Overview
Descriptive analysis addresses fundamental ‘what’ questions related to data, such as identifying trends in sales or understanding customer demographics. This analysis is crucial for organizations seeking to summarize historical data effectively. By gaining insights from this data, organizations can guide strategic decisions, thereby laying the groundwork for more advanced analytical methods. Embracing descriptive analysis not only enhances understanding but also empowers organizations to make informed choices that drive success.
Introduction
In a world inundated with data, the ability to distill meaningful insights from vast amounts of information is more crucial than ever. Descriptive analysis stands as a foundational pillar in data analytics, offering organizations a clear lens to view their historical performance and customer behaviors. By addressing essential questions about trends, patterns, and anomalies, businesses can harness this analytical approach to inform strategic decision-making and drive operational efficiency.
As the landscape of connected devices expands and the volume of data surges, integrating descriptive analysis with advanced technologies like Robotic Process Automation (RPA) becomes paramount. This article delves into the significance of descriptive analysis, its real-world applications across various industries, and the challenges organizations face in leveraging this powerful tool effectively.
Understanding Descriptive Analysis: Definition and Importance
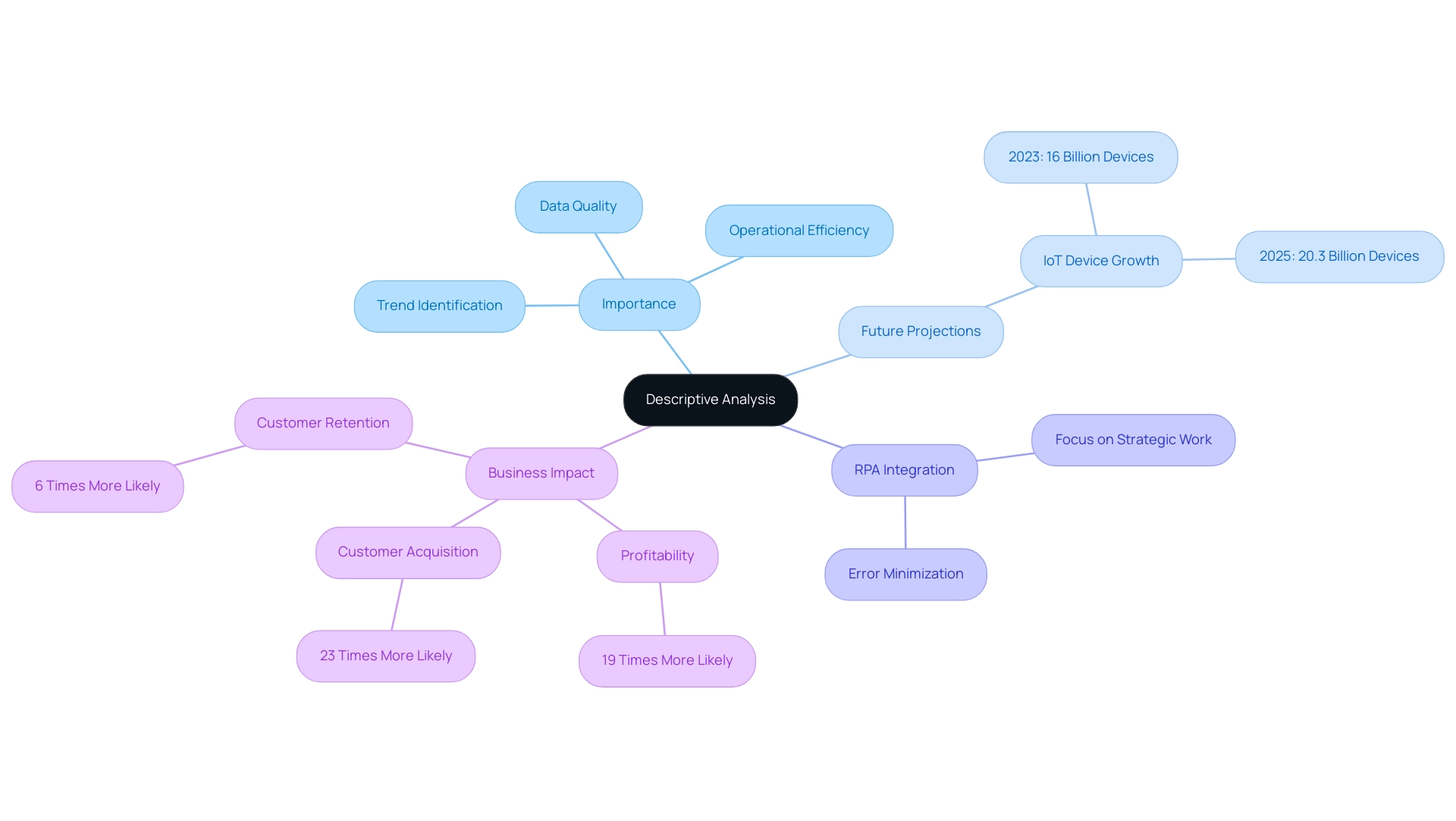
Descriptive examination is a pivotal statistical method that empowers organizations to summarize, interpret, and understand their data effectively. By addressing the fundamental ‘what’ questions, it clarifies the characteristics of the dataset, enabling businesses to identify trends, patterns, and anomalies. This foundational examination is critical, as it lays the groundwork for more advanced methodologies, such as predictive and prescriptive analytics.
