Introduction
In a landscape where operational efficiency is paramount, organizations are increasingly turning to Robotic Process Automation (RPA) as a game-changing solution. This innovative technology not only automates repetitive tasks but also empowers businesses to streamline workflows, enhance productivity, and significantly reduce human error.
As companies across various sectors, from healthcare to finance, embrace RPA, they are witnessing remarkable transformations in their operations. With compelling case studies demonstrating substantial ROI and increased employee satisfaction, the time has never been more critical for organizations to explore the diverse applications and benefits of RPA.
However, the journey to successful implementation is not without its challenges. By understanding the nuances of RPA deployment and the strategies for overcoming common obstacles, businesses can unlock new levels of efficiency and position themselves for sustained growth in an ever-evolving marketplace.
Defining Robotic Process Automation (RPA)
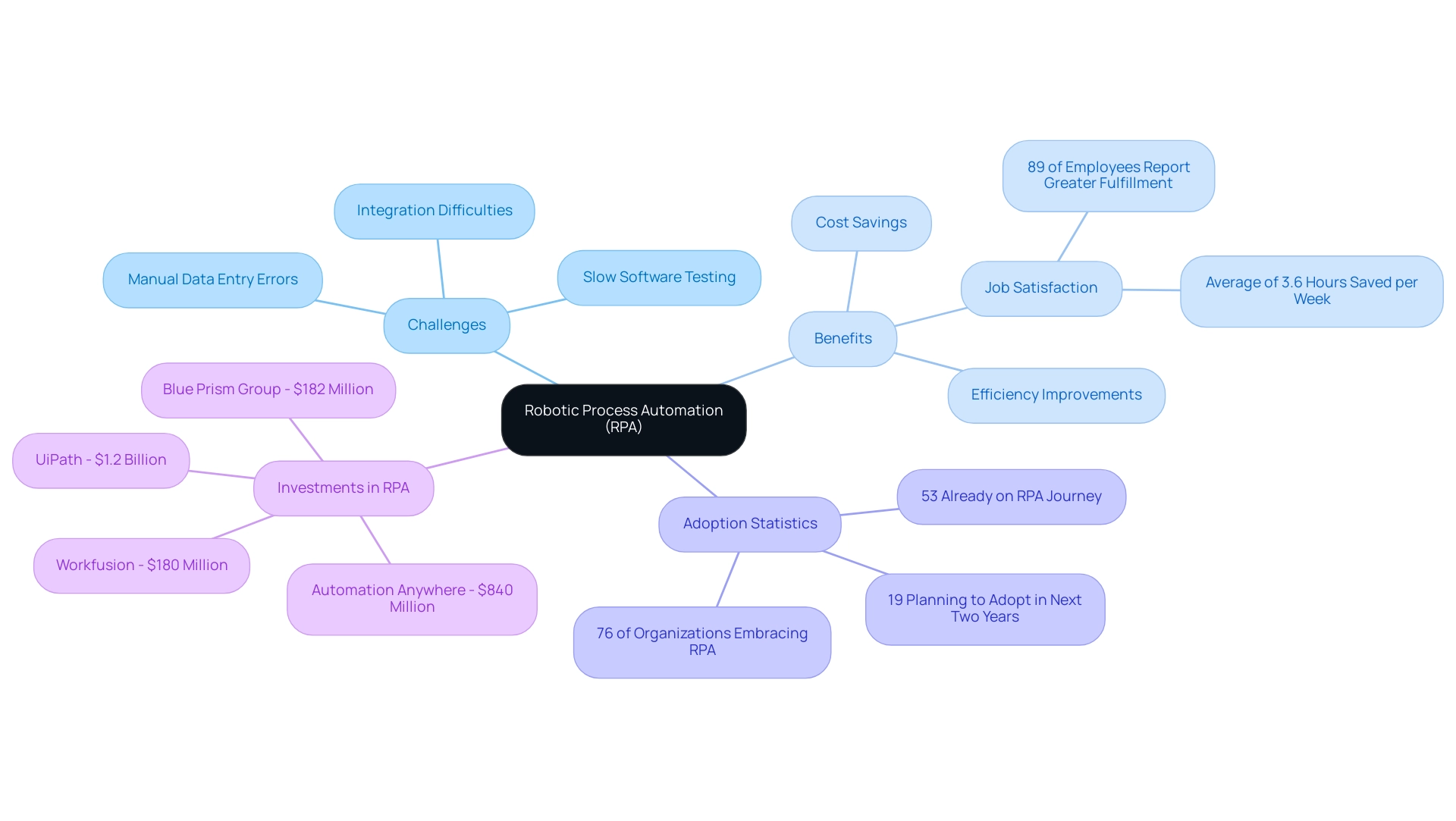
Robotic Process Automation (RPA), which embodies the RPA meaning in software, acts as a crucial technology for companies seeking to improve efficiency by automating repetitive, rule-based tasks usually performed by human workers. A compelling case study from a mid-sized healthcare company illustrates the challenges they faced, including:
- Manual data entry errors
- Slow software testing
- Difficulty integrating outdated systems without APIs
By utilizing GUI techniques, they greatly enhanced their efficiency, decreasing data entry mistakes by 70% and speeding up software testing processes by 50%.
