23% since 2003, demonstrating the effectiveness of predictive data analysis in identifying trends and supporting student success. Finally, prescriptive analysis takes it a step further by suggesting specific actions based on insights.
Through optimization algorithms and simulations, it guides decision-makers in achieving their desired results. Each of these business analytics types serves a unique and crucial purpose, enabling businesses to enhance their intelligence and operational efficiency. However, organizations encounter considerable obstacles to effective utilization, including:
– Privacy and security issues (49%)
– Restricted access to information (33%)
– Insufficient training (29%)
As we navigate the overwhelming AI landscape, it’s crucial to harness tailored solutions that cut through the noise. IDC forecasts that by 2025, consumers will hold a remarkable 36% portion of information, highlighting the necessity for efficient analysis tools to utilize this abundance of knowledge. Companies must also invest in information management solutions and analysis tools to navigate the complexities of large-scale information handling effectively.
Indeed, with 57% of organizations utilizing a chief data officer and 59% depending on system administrators, the strategic execution of these data types, alongside improved Power BI services—including the 3-Day Power BI Sprint for swift report generation and the General Management App for thorough management—combined with AI-driven insights from Small Language Models and GenAI Workshops, is vital for attaining operational efficiency and addressing the challenges posed by big data.
When and Why to Use Each Type of Business Analytics
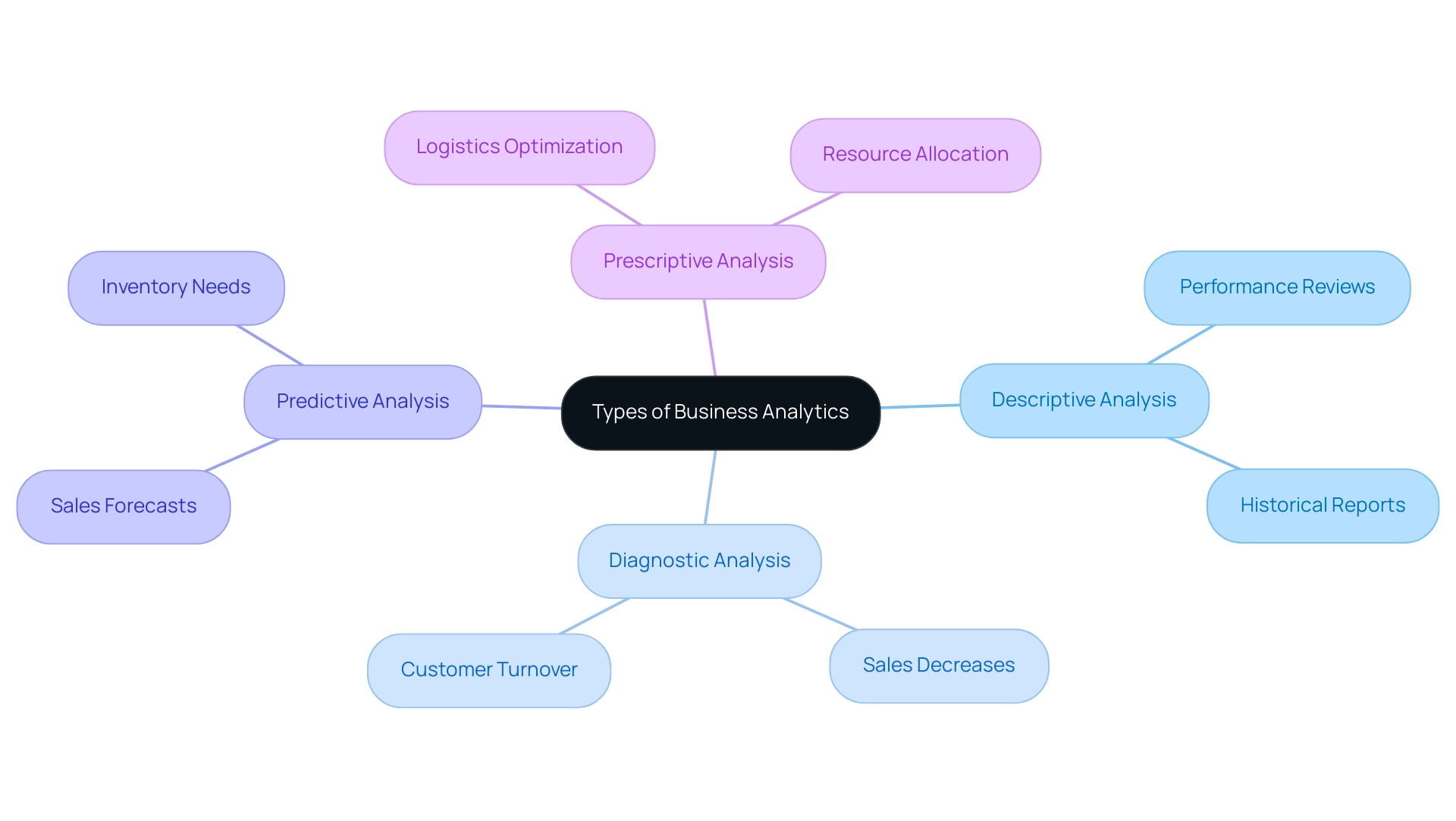
Descriptive analysis serves as a foundational tool for businesses aiming to comprehend past performance, making it particularly effective for conducting performance reviews and producing historical reports. In this context, hospitals track patient admissions over time, leveraging Business Intelligence (BI) to allocate resources more efficiently and optimize care delivery. This practical application underscores the significance of BI in the healthcare sector.