As we look ahead to 2025, the number of connected IoT devices is projected to reach 20.3 billion, leading to an exponential increase in available information for examination. Organizations that leverage this information through detailed analysis can optimize their operations and enhance decision-making processes, particularly when integrated with Robotic Process Automation (RPA). RPA not only minimizes errors but also liberates teams to focus on more strategic, value-adding work.
Statistics reveal that data-driven companies are 19 times more likely to be profitable, underscoring the importance of descriptive analysis in enhancing operational efficiency. Moreover, leveraging RPA addresses challenges related to poor master data quality, a common obstacle to AI adoption. Tailored AI solutions can assist organizations in identifying the right technologies to navigate these challenges.
The Sonata platform exemplifies how small enterprises can utilize descriptive evaluation and RPA to boost efficiency and secure a competitive edge. As illustrated in a case study on overcoming analytics implementation challenges, small enterprises that prioritize data quality and consistency have achieved significant results, including improved resource management and enhanced decision-making outcomes. Expert insights highlight the critical role of descriptive evaluation in business decision-making, with Chris Farr noting that data-driven companies are 23 times more likely to acquire customers and 6 times more likely to retain them.
By harnessing descriptive evaluation and RPA, along with customized AI solutions, enterprises can make informed decisions that ultimately foster growth and innovation.
