Introduction
In the realm of data analysis, histograms emerge as indispensable tools that bridge the gap between raw numbers and actionable insights. By visually representing the distribution of numerical data, they not only simplify complex datasets but also illuminate patterns and trends that might otherwise go unnoticed.
As organizations grapple with the intricacies of Business Intelligence and the rapid evolution of technology, understanding how to effectively utilize histograms in platforms like Power BI becomes crucial.
This article delves into the fundamental concepts of histograms, offering a comprehensive guide on their creation, customization, and troubleshooting, while also highlighting their real-world applications across various industries.
By mastering these techniques, professionals can enhance their analytical capabilities, driving operational efficiency and informed decision-making in an increasingly data-driven world.
Understanding Histograms: Basics and Importance
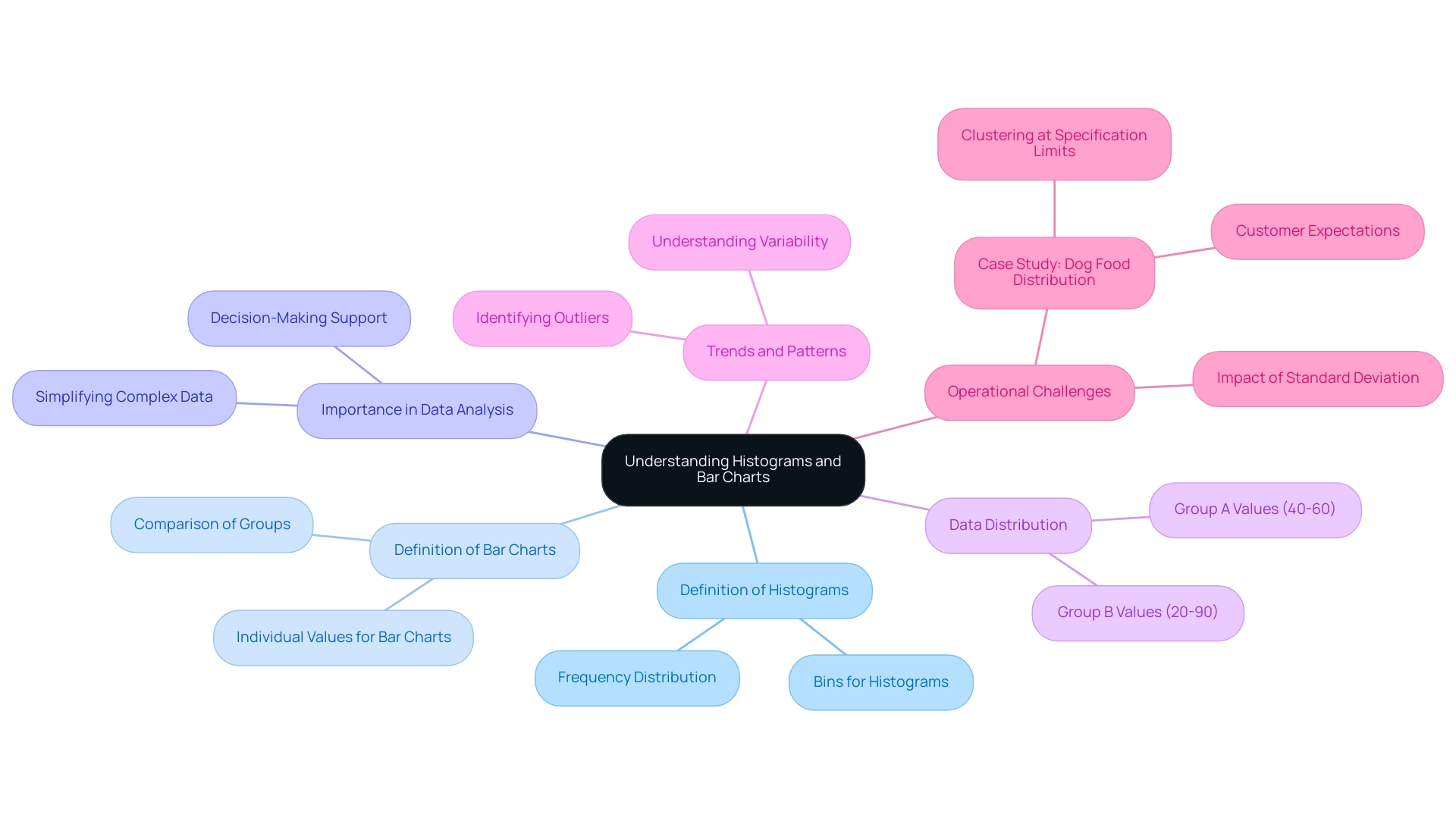
A bar chart functions as a robust visual instrument for illustrating the distribution of numerical information, and when combined with histograms in Power BI, it can greatly improve your analytical abilities. In the context of navigating the overwhelming AI landscape, selecting the right BI tools is essential for effective visualization. By organizing information into bins or intervals, histograms in Power BI enable a clear representation of the frequency of points across these ranges.