Conversely, diagnostic analysis is essential when companies need to explore the underlying causes of specific results, such as uncovering reasons for sales decreases or customer turnover. Insights gained from diagnostic assessments can drive targeted improvements, highlighting the importance of collaboration among cross-functional teams in sharing insights from various evaluations.
Predictive analysis is essential for organizations looking to forecast future trends. By anticipating sales forecasts or inventory needs, companies can make proactive decisions that align with projected demands, which has been shown to enhance overall operational efficiency significantly. Moreover, prescriptive analysis is utilized to identify the optimal course of action, such as in logistics optimization or effective resource allocation.
These business analytics types serve distinct purposes, and their effectiveness hinges on the specific questions that a business seeks to answer. As highlighted in the case study ‘Integrating Four Types of Analysis,’ a cohesive strategy that integrates various business analytics types, including descriptive, diagnostic, predictive, and prescriptive analyses, can significantly improve organizational decision-making, fostering collaboration across departments and enabling a more comprehensive understanding of data-driven insights. Furthermore, the implementation of Robotic Process Automation (RPA) has proven to streamline operations, reduce manual errors by 70%, and free up valuable resources, improving workflow efficiency by 80%.
This makes RPA an essential tool for boosting productivity in healthcare services, particularly in tackling challenges such as manual information entry errors and sluggish software testing.
Benefits and Challenges of Business Analytics Types
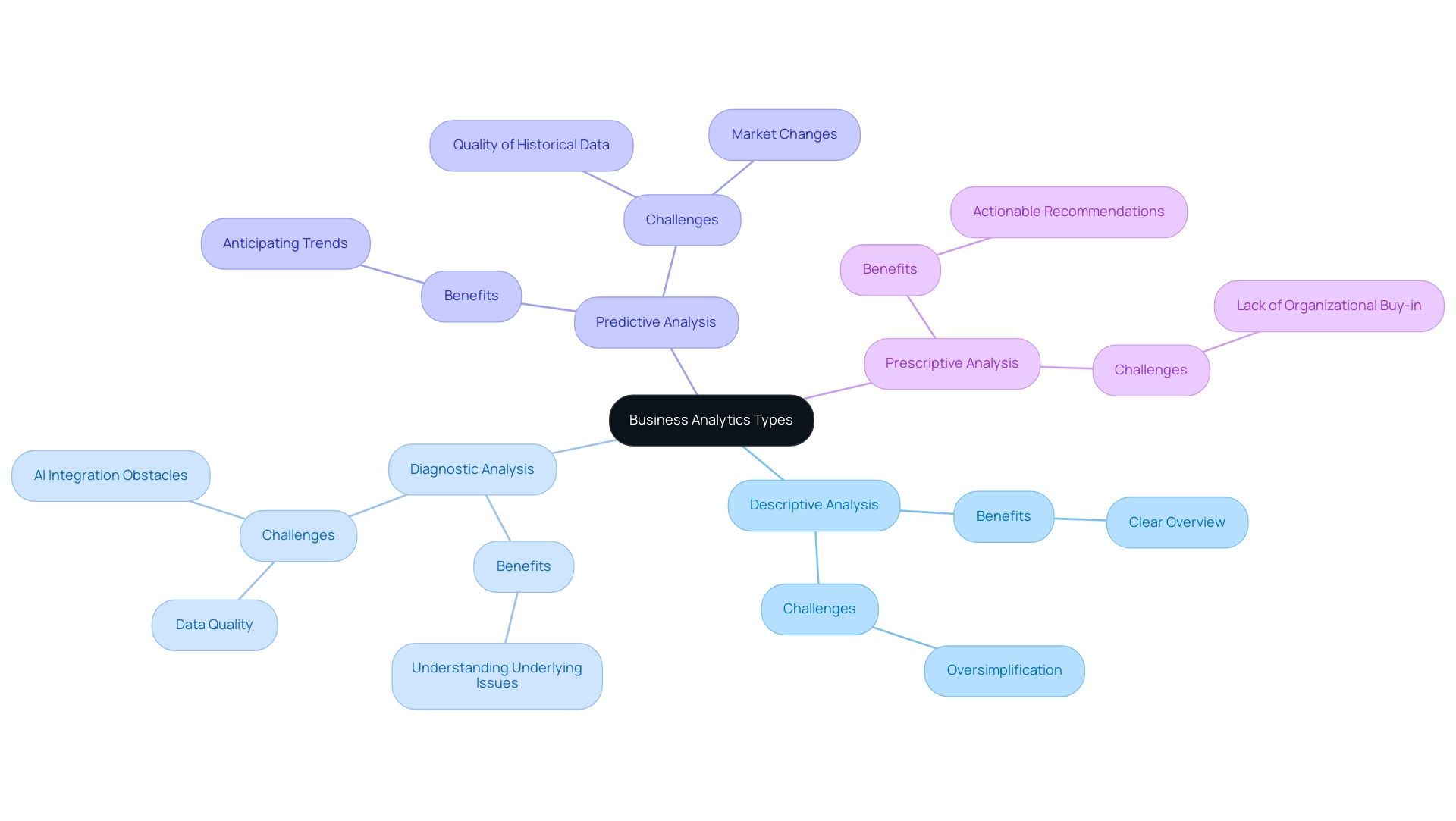
Descriptive analysis acts as a strong instrument for companies, providing a clear overview of historical performance metrics. However, it’s important to acknowledge that this method can sometimes oversimplify complex situations, potentially leading to misinterpretations of information. As businesses look to 2024, the benefits of descriptive analysis are highlighted by emerging statistics, revealing that organizations effectively utilizing these insights, alongside Robotic Process Automation (RPA), are better positioned for strategic decision-making.