Key Questions Addressed by Descriptive Analysis
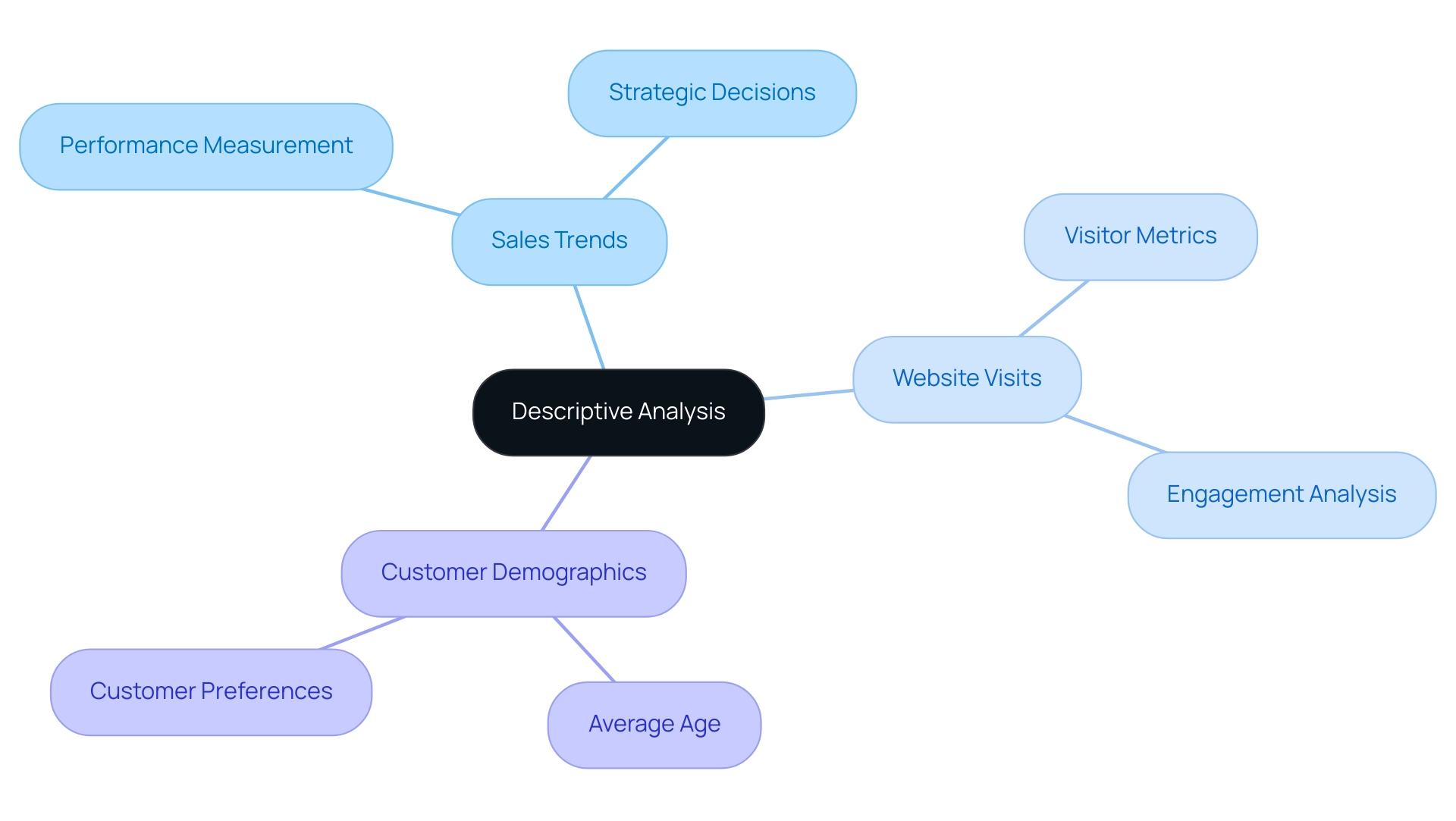
Descriptive analysis plays a pivotal role in addressing essential questions that help entities measure performance and gain insights into their customers. Key inquiries include:
- What are the trends in sales over the past year?
- How many customers visited our website last month?
- What is the average age of our customers?
These fundamental questions enable organizations to identify performance trends and customer preferences, ultimately guiding strategic decisions.
With 16 billion connected IoT devices reported in 2023, companies are increasingly utilizing information to monitor metrics and improve operational efficiency. By integrating Robotic Process Automation (RPA), organizations can automate manual workflows, significantly reducing errors and freeing up teams for strategic tasks such as innovation and customer engagement. A notable case study titled ‘Business Intelligence Empowerment’ highlights how our organization assists businesses in transforming raw information into actionable insights, aiding informed decision-making and driving growth and innovation.
Furthermore, Netflix exemplifies the strength of information evaluation; each year, they leverage extensive datasets, realizing savings of $1 billion. Insights obtained from descriptive examination assist companies in pinpointing areas for improvement and monitoring their progress over time. As companies navigate the complexities of today’s information environment, an essential aspect of informed decision-making is the measurement of performance through descriptive examination, enhanced by customized AI solutions that help firms identify the most relevant technologies for their unique needs amidst the evolving technology landscape.