By leveraging software robots, or ‘bots’, the RPA meaning in software effectively streamlines workflows, minimizes human error, and allows for a more strategic allocation of human resources. This is especially advantageous in high data processing environments, where efficiency improvements can lead to substantial time and cost savings.
Recent data indicates that:
- 76% of organizations have embraced mechanization
- 53% are already on their RPA journey
- An additional 19% are planning to adopt it in the next two years
This shift underscores RPA’s rise as a strategic initiative, essential for attaining excellence in operations by grasping the RPA meaning in software. Notably, a report from Slack revealed that, on average, workers save 3.6 hours per week by utilizing automation, contributing to increased job satisfaction—with 89% of employees reporting greater job fulfillment due to automation.
The Covid-19 pandemic has further accelerated RPA adoption, emphasizing its role in addressing changing functional challenges. The sector has witnessed considerable investment, with firms such as:
- UiPath securing $1.2 billion
- Automation Anywhere $840 million
- Blue Prism Group $182 million
- Workfusion $180 million
As entities strive to address staffing shortages and antiquated systems, the RPA meaning in software highlights the importance of solutions like EMMA RPA and Microsoft Power Automate for boosting productivity and employee morale. By transforming business operations and providing risk-free ROI assessments—achieved within six months—RPA empowers organizations to unlock new levels of operational efficiency, significantly enhancing software quality and revolutionizing processes in healthcare service delivery.
Exploring Different Types of RPA
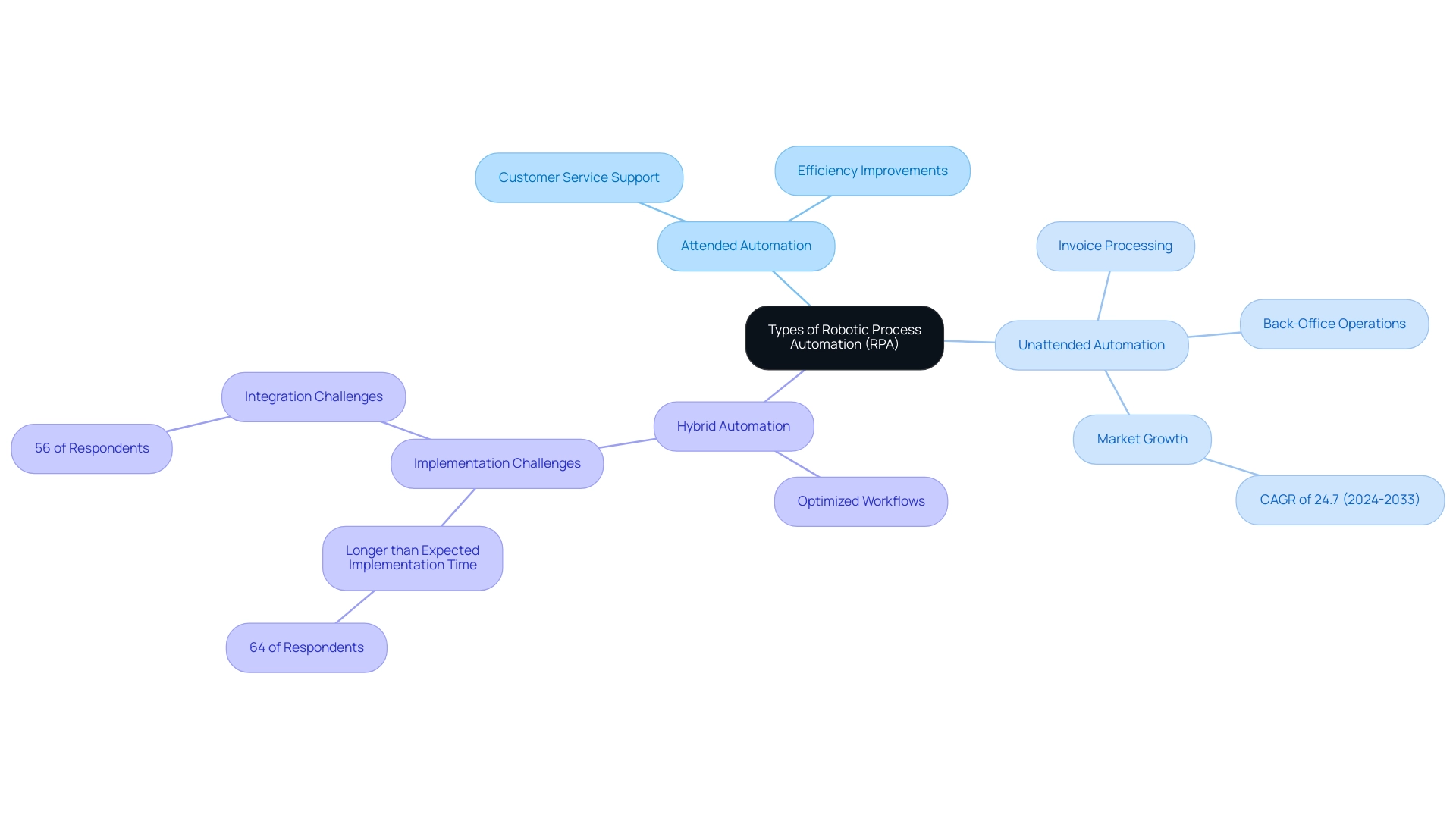
The classification of Robotic Process Automation (RPA) meaning in software includes three primary types: attended, unattended, and hybrid processes.
-
Attended mechanization involves bots that work alongside human employees, providing real-time assistance in scenarios where immediate responses are essential, such as customer service. For example, a retail company implemented attended technology to assist customer service representatives in resolving inquiries quickly, which enhanced efficiency and improved customer satisfaction by enabling quick resolutions to queries, addressing the common workplace challenge of repetitive tasks that can drain employee morale.