RPA streamlines manual workflows, enhancing operational efficiency and allowing teams to concentrate on analysis rather than repetitive tasks. Yet, while descriptive analysis offers foundational benefits, it is diagnostic examination that provides a more profound understanding of underlying issues. This type of analysis reveals the reasons behind past outcomes, but it often requires advanced analytical capabilities and can be time-consuming.
As noted by Jonathan J. Deeks,
They have been shown to have better statistical properties when there are few events,
highlighting the intricacies involved in executing diagnostic evaluations successfully. Organizations encounter difficulties when applying diagnostic analysis, especially in guaranteeing the accessibility and reliability of the essential information, as well as overcoming obstacles to AI integration and tackling inadequate master information quality. Here, the integration of Business Intelligence can help unlock the power of information, providing actionable insights that drive growth and innovation.
The case study on subgroup analyses and meta-regressions highlights that a substantial number of studies is necessary for meaningful investigations of heterogeneity, aligning with the challenges of diagnostic evaluation. In this context, sensitivity analyses—performing evaluations with and without outlying studies—become crucial for deriving meaningful insights while navigating these challenges. Predictive techniques advance the process, allowing companies to anticipate upcoming trends using past information.
Yet, its effectiveness hinges on the quality of that historical data and is susceptible to unforeseen market changes, particularly when the value of correlation coefficients ranges between -1 and +1, underscoring the need for precision in data interpretation. Finally, prescriptive analysis provides actionable recommendations to optimize decision-making; however, the implementation of these recommendations can be hindered by a lack of organizational buy-in. By comprehensively understanding the benefits and challenges across various business analytics types, including the necessity for tailored AI solutions to navigate the overwhelming AI landscape, organizations can more effectively leverage data-driven insights for enhanced operational efficiency through RPA and Business Intelligence.