For instance, in analyzing Group A’s values, which predominantly fall between 40 and 60, and Group B’s range of 20 to 90, bar charts can effectively illustrate how these groups distribute across the specified intervals. This method is particularly effective in identifying patterns, trends, and outliers within datasets, especially in the context of RPA and BI, which drive operational efficiency and data-driven insights. The importance of bar charts in information analysis cannot be overstated; they simplify complex sets, enabling decision-makers to interpret and act upon the visualized information effectively.
The standard deviation, indicating the spread of values, further emphasizes the importance of understanding variability in information. In the dog food allocation case study, a bar chart indicated that the information lacked results around the average, clustering instead at the upper and lower specification limits. This insight underscores how variation can lead to operational challenges, as customers may receive items within specifications but that do not meet their expectations.
Furthermore, while frequency distributions are utilized in histograms in Power BI to group values based on bin ranges, bar charts display each value as an individual bar. As Jim appropriately states, ‘I believe charts are an excellent resource for comprehending the spread of your information.’ Their capacity to offer transparency in information representation, especially when combined with customized BI solutions, renders graphical charts an essential resource in the toolkit of any Director of Operations Efficiency, particularly in tackling the operational challenges presented by the intricacies of information analysis.
Step-by-Step Guide to Creating Histograms in Power BI
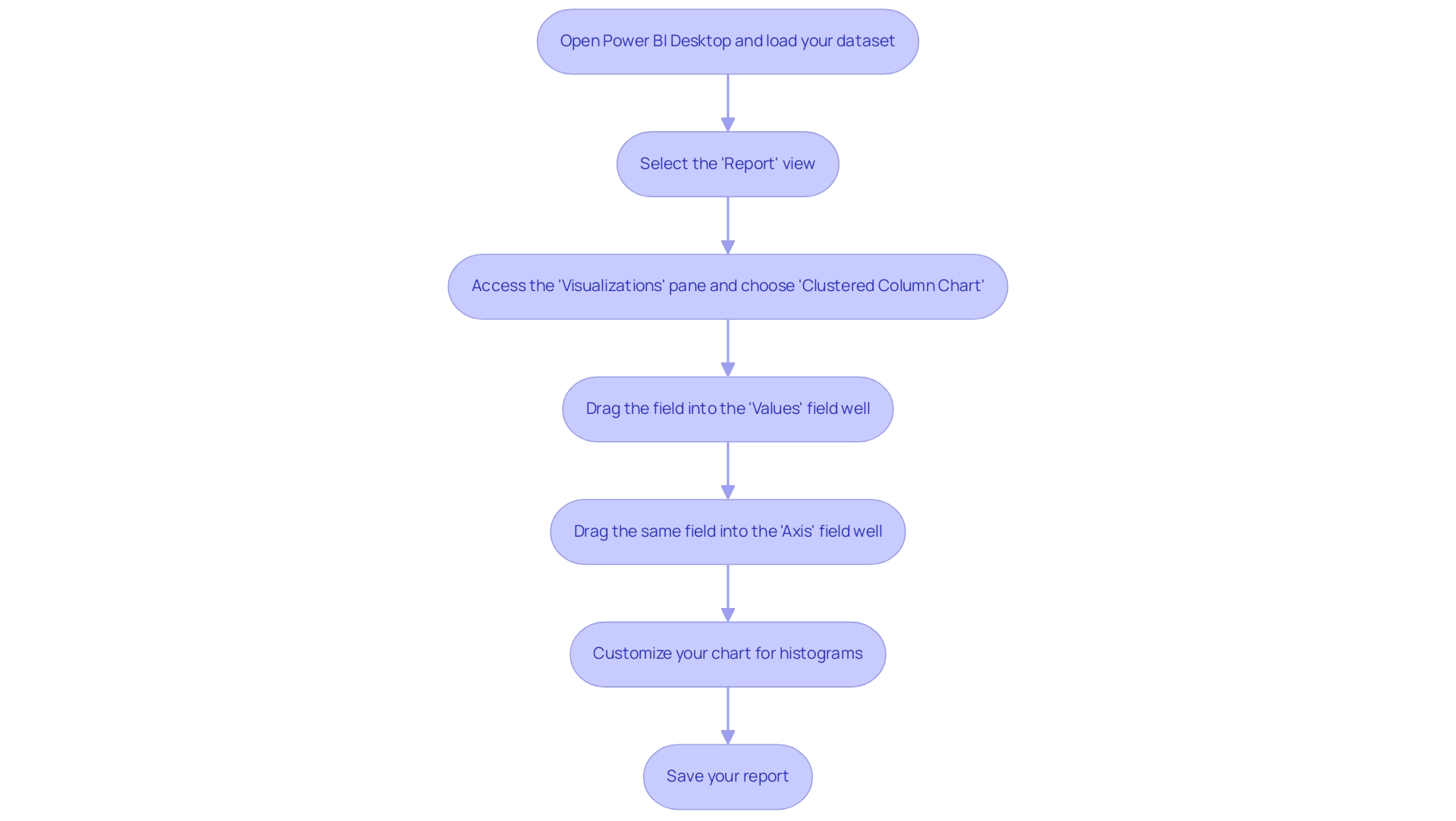
