Overview
This article delves into the DAX COUNTAX function, underscoring its critical role for Power BI users in counting non-blank results derived from expressions across tables. By illuminating COUNTAX’s capabilities, it enhances the accuracy of data analysis. Practical examples illustrate its application, while best practices are highlighted to boost operational efficiency and decision-making within business intelligence contexts.
Why is COUNTAX essential? It empowers users to derive meaningful insights from their data, ensuring that every non-blank result is accounted for. This function not only streamlines analysis but also fosters informed decision-making in a competitive landscape.
With COUNTAX, professionals can transform their approach to data analysis, leading to improved outcomes and strategic advantages. Embrace these insights to elevate your business intelligence practices and drive success.
Introduction
In the realm of data analysis, the COUNTAX function in DAX stands out as a powerful tool for organizations aiming to make sense of their information. As businesses increasingly depend on data-driven insights to guide decision-making, mastering the effective utilization of COUNTAX becomes essential. This function not only counts non-blank results but also evaluates expressions across specified tables. This capability enables analysts to derive meaningful insights that enhance operational efficiency.
In today’s data-rich environment, where the integration of Business Intelligence (BI) and Robotic Process Automation (RPA) is transforming data management approaches, COUNTAX proves particularly valuable. By exploring its features, practical applications, and best practices, organizations can uncover how mastering COUNTAX can elevate reporting capabilities. Ultimately, this mastery leads to more informed business strategies, driving success in a competitive landscape.
Introduction to the COUNTAX Function in DAX
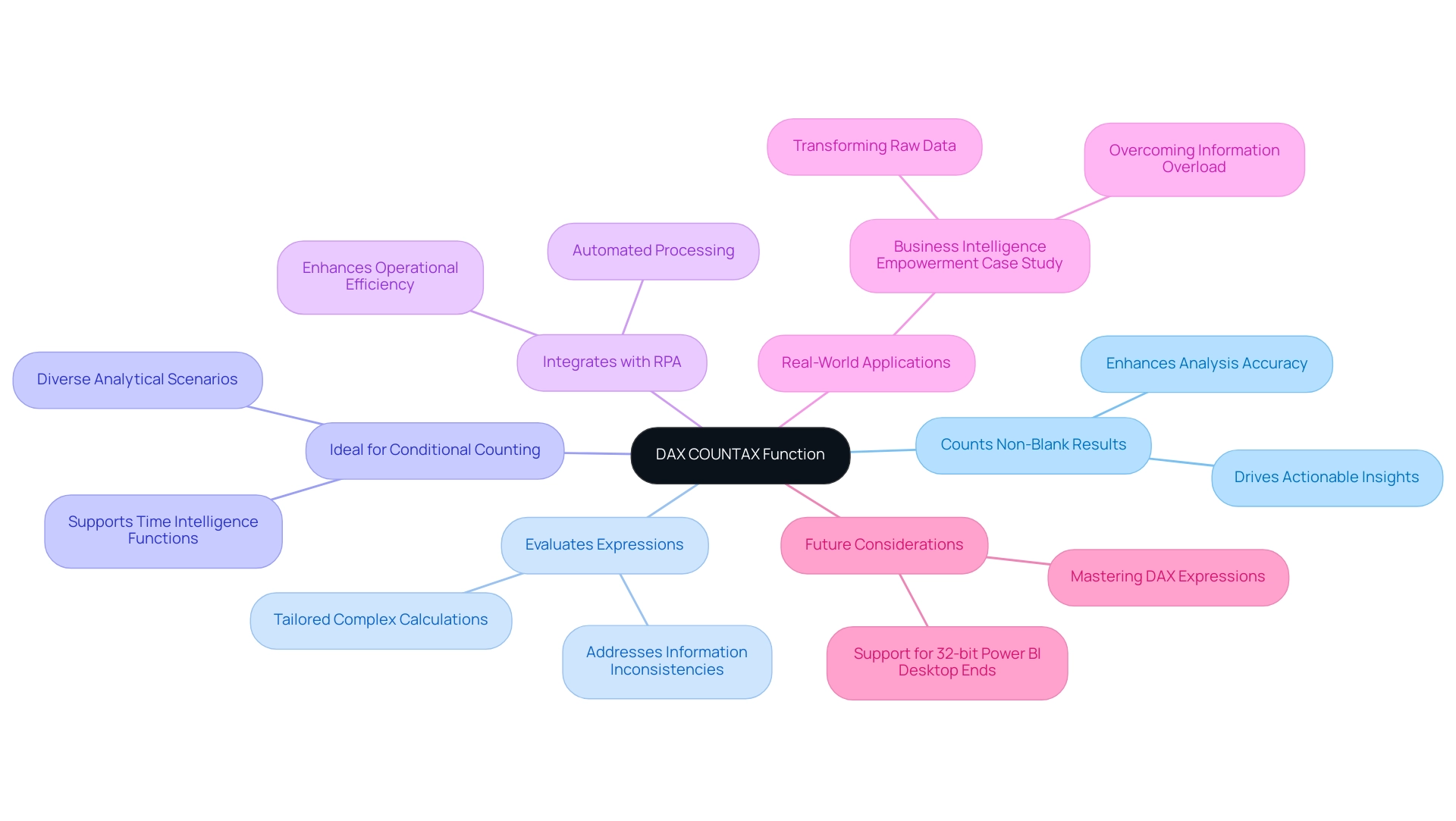
The operation in DAX, specifically the DAX COUNTAX, serves as an essential tool for tallying non-blank outcomes derived from evaluating an expression across a specified table. This capability proves particularly advantageous in scenarios that require conditional counting based on specific calculations or criteria, especially within today’s data-rich environment where the significance of Business Intelligence (BI) and Robotic Process Automation (RPA) is paramount. By iterating through each row of the table and applying the defined expression, the calculation counts only those results that are not blank, thereby enhancing the accuracy and relevance of analysis in Power BI.