Enhancing Business Performance Through Analytics
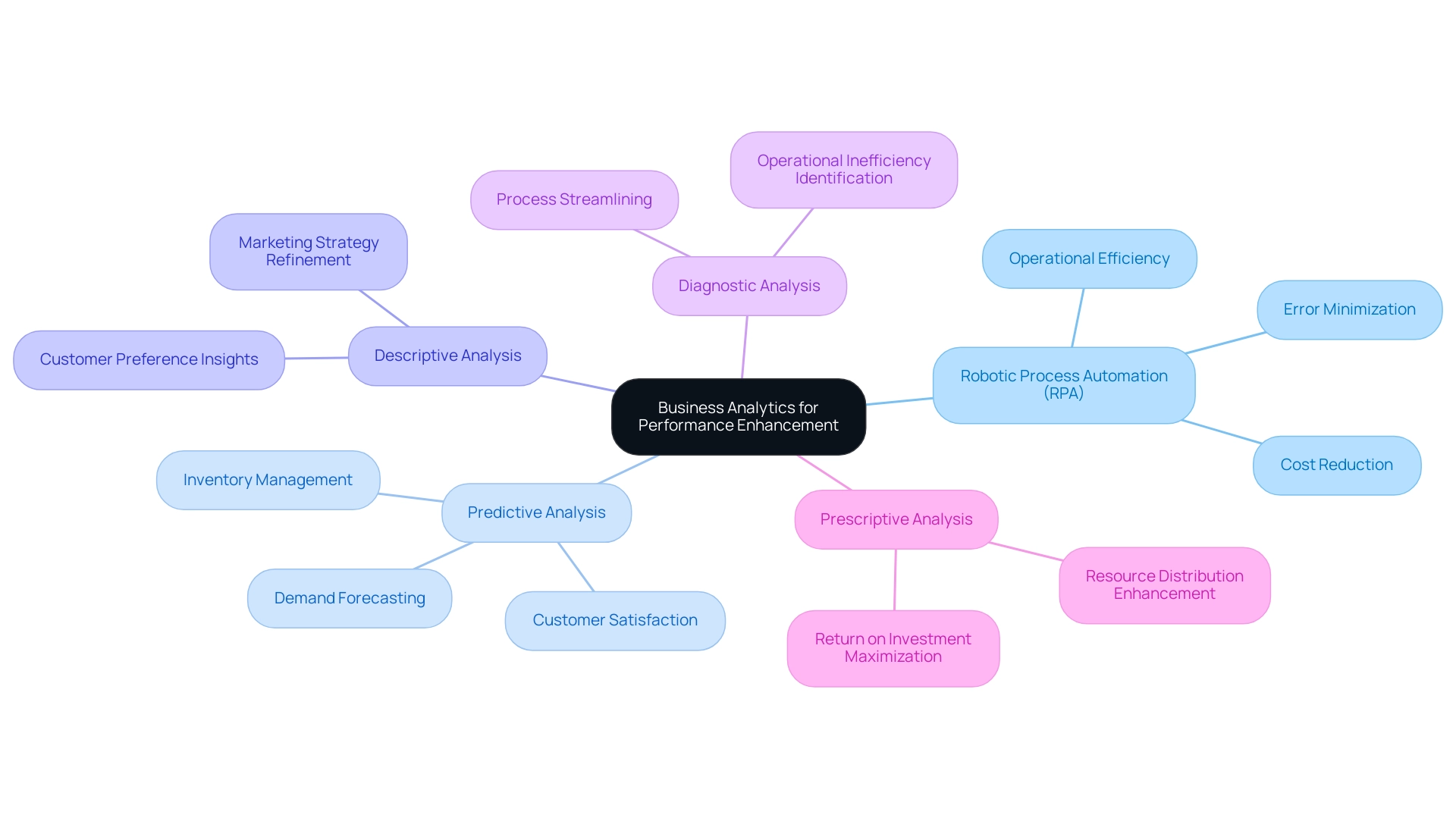
Leveraging the power of business analytics types, including Robotic Process Automation (RPA) and customized AI solutions, offers the potential for transformative improvements in organizational performance across various dimensions. For instance, companies leveraging RPA can automate manual workflows, significantly boosting operational efficiency while reducing costs and minimizing errors. This is especially vital in a rapidly evolving AI landscape where organizations must adapt swiftly.