Generating histograms in Power BI is a simple procedure that can greatly enhance your visualization abilities and promote informed decision-making. As highlighted, many users face the challenge of needing to create separate reports for each workspace, which can be cumbersome and time-consuming. By following these steps, you can effectively create a bar chart and streamline your reporting process:
- Open Power BI Desktop and load your dataset.
- Select the ‘Report’ view from the left sidebar to begin your visualization.
- Access the ‘Visualizations’ pane and choose the ‘Clustered Column Chart’ icon, which functions as the foundation for creating histograms in Power BI.
- Drag the field you wish to analyze into the ‘Values’ field well; this will determine the height of the bars in your histogram.
- Drag the same field into the ‘Axis’ field well. Power BI will automatically create histograms in Power BI based on your information distribution, which facilitates a clear visual representation.
- Customize your chart for histograms in Power BI by adjusting the bin size in the ‘Format’ pane under ‘Data colors’ and ‘X-Axis’ settings. This enables you to customize the visualization to better highlight your insights.
- Save your report to ensure your data visualization is readily available for future analysis and presentations.
Additionally, consider how RPA solutions can automate repetitive tasks in the report creation process, enhancing your operational efficiency and freeing up valuable time for analysis. Don’t forget that the early bird discount for Power BI features ends on December 31, which may be a great opportunity to explore new functionalities that enhance your operational efficiency. Applying these steps not only enables you to create impactful charts but also aligns with the latest Power BI features, significantly enhancing your visualization and user engagement.
The enhanced usage metrics report contains sections for report usage, performance, and FAQs, offering thorough insights into how your data visualizations contribute to overall report engagement and viewer behavior.