Key Features of the Calculation:
- Counts non-blank results, ensuring that only meaningful information contributes to analysis, which is crucial for driving actionable insights.
- Evaluates expressions for each row in a table, allowing for complex calculations tailored to specific needs, addressing challenges such as time-consuming report creation and information inconsistencies.
- Ideal for conditional counting, making it suitable for diverse analytical scenarios.
- Integrates seamlessly with RPA solutions, enabling automated processing that enhances operational efficiency.
Example Usage:
COUNTAX(Sales, Sales[Amount])
In this example, the calculation counts all non-blank sales amounts in the Sales table, offering a clear picture of sales performance.
The importance of the DAX COUNTAX calculation cannot be overstated, particularly in 2025, as organizations increasingly depend on insight-driven approaches to maintain competitiveness. Recent statistics indicate that a notable percentage of Power BI users utilize DAX expressions, with a preference for its effectiveness in managing complex scenarios. Connections in Power BI can be one-to-one, one-to-many, or many-to-many, and understanding these connections is essential for effectively employing specific DAX functions in various analytical contexts.
Real-world applications of the DAX COUNTAX function have demonstrated its effectiveness in transforming raw information into actionable insights. This is highlighted in the case study titled ‘Business Intelligence Empowerment,’ where organizations overcame information overload to make informed decisions. Experts emphasize that mastering this tool can lead to significant advancements in information analysis skills, enabling teams to focus on strategic initiatives rather than becoming overwhelmed by manual information processing.
As Power BI evolves, staying informed about the latest enhancements to the tool will be vital for optimizing its effectiveness in information analysis. Additionally, users must recognize that the 32-bit version of Power BI Desktop will cease to receive support after 6/30/2025, underscoring the importance of mastering DAX expressions in the dynamic landscape of Power BI. Furthermore, addressing errors with operations involving multiple parameters can yield valuable insights for individuals facing similar challenges while utilizing this function in their evaluations.
Call to Action: Discover how integrating this tool with RPA solutions can optimize your analytical processes and enhance your operational efficiency today.