-
Unattended systems operate independently, executing tasks without human oversight, making them particularly effective for back-office operations like data entry and processing. A financial institution employed unattended technology to streamline its invoice processing, alleviating staffing shortages and allowing teams to focus on strategic, value-adding activities. Recent statistics indicate that the use of unattended technology is expected to rise significantly across various industries by 2024, contributing to the overall growth of the RPA market, which is projected to experience a CAGR of 24.7% from 2024 to 2033.
-
Hybrid automation, which combines the strengths of both attended and unattended automation, provides entities the flexibility to optimize workflows across diverse tasks. By utilizing a blend of these strategies, businesses can align RPA solutions with their performance goals, effectively tackling specific challenges such as those highlighted in a survey where 63% of entities faced unmet expectations regarding implementation time, with 64% of participants in the Deloitte Global RPA Survey indicating that the implementation time for RPA was longer than anticipated. Additionally, updating old systems through RPA not only improves efficiency but also enables companies to adjust to changing market demands.
Understanding these distinctions is crucial for developing a tailored RPA strategy that incorporates the RPA meaning in software, drives efficiency, and meets the evolving needs of the workforce in a rapidly changing AI landscape.
Benefits of Implementing RPA in Business
The implementation of Robotic Process Automation (RPA) highlights the rpa meaning in software, providing companies a multitude of benefits, including substantial cost savings, heightened efficiency, and improved accuracy. The rpa meaning in software is that it can manage up to 90% of data entry tasks in clinical research, significantly lowering operational costs while minimizing the risk of human error. This mechanization leads to quicker processing durations, enabling businesses to react promptly to client needs.