This is supported by roles in data science focusing on essential tasks such as information preprocessing and A/B testing, demonstrating how descriptive assessment fits within the broader structure of analytics in business.
Types of Data Analysis: Contextualizing Descriptive Analysis
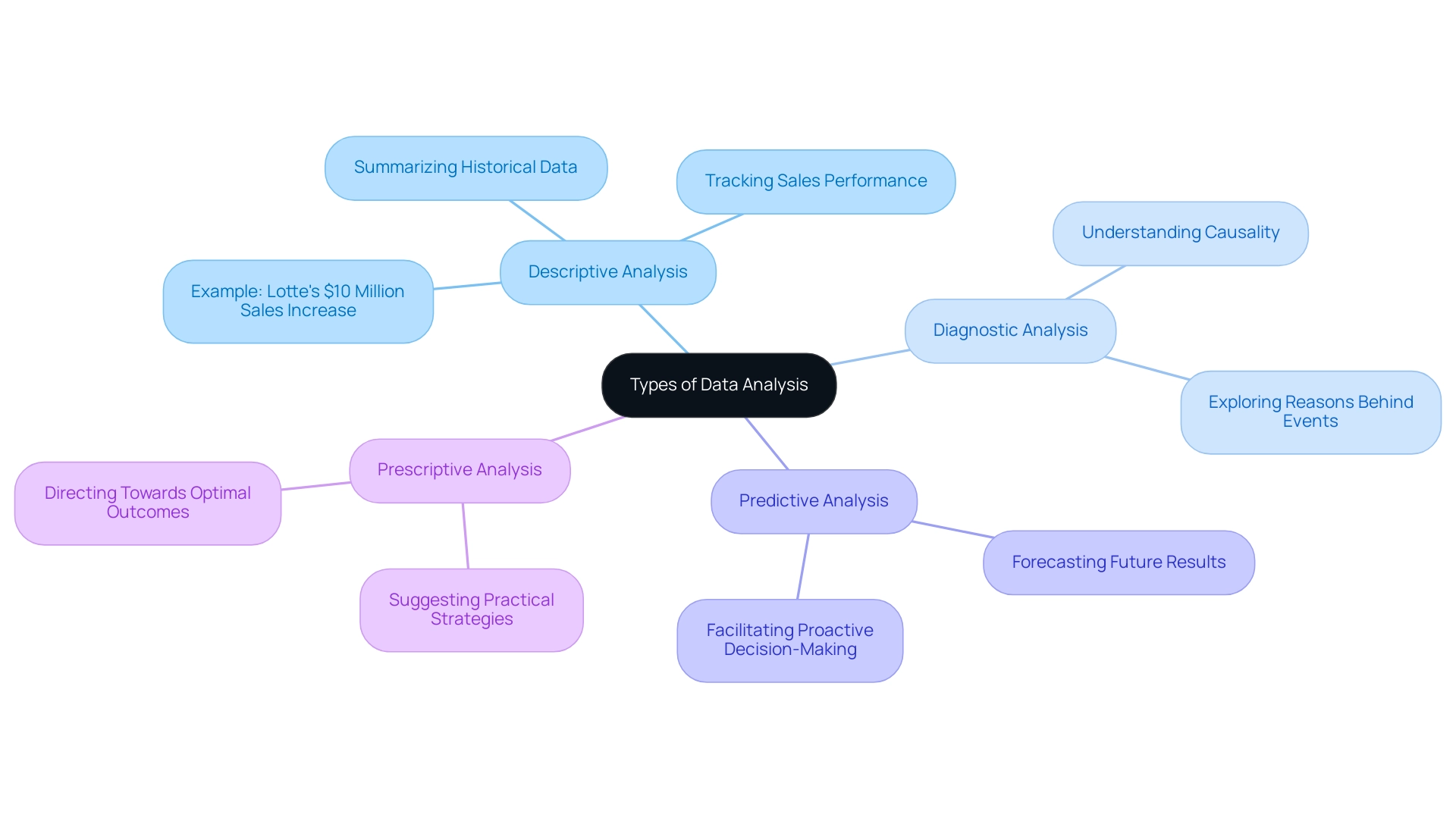
Data examination is crucial for entities aiming to make educated choices, and it can be classified into four primary forms: descriptive, diagnostic, predictive, and prescriptive. Descriptive examination serves as the foundation, focusing on summarizing historical data to provide insights into what has transpired. This prompts the inquiry: which type of question does descriptive analysis address? For instance, organizations frequently employ descriptive statistics to track sales performance or customer behavior, seeking to understand the underlying trends.