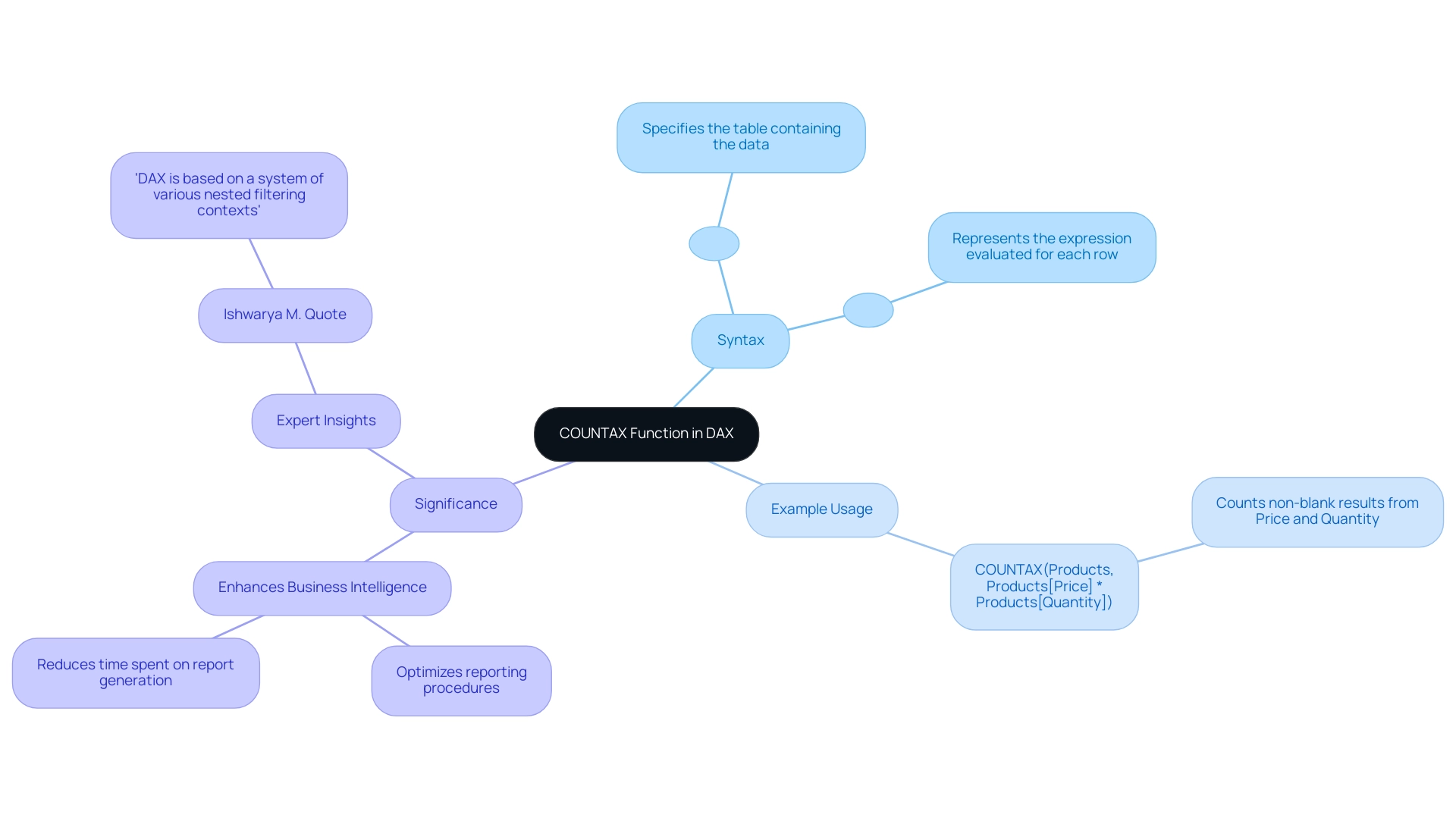
Understanding the Syntax of COUNTAX
The syntax for the COUNTAX function in DAX is structured as follows:
COUNTAX(<Table>, <Expression>)
: This parameter specifies the table containing the data you wish to evaluate.
: This represents the expression evaluated for each row within the specified table. It can be a direct column reference or a more intricate calculation. Example Usage:
COUNTAX(Products, Products[Price] * Products[Quantity])In this example, the COUNTAX function counts the non-blank results derived from multiplying the Price and Quantity for each entry in the Products table. This functionality is particularly valuable in business intelligence, as it empowers analysts to derive meaningful insights from data by focusing on specific calculations that reflect business performance.
As of 2025, grasping the subtleties of certain calculations is vital for Power BI users, especially in light of the evolving landscape of DAX expressions. With the increasing integration of BI solutions and RPA, organizations face challenges such as time-consuming report creation and inconsistencies in information. This tool can assist in optimizing reporting procedures by enabling more effective calculations, thereby reducing the time spent on report generation and enhancing consistency.