Industry leaders such as UiPath and Automation Anywhere exemplify the strategic value of RPA, showcasing remarkable productivity gains post-implementation. According to the Deloitte Global RPA Survey, over 90% of C-level executives employing intelligent processes believe their organizations excel at adapting to evolving business trends. Moreover, understanding the rpa meaning in software enhances performance, ensures compliance, and strengthens cybersecurity—all while driving down costs.
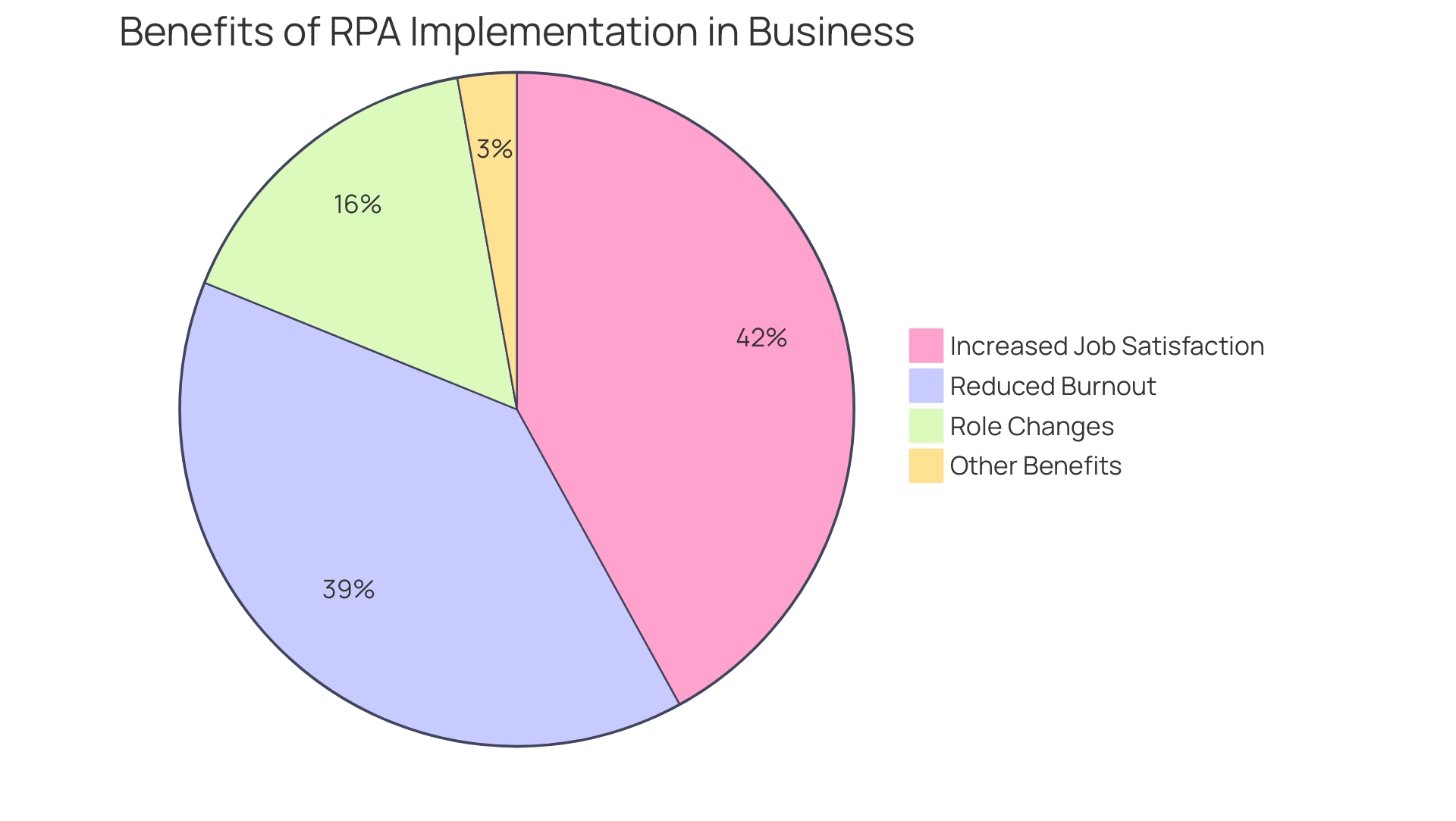
A case study on job satisfaction revealed that:
- 34% of workers experienced role changes due to smart technology
- 89% noted increased job satisfaction
- 83% of employees using AI-powered automation report reduced burnout and enhanced job satisfaction
By adopting RPA, organizations can enhance excellence in operations and nurture a culture of innovation, reflecting the rpa meaning in software, while unlocking new growth opportunities.