A significant example is Lotte, a South Korean conglomerate, which boosted their sales by $10 million through effective Business Intelligence strategies. This case illustrates the tangible results of descriptive evaluation. Notably, roughly 50% of enterprises indicate that they employ descriptive evaluation as their primary method of information assessment, reinforcing the question: which type of question does descriptive analysis address?
Building upon this, diagnostic evaluation explores the reasons behind specific occurrences, enabling businesses to comprehend causality. Predictive evaluation utilizes historical information to forecast future results, facilitating proactive decision-making and strategic planning. Finally, prescriptive examination advances by suggesting practical strategies based on insights, directing entities toward optimal outcomes.
As the need for information-driven decision-making increases, the global Big Data analytics market is projected to reach an impressive $549.73 billion by 2028, according to insights from Fortune Business Insights. This underscores the significance of comprehending the various forms of analysis and their applications.
Furthermore, while the vast AI landscape can be intimidating, our customized AI solutions—including Small Language Models for effective information analysis and privacy enhancement, as well as GenAI Workshops for practical training and custom GPT development—can penetrate the clutter. These focused technologies align with your specific business objectives and challenges. By harnessing Business Intelligence, organizations can unlock the power of information to transform raw content into actionable insights, driving growth and innovation. Moreover, our Power BI services, including the 3-Day Sprint for rapid report creation and the General Management App for thorough management, guarantee efficient reporting and consistency.
With roughly 30% of the Global DataSphere anticipated to consist of real-time information by 2025, companies must select suitable evaluation techniques that align with their strategic goals. The significance of web scraping in this context cannot be disregarded, as it enables organizations to leverage large information sets for strategic decision-making, further enhancing their analytical capabilities. This dialogue between human curiosity and artificial intelligence emphasizes the role of AI in problem-solving and innovation.