Recent statistics indicate that the function has seen heightened usage among Power BI professionals, underscoring its significance in analysis workflows, particularly in addressing these challenges. Experts emphasize that mastering this software not only enhances evaluation but also streamlines reporting processes, making it an essential tool for any analyst. As Ishwarya M., a Technical Content Writer, observes, ‘DAX is based on a system of various nested filtering contexts where performance is important, which alters the way you consider filtering tables and information.’
This understanding highlights the importance of comprehending the function of COUNTAX within DAX’s broader structure and its capacity to enhance operational efficiency through effective information management.
Additionally, the resemblance of DAX syntax to Excel formulas can aid users in leveraging their existing knowledge when working with this function. For instance, the Hevo Data Pipeline case study illustrates how organizations can employ DAX operations to streamline information management processes. This aligns with the organization’s unique value in providing tailored solutions that enhance information quality, ultimately supporting business growth and innovation.
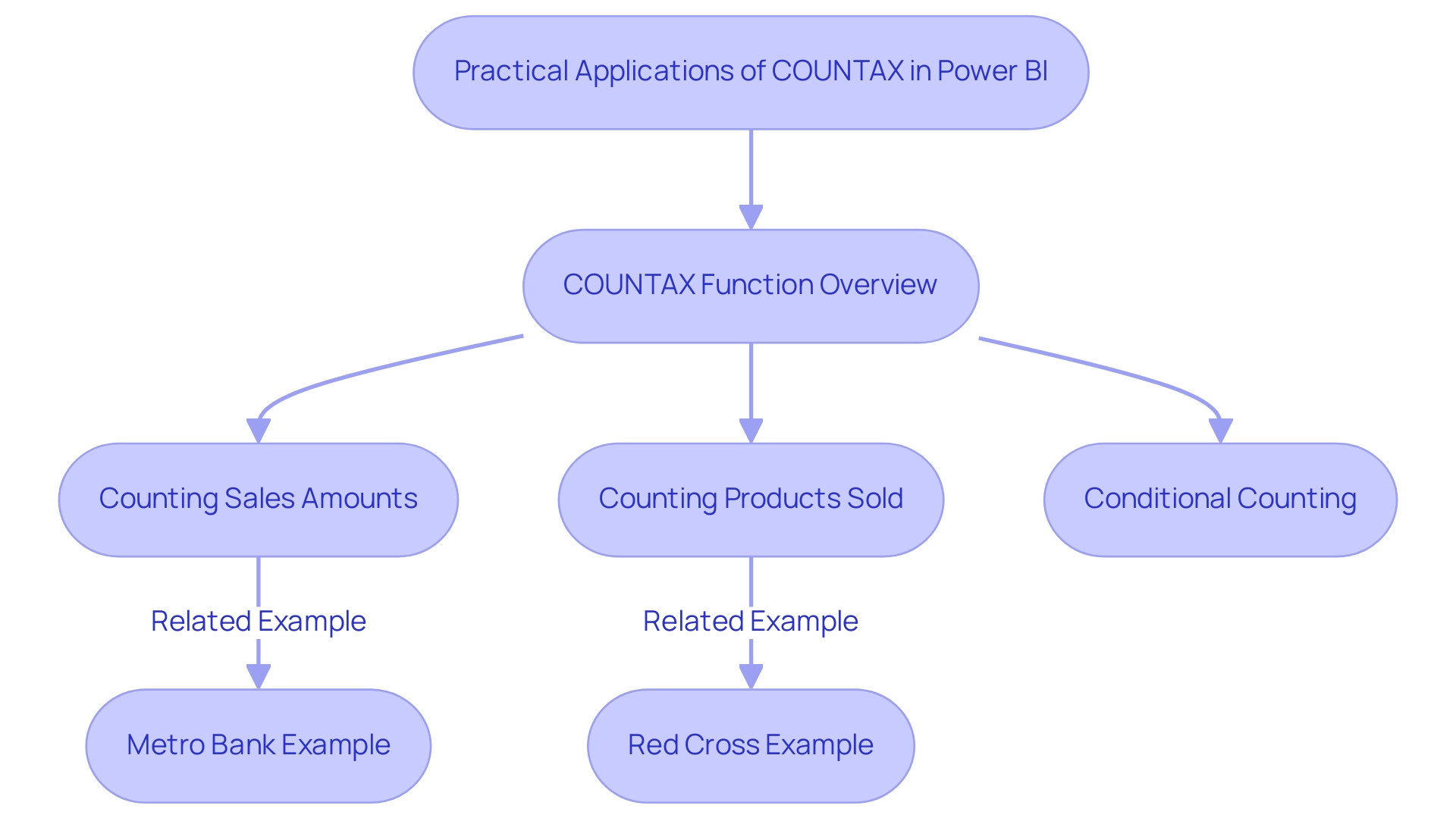
Practical Examples of COUNTAX in Action
Practical applications of the counting function in Power BI significantly enhance data analysis capabilities, serving as a vital tool for Directors of Operations Efficiency to unlock actionable insights. Consider the following compelling examples:
-
Counting Sales Amounts:
Total Sales Count = COUNTAX(Sales, Sales[Amount])This formula effectively counts all non-blank sales amounts in the Sales table, providing a clear overview of total sales activity—crucial in a data-rich environment.