Predictive analysis, which is one of the business analytics types, can optimize inventory management, effectively cutting costs while simultaneously boosting customer satisfaction through improved product availability. Such an approach not only minimizes stockouts but also allows businesses to anticipate demand fluctuations. Descriptive analysis, which is one of the business analytics types, further refines marketing strategies by identifying successful campaigns and discerning customer preferences, enabling targeted efforts that resonate with the audience.
Meanwhile, one of the important business analytics types, diagnostic analysis, plays a crucial role in uncovering operational inefficiencies, enabling organizations to streamline processes and achieve significant cost savings. Furthermore, among the business analytics types, prescriptive analysis enables companies to enhance resource distribution, aiding in the maximization of return on investment—a vital factor in today’s competitive environment. In fact, the average ROI for enterprises utilizing business intelligence and data analysis is an impressive 1300%, underscoring the substantial benefits these tools can provide.
By integrating data analysis into their decision-making frameworks, companies can cultivate a robust data-driven culture that enhances overall performance. A case in point is a financial services firm that utilized trend analysis to adjust its investment strategies in anticipation of market shifts, exemplifying how data insights can effectively inform strategic decisions. Furthermore, as the business intelligence software market is anticipated to hit around $177 billion by 2030, it is clear that companies are progressively acknowledging the significance of data analysis, RPA, and BI in fostering success.
As entities continue to embrace these analytical tools, they position themselves for sustained growth and success in an increasingly data-centric world. According to the U.S. Bureau of Labor Statistics, the median yearly salary for management analysts was $99,410 in May 2023, emphasizing the importance of skilled professionals who utilize data analysis to enhance organizational performance and decision-making. Moreover, unlocking practical insights from information is vital, as it offers a competitive edge that can distinguish enterprises in the marketplace.
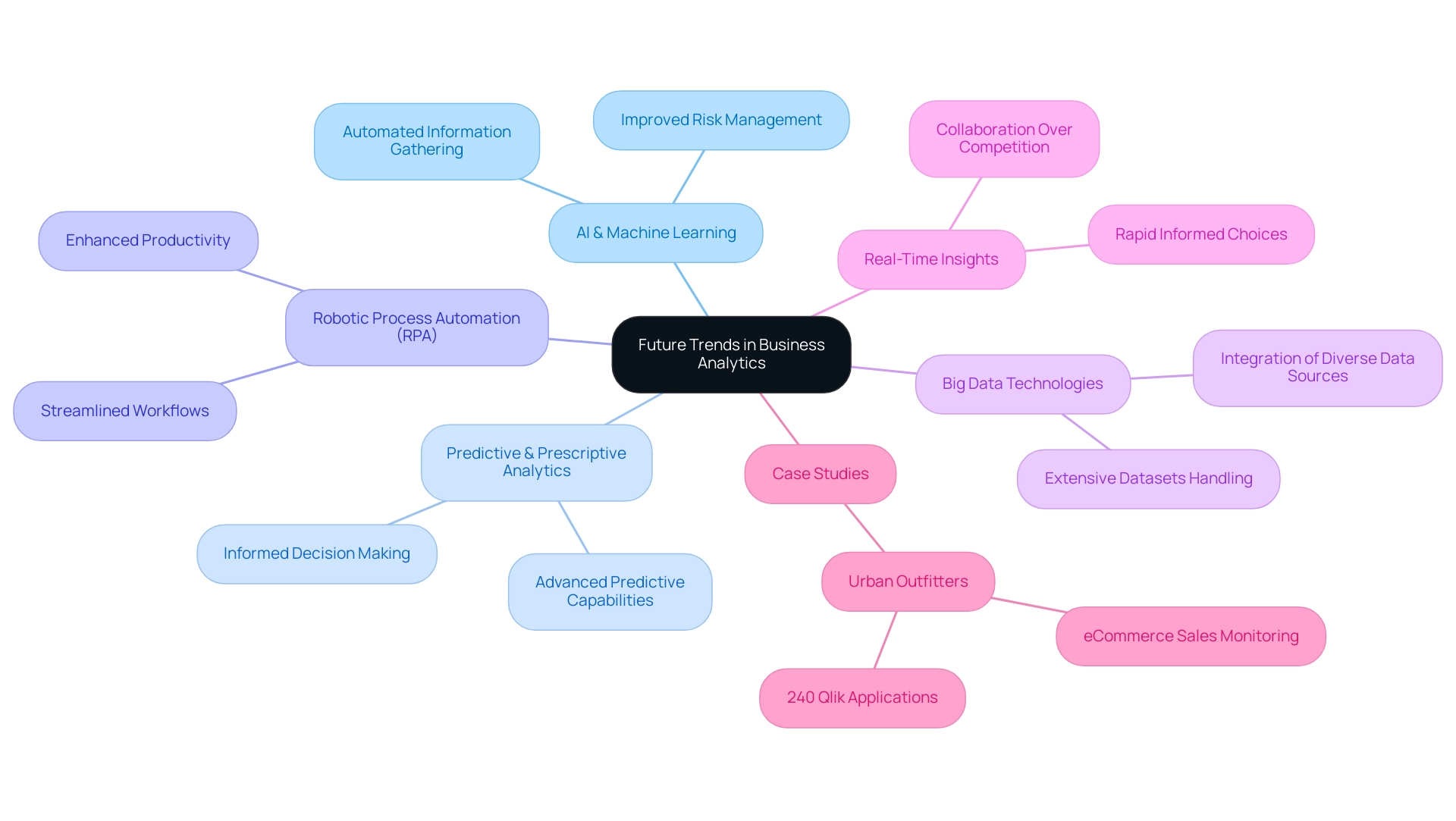
Future Trends in Business Analytics
The landscape of business analysis is undergoing a significant transformation, influenced by advancements in artificial intelligence and machine learning. These technologies not only transform how entities assess information but also enable the application of advanced predictive and prescriptive analytics capabilities. For instance, AI can automate information gathering and analysis, which is essential for addressing poor master information quality, including issues of inconsistent, incomplete, or flawed information that often hamper operational efficiency.