Real-World Applications of Descriptive Analysis
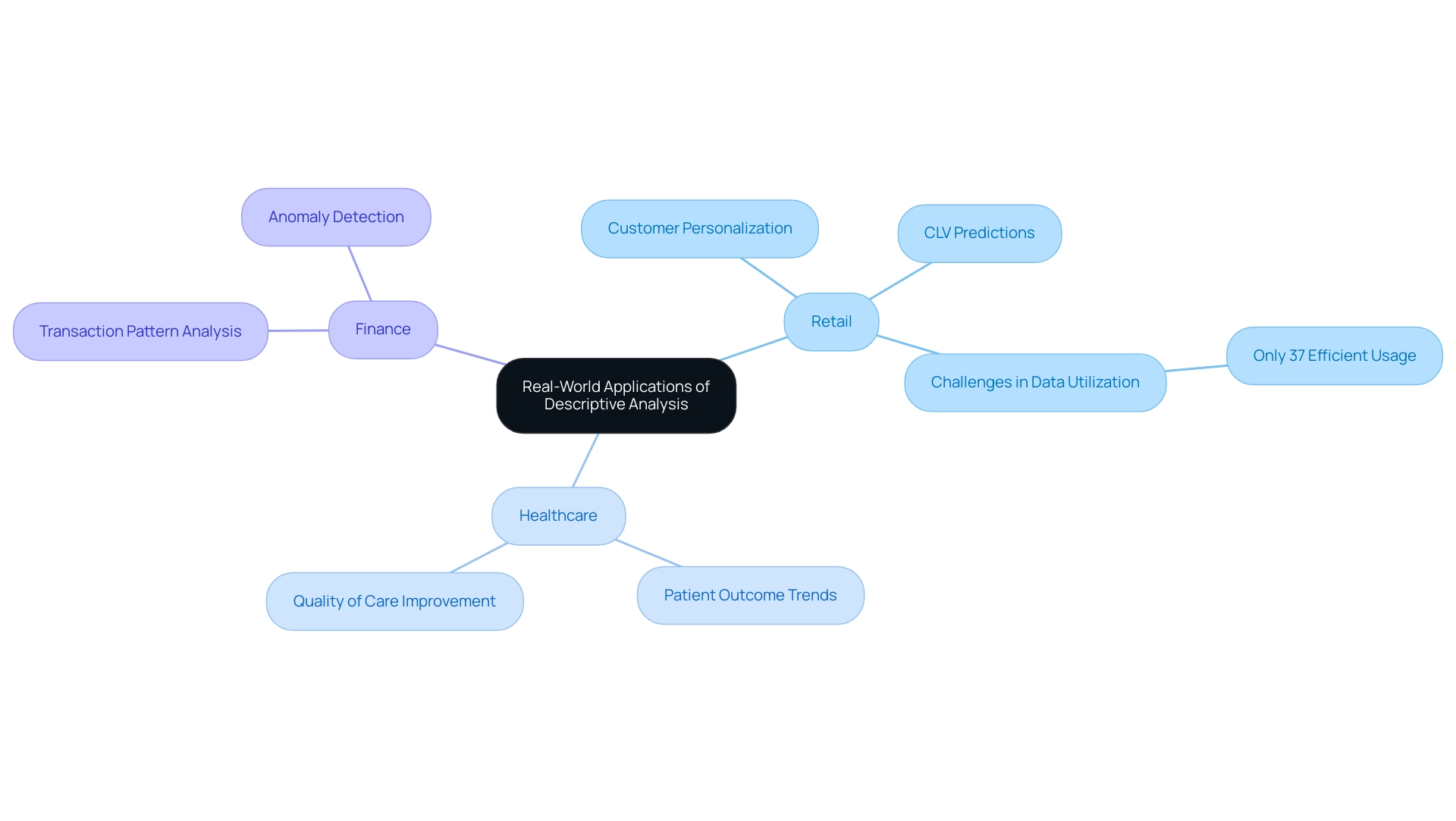
Descriptive evaluation serves as a vital tool across a multitude of industries, unlocking valuable insights that drive strategic decision-making. This is particularly relevant in understanding which type of question descriptive analysis addresses in an era marked by overwhelming AI options. In the retail sector, businesses utilize this examination to explore sales information and customer demographics, enabling the personalization of marketing strategies that resonate with target audiences. For instance, understanding customer lifetime value (CLV) predictions allows retailers to gauge potential revenue streams and refine their outreach efforts accordingly.
However, it is noteworthy that only 37% of enterprises manage to utilize information efficiently, despite it being a top priority. This statistic highlights the challenges organizations face in leveraging information effectively.
In healthcare, descriptive analysis plays a crucial role in summarizing patient information, specifically in addressing which type of question descriptive analysis addresses regarding treatment outcome trends. By closely examining patterns in patient records, healthcare providers can enhance the quality of care and tailor interventions for better health outcomes. Furthermore, unlocking the power of Business Intelligence (BI) can transform raw information into actionable insights, enabling informed decision-making that drives growth and innovation.
Financial institutions are also leveraging descriptive analytics to scrutinize transaction patterns, raising the question of which type of question descriptive analysis addresses in facilitating the detection of anomalies and potential fraud. This proactive approach not only safeguards assets but also enhances operational efficiency. The integration of Robotic Process Automation (RPA) alongside BI further amplifies the ability to derive insight-driven conclusions, streamlining operations and fostering business growth.