-
Counting Products Sold:
Products Sold = COUNTAX(Products, IF(Products[Quantity] > 0, Products[ProductID]))This example counts the number of products sold, focusing specifically on instances where the quantity exceeds zero, ensuring only relevant sales are considered and mitigating time-consuming report creation.
-
Conditional Counting:
High Value Sales = COUNTAX(Sales, IF(Sales[Amount] > 1000, Sales[Amount]))This function counts the number of sales transactions where the amount exceeds 1000, allowing businesses to identify high-value sales and tailor their strategies accordingly.
These examples demonstrate the adaptability of the tool in various situations, enabling organizations to gain valuable insights from their information, thereby enhancing operational efficiency. For instance, Metro Bank utilized Power BI to improve their information collection and reporting processes, resulting in increased accuracy and reduced reporting time. By employing the counting method, they could further enhance their sales data analysis, ensuring that only pertinent sales figures were included, thus boosting their reporting efficiency.
Similarly, the Red Cross leveraged Power BI to gain deeper insights into donor behavior, optimizing their fundraising strategies and improving campaign performance. This tool was essential in examining donor contributions by tallying non-empty donation amounts, offering clearer insights into fundraising effectiveness. As Amazon noted, “To overcome this challenge, Amazon implemented Power BI to visualize and analyze sales and customer insights,” highlighting the critical role of such functions in driving data-driven decision-making.
Furthermore, combining RPA solutions with DAX COUNTAX can further automate analysis processes, decreasing task repetition and improving overall efficiency. Failing to leverage such tools hampers the ability to extract actionable insights and places organizations at a competitive disadvantage in today’s data-driven landscape. Mastering DAX formulas such as COUNTAX is crucial for efficient analysis and sustaining a competitive advantage in 2025.
Comparing COUNTAX with Other DAX Functions
Grasping the subtleties of DAX operations is essential for efficient analysis in Power BI, particularly in an environment where insights derived from information are vital for operational effectiveness. Here’s a detailed comparison of the primary counting functions:
-
COUNT: This function counts the number of rows in a specified column that contain numeric values. It is straightforward and does not evaluate any expressions, making it ideal for scenarios where only numeric information is relevant.
-
COUNTA: COUNTA counts all non-blank values in a column, regardless of their type. However, like COUNT, it does not evaluate expressions. This method is useful when you need a comprehensive count of entries, including text and other non-numeric data.
-
COUNTX: COUNTX functions similarly to other counting methods but emphasizes tallying the number of rows that arise from assessing an expression for a specified table. It treats blank results as zero, which can be beneficial in certain analytical contexts.
-
COUNTAX: This function is particularly powerful when you need to evaluate an expression and count only the non-blank results. It allows for more complex calculations and is essential when working with derived metrics.
When to Use Each Function:
- COUNTAX is best utilized when evaluating expressions is necessary, and you want to count only non-blank results. This is especially beneficial in situations where derived metrics are involved, tackling challenges in report creation and consistency.
- COUNTA should be your go-to when you need to count all non-blank entries in a column without the need for expression evaluation, providing a broad overview of presence and enhancing overall insights.
- COUNT is appropriate when your focus is solely on counting numeric entries in a column, ensuring that your analysis remains precise and relevant.