Companies like [Company Name] have reported significant productivity gains, stating, ‘[insert quote here],’ which underscores the tangible benefits of RPA in real-world applications. To further enhance your operational efficiency, consider exploring our tailored AI solutions that complement RPA and leverage Business Intelligence to transform data into actionable insights, driving informed decision-making. Engage with us to discover how we can support your journey towards greater productivity and lower costs.
Real-World Applications of RPA Across Industries
Robotic Process Automation (RPA) is revolutionizing operations across various industries, and understanding RPA meaning in software is essential for leveraging its benefits in finance, healthcare, and manufacturing. A compelling case study demonstrates how a mid-sized healthcare company employed GUI processes to streamline operations, addressing challenges such as:
- Manual data entry errors
- Slow software testing
- Difficulty integrating outdated systems without APIs
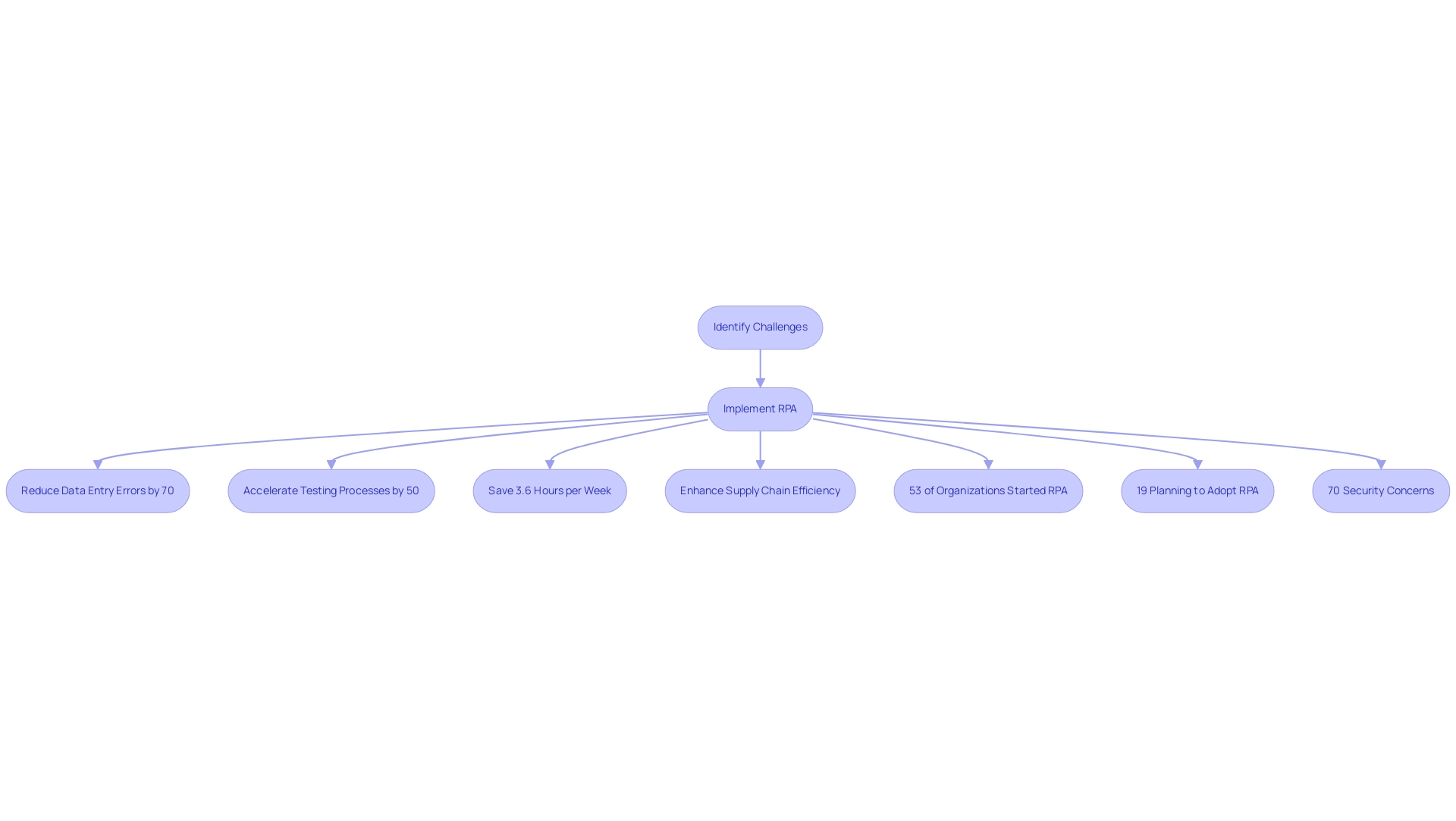
By implementing RPA, the company reduced data entry errors by 70%, accelerated testing processes by 50%, and improved overall workflow efficiency by 80%, achieving ROI within just six months.