To navigate the overwhelming AI landscape, tailored AI solutions such as predictive analytics and machine learning algorithms can assist businesses in identifying the most relevant information and insights for their specific needs. Dmytro Tymofiiev, Delivery Manager at SPD Technology, emphasizes the necessity of analytics in retail, stating, ‘The reality is that analytics in retail is no longer an option for those who want to stay competitive—it’s a necessity.’ This sentiment reflects a broader industry shift, as organizations recognize that even small, incremental steps toward evidence-based strategies can lead to significant improvements over time.
Furthermore, recent developments in the industry, such as SoundCommerce raising $15 million in early 2024 to expand its analytics solutions for retail insights, underscore the growing investment in analytics capabilities. Additionally, case studies reveal that data mining techniques employed in descriptive analytics—such as clustering and anomaly detection—can uncover hidden insights, thereby addressing the question of which type of question descriptive analysis addresses, amplifying the effectiveness of these analytical processes. As we progress through 2025, the ongoing development of descriptive examination highlights its essential role in enhancing decision-making across various sectors, driving both growth and innovation while assisting businesses in navigating the complexities of AI.
The failure to extract meaningful insights can leave organizations at a competitive disadvantage, underscoring the urgency of leveraging BI effectively.
Challenges and Limitations of Descriptive Analysis
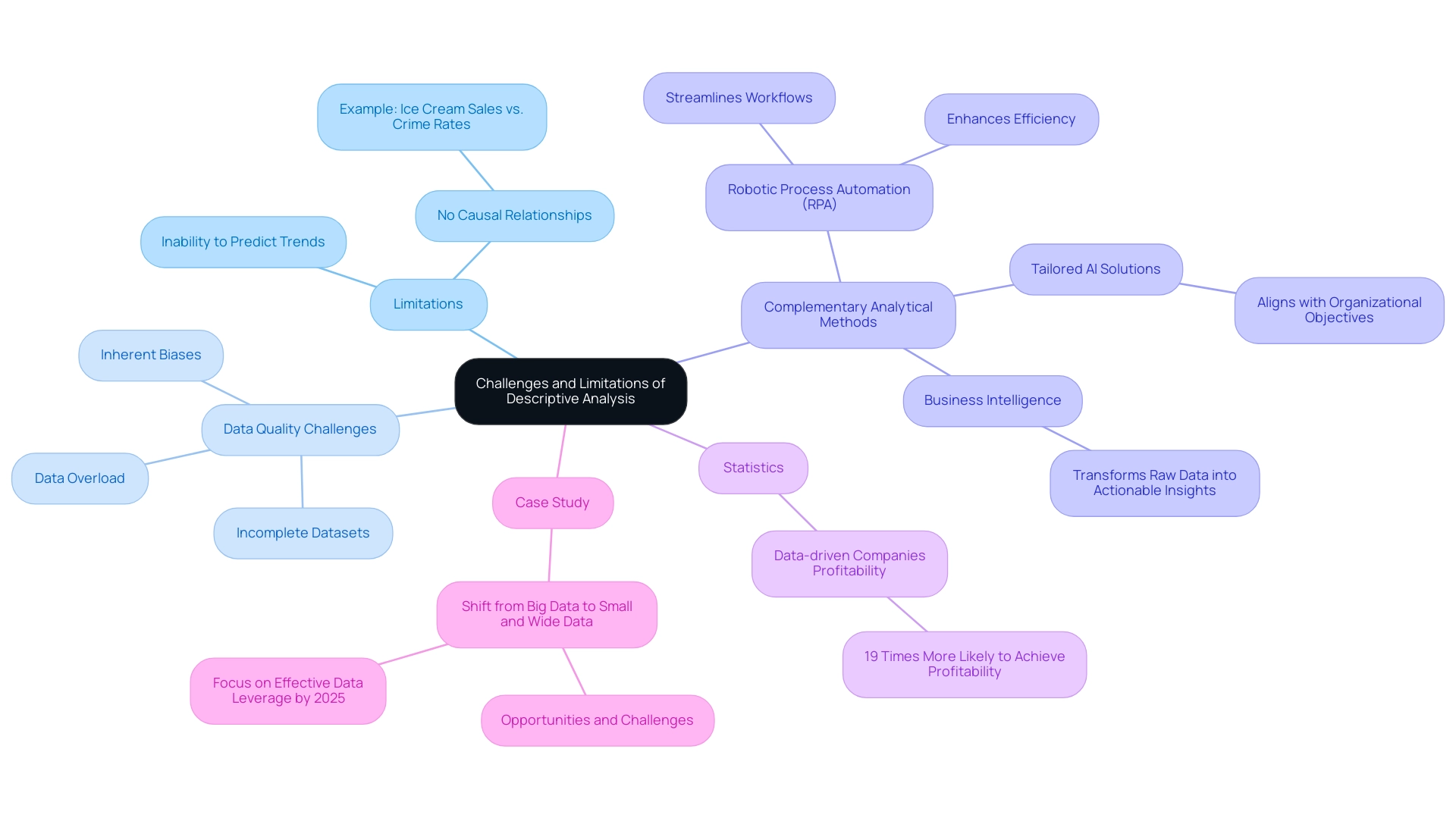
Descriptive analysis, while offering valuable insights into historical data, presents notable limitations. Most significantly, this method is incapable of predicting future trends or establishing causal relationships between variables. As Tom Bzik, a statistical consulting expert, asserts, ‘One major limitation of descriptive statistics is that they can’t determine causality.’ Although they summarize critical information, such as averages and standard deviations, they fail to indicate whether one variable influences another. This gap in understanding can lead organizations to draw erroneous conclusions from their data.
Moreover, the effectiveness of descriptive evaluation is heavily dependent on the quality of the data collected. In 2025, organizations increasingly face challenges such as data overload, incomplete datasets, and inherent biases that can skew results. These issues underscore the importance of acknowledging the limitations of descriptive analysis and complementing it with more robust analytical methods, such as:
- Robotic Process Automation (RPA)
- Tailored AI solutions
- Business Intelligence
RPA can streamline workflows, enhancing efficiency and reducing errors, while tailored AI solutions aid organizations in navigating the complex landscape of available technologies, aligning with specific organizational objectives. Notably, data-driven companies are 19 times more likely to achieve profitability, emphasizing the critical role of effective analytics in fostering success.
Furthermore, the case study titled ‘Shift from Big Information to Small and Wide Information’ exemplifies the practical implications of evolving management strategies. As the industry transitions towards leveraging small and wide data approaches, organizations must adeptly navigate these challenges to enhance data quality and extract actionable insights, ensuring their analytical practices evolve in tandem with changing business needs.
Conclusion
Descriptive analysis stands as a cornerstone of data analytics, empowering organizations to make informed decisions through the summarization of historical data and the identification of trends, patterns, and anomalies. As data volume continues to surge—especially with the proliferation of connected devices—the integration of descriptive analysis with advanced technologies like Robotic Process Automation (RPA) becomes increasingly vital. This strategic combination not only enhances operational efficiency but also addresses challenges related to data quality, which can impede effective decision-making.
The real-world applications of descriptive analysis span various industries, including retail, healthcare, and finance. Each sector leverages this analytical approach to derive actionable insights that inform strategic decisions, improve customer engagement, and drive growth. However, despite its many benefits, organizations must remain cognizant of the limitations inherent in descriptive analysis, particularly its inability to predict future outcomes or establish causality. This limitation underscores the necessity of complementing descriptive analysis with more advanced methodologies to ensure comprehensive insights.
In conclusion, as businesses navigate an increasingly complex data landscape, the ability to harness descriptive analysis effectively is paramount for success. Organizations that prioritize data-driven decision-making are not only more likely to achieve profitability but are also better positioned to adapt to the challenges and opportunities that lie ahead. By embracing descriptive analysis alongside tailored AI solutions and RPA, companies can unlock the full potential of their data, fostering innovation and maintaining a competitive edge in their respective markets.