Practical Insights:
In 2025, data professionals emphasize the importance of choosing the right counting function based on the specific requirements of the analysis. For instance, when comparing DAX COUNTAX with COUNTA and COUNT, experts note that DAX COUNTAX offers greater flexibility in scenarios requiring expression evaluation. This distinction is crucial for optimizing models and ensuring accurate reporting.Significantly, Power BI can manage up to 20,000 or 30,000 rows of information without encountering problems, emphasizing the effectiveness of utilizing DAX capabilities in processing large datasets and the benefits of incorporating RPA solutions for automating repetitive tasks, thus enhancing overall operational efficiency.
Case Study:
Consider a scenario where a business needs to analyze customer churn rates. By employing the RELATED tool alongside a counting method, analysts can seamlessly gather and tally associated data, enriching the thoroughness of their analysis. This approach not only streamlines the process but also provides richer insights into customer behavior.As noted by Sam Zha from the Community Support Team, “You may try the measure below:
Measure = AVERAGEX ( ALLSELECTED ( 'Table'[WeekId] ), [ChurnCalc] ) - [ChurnCalc]“
which illustrates practical application of DAX calculations in real-world scenarios.Recent surveys indicate a growing preference for DAX COUNTAX among Power BI users, particularly due to its ability to handle complex calculations. As organizations increasingly depend on data-driven decision-making, understanding the strengths of each DAX capability becomes essential for maximizing operational efficiency. Moreover, an extensive course on Microsoft Excel instructs on analysis utilizing key formulas, tools, and Lookup resources, emphasizing the significance of mastering DAX expressions within the framework of wider analytical skills, especially in addressing obstacles in report generation and consistency.
Additionally, RPA solutions can significantly alleviate the burden of repetitive tasks in preparation, allowing analysts to focus on deriving insights rather than getting bogged down by manual processes.
Key Point:
To process data for the usage metrics report, content must be viewed from the workspace at least once, which is relevant for users analyzing data with DAX functions.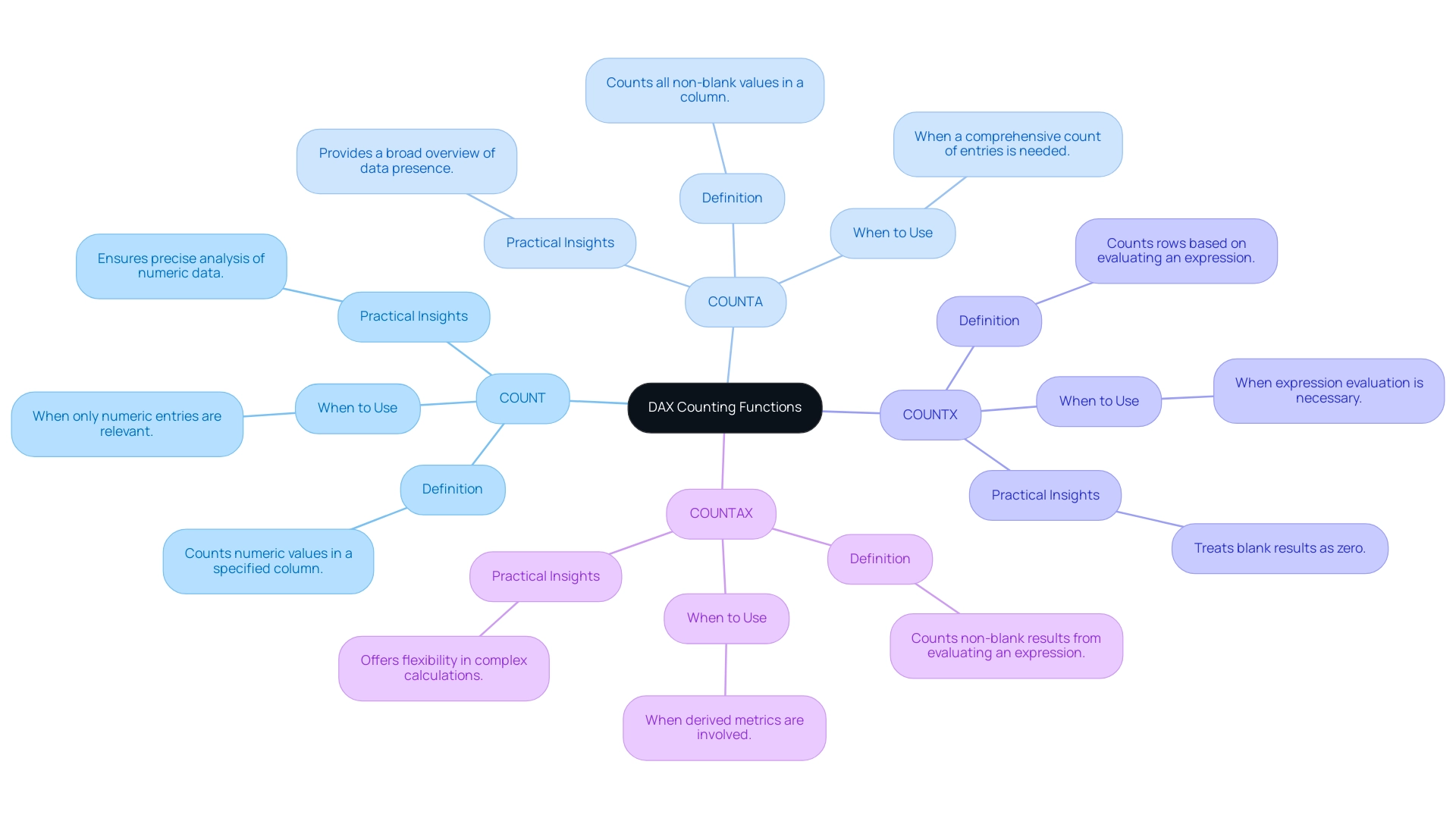
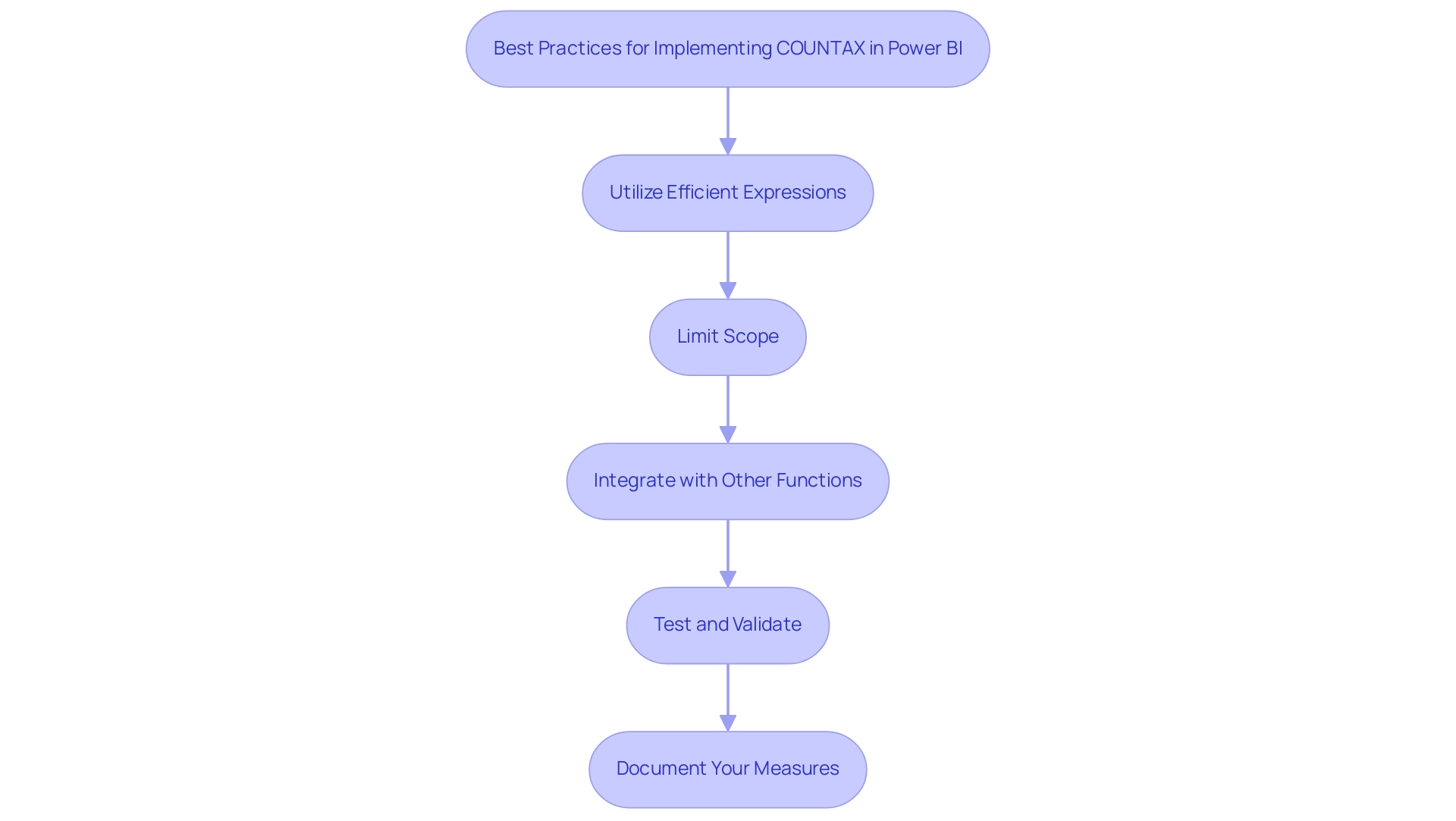
Best Practices for Implementing COUNTAX in Power BI
To maximize the effectiveness of the COUNTAX function in Power BI, it is essential to adopt several best practices that enhance performance and usability, particularly in ensuring actionable insights and operational efficiency.