This efficiency not only transformed their administrative tasks but also allowed healthcare professionals to dedicate more time to patient interaction, enhancing overall patient care.
In finance, RPA is streamlining processes like invoice processing and compliance reporting, leading to significant reductions in processing times. Workers save an average of 3.6 hours per week through automation, enabling them to focus on more strategic tasks. The manufacturing sector is also benefiting, utilizing RPA for inventory management and order processing to enhance supply chain efficiency.
Moreover, the integration of AI technologies within RPA platforms is evolving, with tailored AI solutions providing targeted technologies that align with specific business goals.
However, security concerns remain a barrier for 70% of executives. Recent statistics reveal that:
- 53% of entities have initiated RPA implementations
- 19% planning to adopt it within the next two years
- 78% of existing RPA users expect increased investment in the next three years
This indicates a growing recognition of the RPA meaning in software to enhance operational capabilities. These real-world applications illustrate RPA’s adaptability and effectiveness, making it an essential tool for entities aiming to optimize their processes and drive productivity.
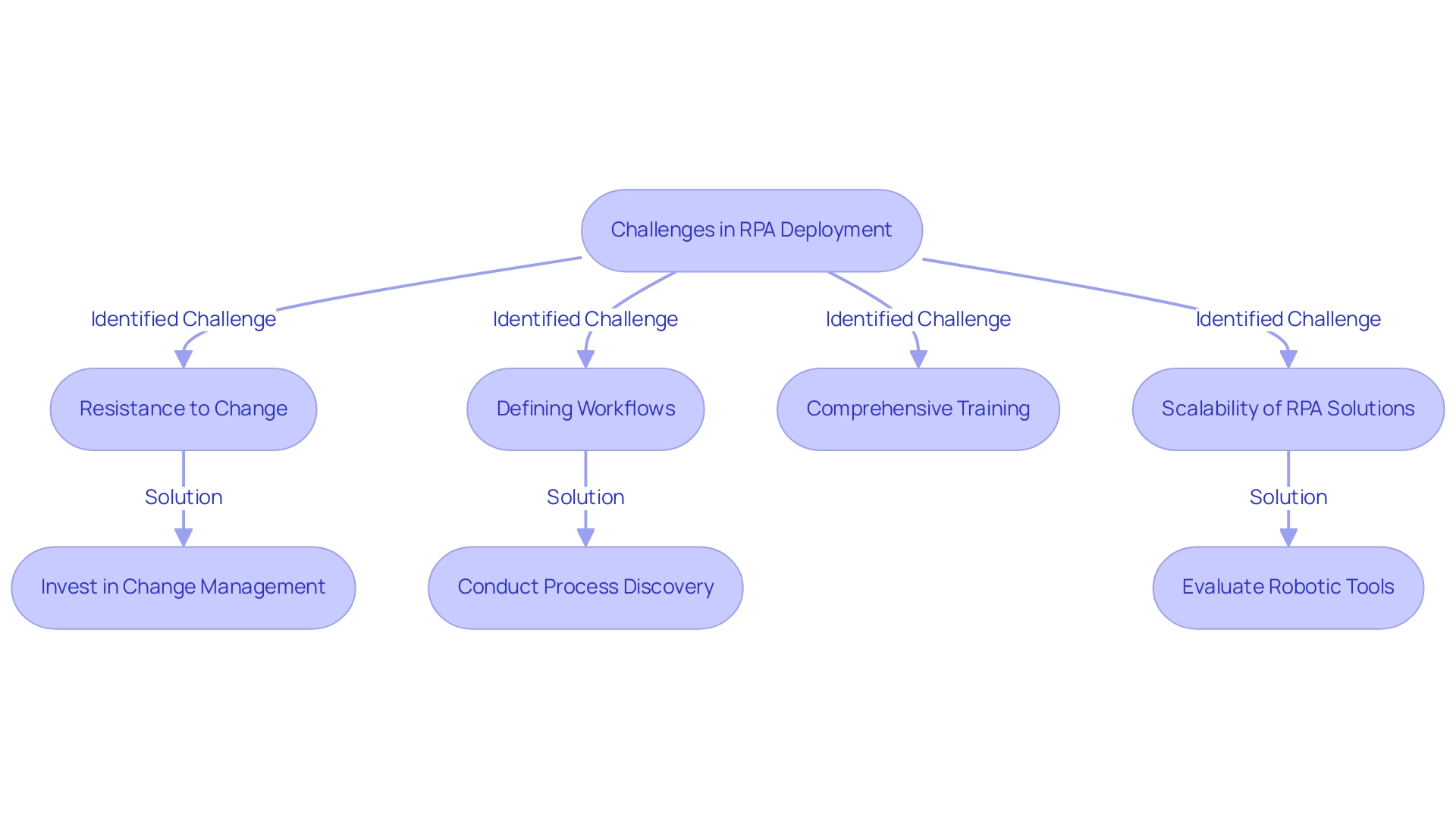
Challenges and Considerations in RPA Deployment
While understanding the RPA meaning in software offers significant advantages, companies must navigate several challenges during deployment. Resistance to change from employees can emerge as a primary obstacle, potentially stalling the adoption process. To address this, it’s crucial for entities to ensure that existing workflows are meticulously defined before starting mechanization, which helps prevent confusion and inefficiencies.
Furthermore, investing in comprehensive training programs and robust change management strategies is essential to facilitate a seamless transition, fostering an environment conducive to acceptance and adaptation. The concept of RPA meaning in software indicates that automated processes are less prone to human error, leading to improved accuracy and compliance with regulations; this reinforces the need for effective training and management. Additionally, the RPA meaning in software highlights how it can significantly reduce operational costs and free up personnel to focus on more strategic, value-adding tasks.