Enhancing Your Histograms: Customization Techniques
To enhance the effectiveness of your graphical representations in Power BI, consider applying the following advanced customization techniques:
-
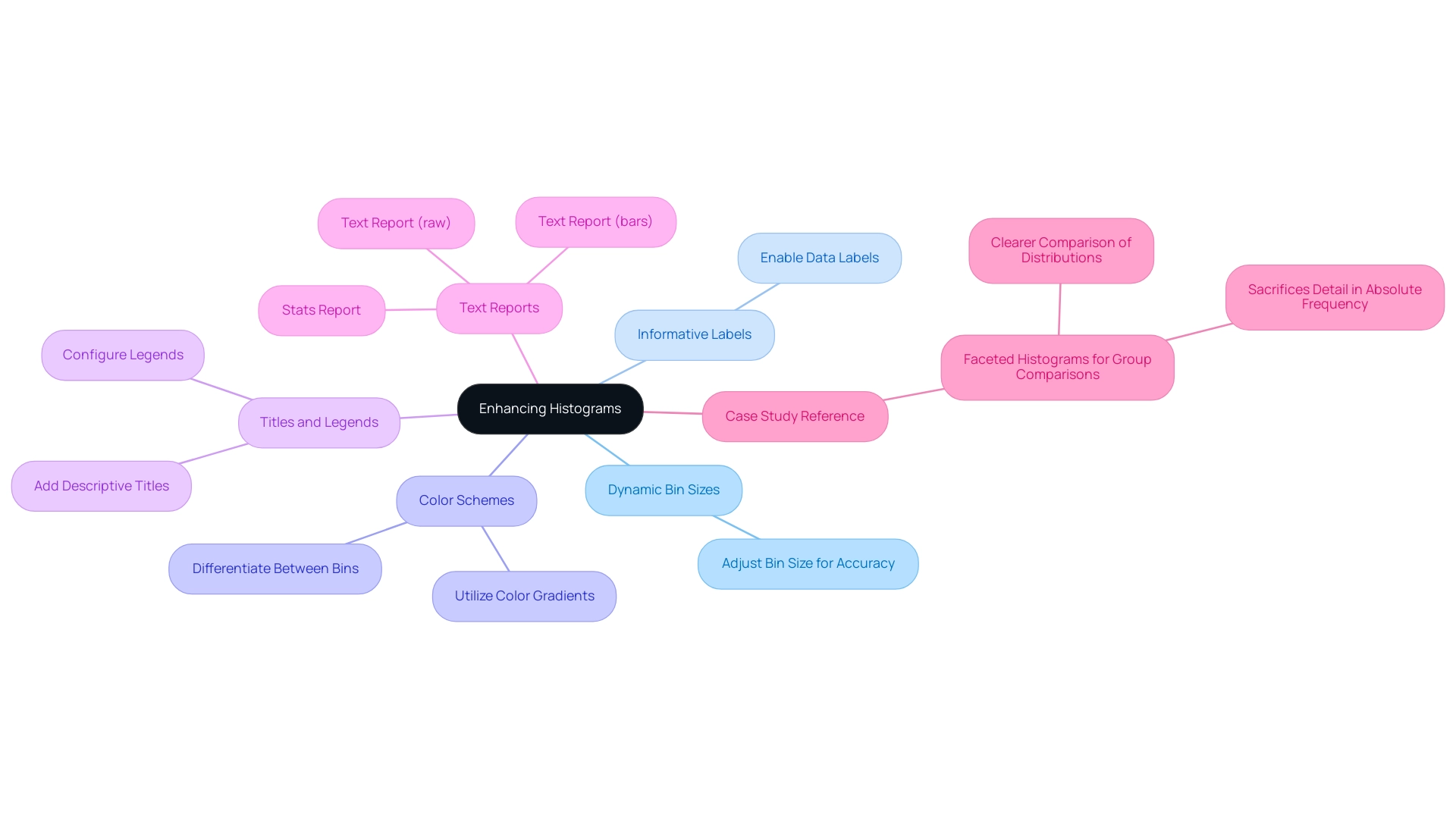
Dynamic Bin Sizes: Adjust the bin sizes to better represent the underlying information accurately. For instance, when visualizing the distribution of outcomes from summing the result of five die rolls, repeated 20,000 times, adjusting the ‘Bin size’ settings within the ‘Information’ section can significantly enhance the accuracy of histograms in Power BI.
-
Informative Labels: Incorporate information labels to give viewers immediate context about your information. By enabling data labels in the ‘Format’ pane, you allow your audience to see precise values, making the chart more informative.
-
Color Schemes: Utilize color gradients or distinct hues to differentiate between bins, effectively highlighting trends or critical data points. This visual distinction can guide viewers in quickly identifying significant patterns within the data.
-
Titles and Legends: Ensure clarity by adding descriptive titles and legends that explain what your graphical representation shows. These elements can be easily configured in the ‘Format’ pane under ‘Title’ and ‘Legend’ settings, contributing to a more interpretable visualization.
-
Text Reports: Remember that three types of text reports can be generated from bar charts: Text Report (bars), Text Report (raw), and Stats Report. These reports offer significant perspectives on your information, further improving the usefulness of your charts.
-
Case Study Reference: Consider the case study on faceted charts for group comparisons. This approach enables a more distinct comparison of distributions among various groups, demonstrating how the mentioned customization strategies can be utilized in a practical context.
By utilizing these strategies, you can produce graphical representations that not only communicate information effectively but also involve your audience in significant analysis.