-
Utilize Efficient Expressions: Craft streamlined and optimized expressions for aggregation functions. Avoid overly complex calculations that may hinder report performance; efficiency is key in analysis.
-
Limit Scope: Before applying the function, filter your information to reduce the number of rows assessed. This practice improves performance and ensures that your analysis is focused and relevant, addressing the common challenge of time-consuming report creation.
-
Integrate with Other Functions: Enhance the power of DAX COUNTAX by combining it with other DAX functions, such as CALCULATE. This approach permits the creation of more dynamic and flexible measures, enabling deeper insights and mitigating issues with inconsistencies. Implementing a robust governance strategy can further ensure consistency across reports, fostering trust in the insights generated.
-
Test and Validate: Thoroughly evaluate your expressions using example information. This step ensures that the expressions yield expected results, preventing potential issues when deployed in production reports, which can lead to a lack of actionable guidance for stakeholders.
-
Document Your Measures: Maintain comprehensive documentation of your DAX measures, particularly those employing COUNT functions. Clear documentation facilitates easier maintenance and updates, ensuring that your reporting remains accurate and efficient, thus enhancing overall business intelligence efforts.
By implementing these best practices, users can significantly enhance the performance of DAX COUNTAX expressions in Power BI, leading to more effective analysis and decision-making. For example, utilizing the RELATED feature can improve information retrieval from associated tables, enhancing the depth of analysis in Power BI. As Paul Turley, a Microsoft Data Platform MVP, states, “Same best practice guidelines… different scale, and different focus,” emphasizing the need to adapt practices to fit the unique context of your organization.
Furthermore, comprehending information limitations, such as the DoubleClick cookie expiry of 1 year, is crucial for optimizing expressions. For those looking to deepen their knowledge, a comprehensive course on Microsoft Excel offers valuable insights into data analysis using key formulas and functions, supporting the overall goal of driving growth and innovation through data-driven insights.
Conclusion
Mastering the COUNTAX function in DAX is essential for organizations striving to enhance their data analysis capabilities. This powerful function not only counts non-blank results but also evaluates expressions across specified tables, allowing analysts to derive meaningful insights that directly impact operational efficiency. By understanding its syntax and practical applications, users can implement COUNTAX effectively to address common challenges such as time-consuming report creation and data inconsistencies.
The versatility of COUNTAX shines through in various real-world scenarios, from counting sales amounts to conducting conditional counting for high-value transactions. These practical examples illustrate how organizations can leverage the function to transform raw data into actionable insights, ultimately driving informed decision-making. Furthermore, comparing COUNTAX with other DAX functions highlights its unique strengths, particularly in contexts requiring expression evaluation and complex calculations.
To fully harness the potential of COUNTAX, adopting best practices is crucial. Streamlining expressions, limiting data scope, and integrating COUNTAX with other functions can significantly enhance performance and ensure the reliability of insights generated. As businesses increasingly rely on data-driven strategies, mastering COUNTAX will be a pivotal component in maintaining a competitive edge.
In conclusion, as the landscape of data analysis continues to evolve, the importance of COUNTAX cannot be overstated. Organizations that invest time and resources into understanding and implementing this function will find themselves better equipped to navigate the complexities of data management, ultimately fostering a culture of informed decision-making and operational excellence.