Understanding RPA meaning in software is crucial, as the scalability of RPA solutions is an essential element; entities should evaluate their robotic tools to ensure they can progress with business expansion. A case study titled ‘Identifying and Prioritizing Processes for Streamlining’ highlights the challenges of pinpointing processes for enhancement, particularly within complex organizational workflows. By conducting process discovery exercises and involving subject matter experts, organizations can better identify automation opportunities.
By proactively addressing these challenges and modernizing outdated systems, businesses not only enhance their operational efficiency but also foster a culture of continuous improvement that empowers employees and drives innovation, ultimately improving the overall customer experience.
Conclusion
Embracing Robotic Process Automation (RPA) is a transformative step for organizations aiming to enhance operational efficiency and productivity. By automating repetitive tasks, RPA not only minimizes human error but also liberates valuable human resources for more strategic initiatives. The compelling case studies presented illustrate how businesses across various sectors, such as healthcare and finance, have successfully implemented RPA to achieve substantial improvements in workflow efficiency, resulting in significant cost savings and increased employee satisfaction.
However, the journey to effective RPA deployment is not without its challenges. Resistance to change, the need for comprehensive training, and the careful selection of processes for automation are critical factors that organizations must address to ensure a smooth transition. By focusing on these areas and leveraging the right mix of attended, unattended, and hybrid automation, companies can seamlessly integrate RPA into their operations, paving the way for sustained growth and innovation.
As industries continue to adapt to evolving market demands, the value of RPA becomes increasingly evident. Organizations that proactively embrace this technology will not only enhance their operational capabilities but also position themselves as leaders in their respective fields. The time to explore and invest in RPA is now, as it holds the key to unlocking new levels of efficiency and driving long-term success in an ever-competitive landscape.