Troubleshooting Common Histogram Issues in Power BI
Generating bar charts in Power BI can pose several challenges that mirror wider issues in analytics and visualization, especially for individuals aiming for operational efficiency. Comprehending these typical problems and their remedies can greatly improve your visual representation skills:
-
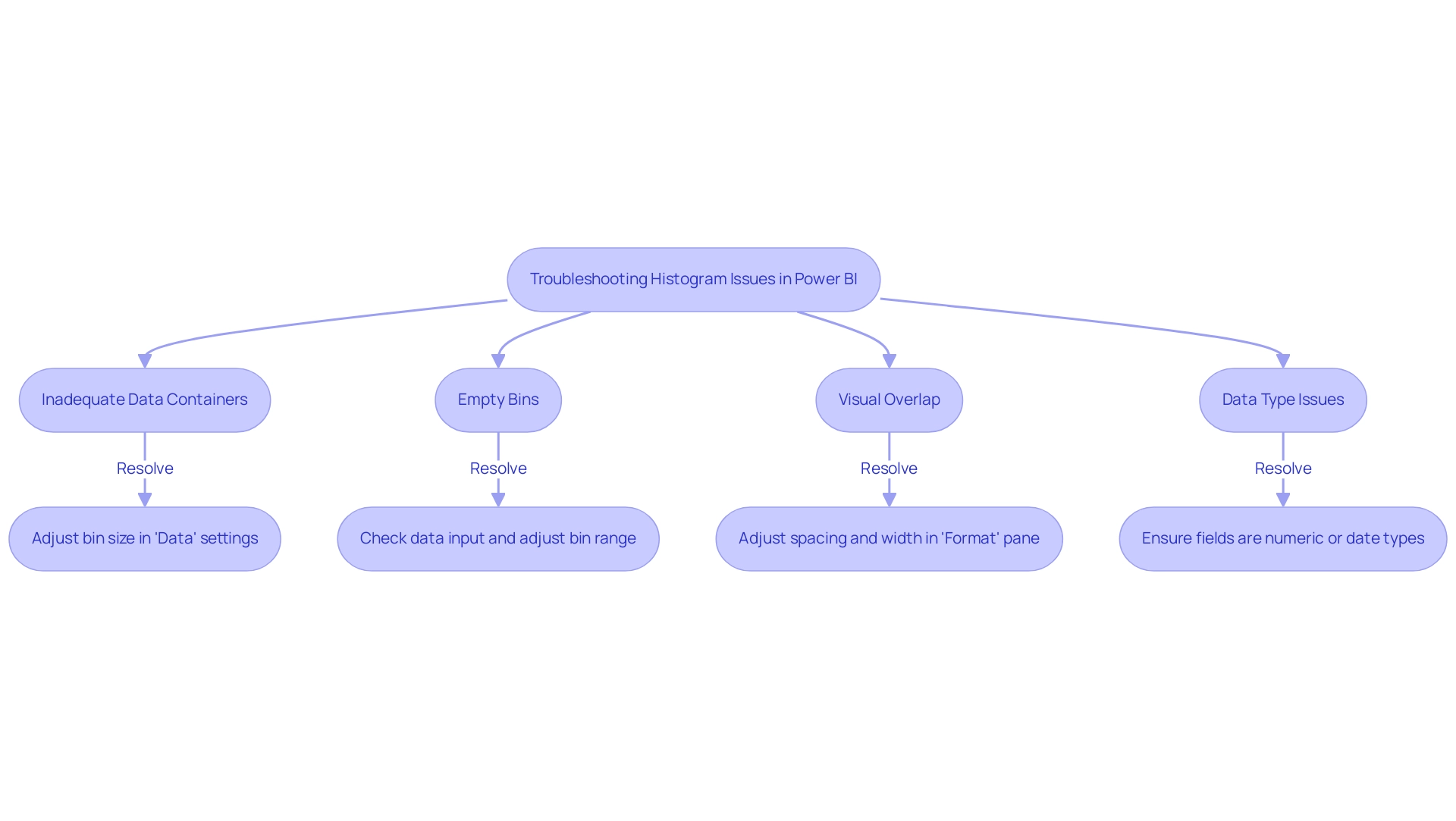
Inadequate Data Containers: A chart’s effectiveness largely relies on the quantity of containers utilized. If your graph does not reflect the desired arrangement, it may be because of an insufficient quantity of intervals. To address this, navigate to the ‘Data’ settings and adjust the bin size accordingly. Histograms in Power BI that are well-constructed will clearly illustrate the general shape and distribution of your variable. Figures 2 and 3 illustrate how changing the number of bins affects the visibility of the center, shape, and spread of the information.