As numerous entities grapple with the perception that AI projects are costly, complex, and time-intensive, it is crucial to recognize how tailored AI solutions can alleviate these concerns and streamline integration into existing processes. Additionally, leveraging Robotic Process Automation (RPA) can significantly enhance productivity by automating manual workflows, allowing teams to focus on strategic initiatives. The increasing focus on real-time insights enables businesses to make rapid, informed choices based on the most recent information accessible, which is essential as 75% of executives indicate that business functions frequently compete instead of collaborating.
Moreover, the incorporation of big data technologies expands the scope of analysis, allowing entities to handle extensive datasets from various sources effortlessly. As industry leaders like Google and Alibaba invest in decision intelligence, the significance of adopting responsible data practices becomes paramount. Reports suggest that incorporating data analysis will expand considerably across multiple sectors, including healthcare, further highlighting the necessity for enterprises to adopt these advancements for a competitive advantage.
The success story of Urban Outfitters exemplifies this; by utilizing over 240 Qlik applications to monitor eCommerce sales and supply chain management, they demonstrate how cloud-based analytics can enhance operational efficiency. By embracing these trends, organizations can overcome the challenges of AI implementation and position themselves to thrive in a rapidly evolving business environment.
Conclusion
Embracing the diverse types of business analytics—descriptive, diagnostic, predictive, and prescriptive—empowers organizations to navigate the complexities of today’s data-driven landscape. Each type serves a unique purpose, from providing insights into past performance to forecasting future trends and recommending actionable strategies. By effectively utilizing these analytics, businesses can make informed decisions that enhance operational efficiency and drive growth.
However, the journey towards optimizing analytics is not without its challenges. Organizations must address:
– Data privacy concerns
– Ensure data integrity
– Invest in training to harness the full potential of these tools
The integration of Robotic Process Automation and tailored AI solutions can significantly alleviate these challenges, streamlining processes and enabling teams to focus on strategic initiatives rather than repetitive tasks.
The future of business analytics is promising, with advancements in AI and machine learning paving the way for more sophisticated analytical capabilities. As organizations continue to embrace these technologies, they position themselves to unlock actionable insights that can differentiate them in a competitive marketplace. By embedding analytics into their decision-making processes, businesses not only enhance their performance but also cultivate a culture of data-driven decision-making that is essential for sustained success in an ever-evolving business environment.