-
Empty Bins: It’s not uncommon for bins to appear empty, particularly if the range of values is not aligned with the selected bins. To resolve this, double-check your information input and adjust the bin range to ensure all relevant points are captured. This practice helps reduce inconsistencies that can lead to confusion and mistrust in your insights.
-
Visual Overlap: Overlapping bars can obscure your message. To improve visual clarity, adjust the spacing and width settings in the ‘Format’ pane. This adjustment can help delineate the bars, making the graphical representation more interpretable and actionable for stakeholders.
-
Data Type Issues: Ensure that the fields designated for your chart are of numeric or date types. Utilizing unsuitable information types can result in mistakes in representation, detracting from the chart’s effectiveness and adding to the overall challenge of inadequate master quality.
Furthermore, it’s crucial to distinguish between frequency charts and bar graphs. While bar charts are more appropriate for discrete or categorical variables and exhibit gaps between bars, frequency distributions represent continuous information without gaps, offering a clearer picture of distribution. This distinction is crucial in selecting the appropriate visualization for your information.
By grasping these troubleshooting tips, you not only streamline the creation process but also enhance the overall effectiveness of your visualizations in Power BI. As you improve your data representations, consider that nearly half of user tickets are responded to within five hours. Implementing effective information visualization practices can significantly reduce user errors, ultimately improving response times and operational efficiency.
Furthermore, addressing these challenges related to histograms in Power BI can provide clearer insights and actionable guidance for stakeholders, thereby facilitating better decision-making and overcoming barriers to AI adoption. Adopting these techniques can enable your organization to leverage insights more effectively and navigate the complexities of governance and AI integration.
Real-World Applications of Histograms in Data Analysis
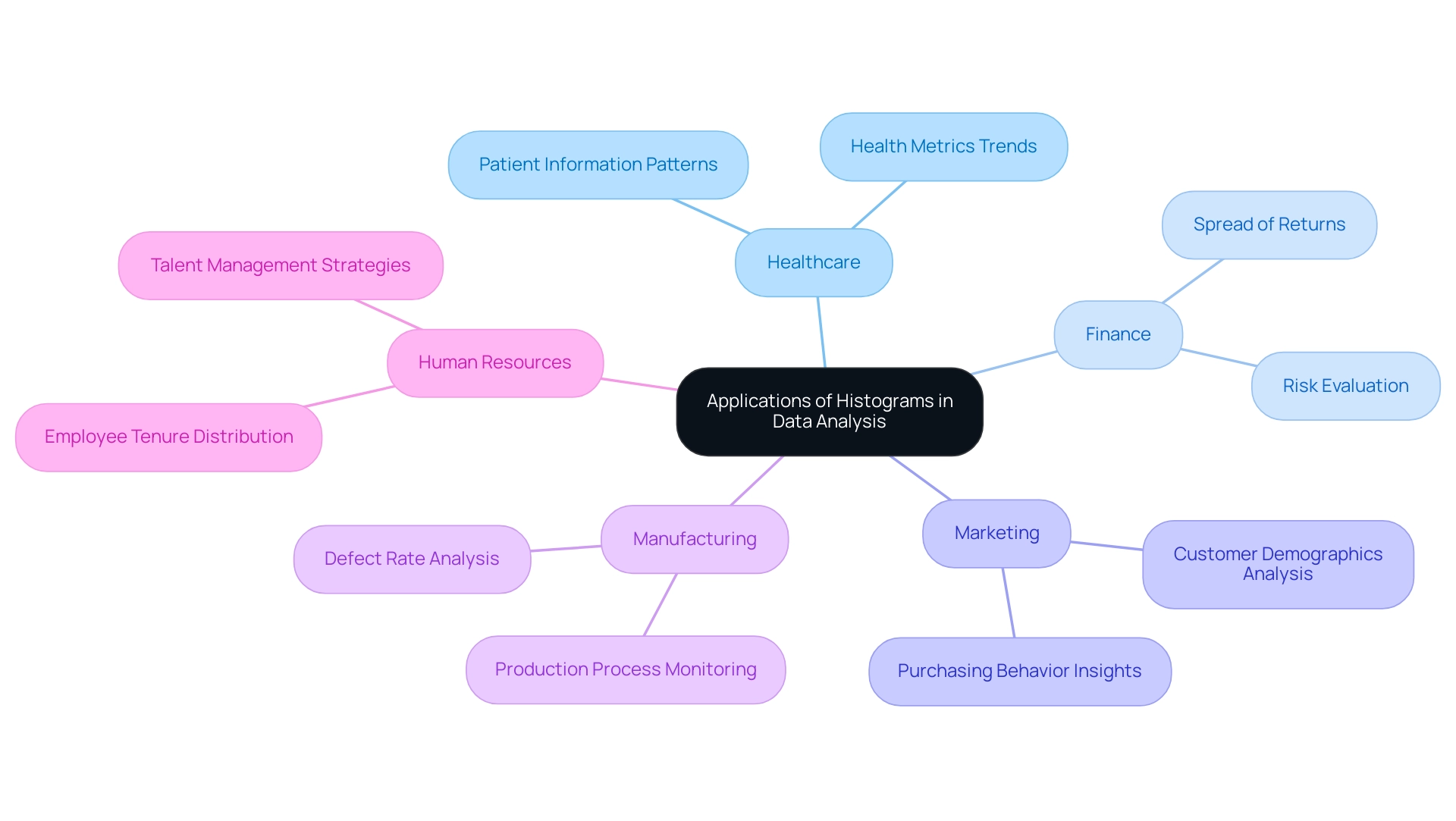
Histograms serve as a powerful tool in diverse fields for effective analysis, particularly within the framework of Business Intelligence and Robotic Process Automation (RPA). Their applications encompass:
- Healthcare: By examining patient information patterns, healthcare professionals can recognize important trends in health metrics, resulting in enhanced patient outcomes and focused interventions.
- Finance: Financial analysts employ graphical representations to illustrate the spread of returns, assisting in risk evaluation and investment strategy development. This method enables clearer insights into performance variability, addressing common challenges like information inconsistencies.
- Marketing: Marketers can leverage graphical representations to dissect customer demographics, analyzing purchasing behaviors to refine targeting and enhance engagement strategies, thus driving growth through informed decision-making.
- Manufacturing: In manufacturing settings, graphical representations are employed to monitor production processes by analyzing defect rates, assisting in quality control and process optimization, which are crucial for operational efficiency.
- Human Resources: HR professionals can develop talent management strategies based on employee tenure information. For instance, the case study named ‘Distribution of Employee Tenure in Company XYZ’ demonstrates how examining employee tenure distributions can evaluate staff stability and guide personnel management strategies.
Moreover, bins for a bar chart can be defined by decade, such as 0-10 years, 11-20 years, and so forth, offering a structured method to visualize distributions.
By mastering bar chart techniques in Power BI, professionals can convert raw information into actionable insights, enabling them to make informed, strategic decisions suited to their specific operational requirements. As organizations increasingly adopt information-driven approaches, the relevance of histograms in analysis continues to grow, solidifying their status as an essential analytical tool in 2024 and beyond. RPA further enhances this capability by automating repetitive tasks associated with report generation, allowing teams to focus on strategic analysis and innovation.
However, many businesses still face a lack of data-driven insights, which can hinder their decision-making processes. By utilizing specific RPA tools like EMMA RPA and Power Automate, organizations can streamline their workflows and enhance operational efficiency, ultimately transforming their data into valuable insights.
Conclusion
Histograms stand as a cornerstone in the landscape of data analysis, offering clarity and insight into the distribution of numerical data. By mastering their creation and customization in platforms like Power BI, professionals can transform overwhelming datasets into visual narratives that drive informed decision-making. The step-by-step guide provided illustrates how to streamline the creation process, while advanced customization techniques enhance the interpretability and engagement of the visualizations.
Addressing common challenges associated with histograms ensures that data is accurately represented and easily understood. By troubleshooting issues like insufficient data bins or visual overlap, analysts can refine their visual tools to convey meaningful insights. This proactive approach not only improves data visualization but also fosters a culture of operational efficiency and informed strategy.
The real-world applications of histograms across various industries underscore their versatility and importance. From healthcare to finance, the ability to visualize data distributions empowers professionals to identify trends, optimize processes, and enhance decision-making. As organizations increasingly embrace data-driven strategies, the role of histograms will only grow in significance, solidifying their place as essential instruments for navigating the complexities of data analysis in 2024 and beyond. Embracing these techniques will enable teams to unlock the full potential of their data, driving operational excellence and strategic innovation.

